Psalodon is an extinct genus of North American mammal that lived during the Upper Jurassic period. It's a member of the family Allodontidae within the order Multituberculata.
Glirodon is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also-extinct order of Multituberculata, suborder "Plagiaulacida". These mammals lived in North America during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs".
Bathmochoffatia is an extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata. It lived in Portugal at about the same time as the far more famous dinosaur, Allosaurus. It is in the suborder "Plagiaulacida", family Paulchoffatiidae. The genus Bathmochoffatia was named by Hahn G. and Hahn R. in 1998.
Guimarotodon is an extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It made its living nibbling plants as great big, and small, dinosaurs roamed the world.
Kielanodon is an extinct mammal of the Portuguese Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It eked out a living during the Mesozoic era, also known as the "Age of the Dinosaurs." It is in the suborder Plagiaulacida, family Paulchoffatiidae.
Plesiochoffatia is an extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata. It was a resident of Portugal during the "age of the dinosaurs." It's in the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Paulchoffatiidae.

Sunnyodon is a genus of tiny, extinct mammal, probably of the Lower Cretaceous. Found in what is now southern England and Denmark, it was a relatively early member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It is part of the suborder Plagiaulacida and family Paulchoffatiidae.
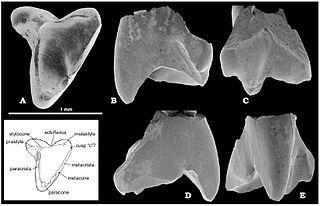
Morrisonodon brentbaatar is an extinct multituberculate mammal from the Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of North America.

Castorocauda is an extinct, semi-aquatic, superficially otter-like genus of docodont mammaliaforms with one species, C. lutrasimilis. It is part of the Yanliao Biota, found in the Daohugou Beds of Inner Mongolia, China dating to the Middle to Late Jurassic. It was part of an explosive Middle Jurassic radiation of Mammaliaformes moving into diverse habitats and niches. Its discovery in 2006, along with the discovery of other unusual mammaliaforms, disproves the previous hypothesis of Mammaliaformes remaining evolutionarily stagnant until the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs.
Crusafontia is an extinct genus of mammal from the Cretaceous Camarillas, El Castellar and La Huérguina Formations of Spain. The name of the animal was given in honour of the Spanish paleontologist Miquel Crusafont Pairó.

Docodon is an extinct docodont mammaliaform from the Late Jurassic of western North America. It was the first docodont to be named.

Pseudotribos is an extinct genus of mammaliaform that lived in Northern China during the Middle Jurassic some 165 million years ago, possibly more closely related to monotremes than to theria, although other studies indicate that these shuotheres are closer to therians than to monotremes. The only known specimen was found in the Daohugou Bed in Inner Mongolia.

Dryolestidae is an extinct family of Mesozoic mammals, known from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous of the North Hemisphere. The oldest known member, Anthracolestes, is known from the Middle Jurassic Itat Formation of Western Siberia, but most other representatives are known from the Late Jurassic of North America and the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Europe. Most members are only known from isolated teeth and jaw fragments. Like many other groups of early mammals, they are thought to have been insectivores. They are generally classified in Cladotheria, meaning that they are considered to be more closely related to marsupials and placentals than to monotremes. They are placed as part of the broader Dryolestida, which also includes the Paurodontidae, and also sometimes the South American-Antarctic Meridiolestida, which are often considered unrelated cladotherians. Dryolestidae taxon is not based on a phylogenetic definition, but instead on the possession of unequal roots for the molars of the lower jaw. Additionally, the clade is distinguished by hypsodonty in lower molars, and uneven labio-lingual height for the alveolar borders of the dentary.
Asfaltomylos is an extinct genus of the primitive mammal subclass Australosphenida from the Jurassic of Argentina. The type and only species is Asfaltomylos patagonicus, recovered from and named after the Cañadón Asfalto Formation, Cañadón Asfalto Basin of Chubut Province, Patagonia.
Henosferus is an extinct genus of australosphenidan mammal from Lower Jurassic of Argentina. The only recorded species, Henosferus molus, was found in the Cañadón Asfalto Formation of the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Chubut Province, Patagonia.
Amphilestes is a genus of extinct eutriconodont mammal from the Middle Jurassic of the United Kingdom. It was one of the first Mesozoic mammals discovered and described.
Trioracodon is an extinct genus of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous eutriconodont mammal found in North America and the British Isles. It was named in 1928
Comodon is an extinct genus of Late Jurassic mammal from the Morrison Formation of Wyoming. Fossils of this taxon are present in stratigraphic zone 5.
Euthlastus is an extinct genus of Late Jurassic mammal from the Morrison Formation. Present in stratigraphic zones 5 and 6. It is represented by only five upper molars.
Arboroharamiya is an extinct genus of early mammal from the Middle Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of Inner Mongolia, China. Arboroharamiya belongs to a group of mammaliaforms called Haramiyida. The type species Arboroharamiya jenkinsi was described in the journal Nature in 2013 alongside a description of the closely related haramiyidan Megaconus. Unlike Megaconus, which is thought to have been ground-dwelling, Arboroharamiya was arboreal. It has a long tail that might have been prehensile, and very long fingers. Based on the shape of its teeth, Arboroharamiya might have been an omnivore or a seed eater. Recent interpretations of its specimen suggest that it possessed patagia and was a glider.










