
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa, and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene. Until recently, they were known only from fragmentary remains. They are generally considered to be closely related to the multituberculates and likely the euharamiyidians, well known from the Northern Hemisphere, with which they form the clade Allotheria.
Ferugliotherium is a genus of fossil mammals in the family Ferugliotheriidae from the Campanian and/or Maastrichtian period of Argentina. It contains a single species, Ferugliotherium windhauseni, which was first described in 1986. Although originally interpreted on the basis of a single brachydont (low-crowned) molar as a member of Multituberculata, an extinct group of small, rodent-like mammals, it was recognized as related to the hypsodont (high-crowned) Sudamericidae following the discovery of additional material in the early 1990s. After a jaw of the sudamericid Sudamerica was described in 1999, these animals were no longer considered to be multituberculates and a few fossils that were previously considered to be Ferugliotherium were assigned to unspecified multituberculates instead. Since 2005, a relationship between gondwanatheres and multituberculates has again received support. A closely related animal, Trapalcotherium, was described in 2009 on the basis of a single tooth.
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammalian order. The best-known representative of Ferugliotheriidae is the genus Ferugliotherium from the Late Cretaceous epoch in Argentina. A second genus, Trapalcotherium, is known from a single tooth, a first lower molariform, from a different Late Cretaceous Argentinean locality. Another genus known from a single tooth, Argentodites, was first described as an unrelated multituberculate, but later identified as possibly related to Ferugliotherium. Finally, a single tooth from the Paleogene of Peru, LACM 149371, perhaps a last upper molariform, and a recent specimen from Mexico, may represent related animals.

Theriiformes is a clade of mammals. The term was coined by Timothy B. Rowe in his doctoral dissertation, and is defined as the clade formed by the most recent common ancestor of multituberculates and Theria. Mammals more closely related to therians than to multituberculates are included in the clade Trechnotheria. As multituberculates are usually considered more closely related to therians than monotremes are, it is considered to be a subgroup of the mammalian crown group.

Volaticotherium antiquum is an extinct, gliding, insectivorous mammal that lived in Asia during the Jurassic period, around 164 mya. It is the only member of the genus Volaticotherium.

Eutriconodonta is an order of early mammals. Eutriconodonts existed in Asia, Africa, Europe, North and South America during the Jurassic and the Cretaceous periods. The order was named by Kermack et al. in 1973 as a replacement name for the paraphyletic Triconodonta.

Vincelestes is an extinct genus of mammal that lived in what is now South America during the Early Cretaceous. It is closely related to modern therian mammals as part of Cladotheria.

Dryolestida is an extinct order of mammals, known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous. They are considered basal members of the clade Cladotheria, close to the ancestry of therian mammals. It is also believed that they developed a fully mammalian jaw and also had the three middle ear bones. Most members of the group, as with most Mesozoic mammals, are only known from fragmentary tooth and jaw remains.
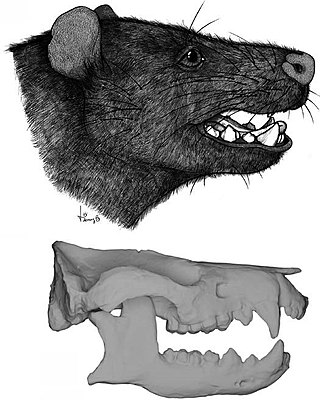
Peligrotherium is an extinct meridiolestidan mammal from the Paleocene of Patagonia, originally interpreted as a stem-ungulate. Its remains have been found in the Salamanca Formation. It was a dog-sized mammal, among the largest of all non-therian mammals. It is a member of Mesungulatoidea, a clade of herbivorous meridiolestidans with molars that had rounded (bunodont) cusps.

The La Colonia Formation is a geological formation in Argentina whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
Argentodites is a possible multituberculate mammal from the Cretaceous of Argentina. The single species, Argentodites coloniensis, is known from a single blade-like fourth lower premolar (p4) from the La Colonia Formation, which is mostly or entirely Maastrichtian in age. The p4 is 4.15 mm long and bears eight cusps on its upper margin and long associated ridges on both sides. The enamel consists of prisms that are completely or partly surrounded by a sheath and that are on average 6.57 μm apart. Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, who described and named the fossil in 2007, regarded it as a multituberculate, perhaps a cimolodontan—and thus, a member of a mostly Laurasian (northern) group and an immigrant to Argentina from North America—on the basis of the shape of the tooth and features of its enamel. In 2009, however, two teams argued that Argentodites may in fact be close to or identical with Ferugliotherium, a member of the small Gondwanan (southern) group Gondwanatheria; although their relationships are disputed, gondwanatheres may themselves be multituberculates.
Trapalcotherium is a fossil mammal from the Cretaceous of Argentina in the family Ferugliotheriidae. The single species, T. matuastensis, is known from one tooth, a first lower molar. It is from the Allen Formation, which is probably Maastrichtian in age, and was first described in 2009. The tooth bears two rows of cusps, one at the inner (lingual) side and the other at the outer (labial) side, which are connected by transverse ridges separated by deep valleys. This pattern is reminiscent of Ferugliotherium, a gondwanathere mammal from similarly aged deposits in Argentina, and Trapalcotherium is therefore recognized as a member of the same family Ferugliotheriidae. Ferugliotheriidae is one of two families of gondwanatheres, an enigmatic group without close relationships to any living mammals.
Reigitherium was a mammal that lived during the Late Cretaceous, in the. Its fossils have been found in the Los Alamitos and the La Colonia Formations of Argentina.
Coloniatherium is a meridiolestid mammal from the Late Cretaceous of Argentina. The single species, Coloniatherium cilinskii, was a large member of the family Mesungulatidae.
Donodon is an extinct genus of mammal from the Ksar Metlili Formation of Talssint, Morocco, which has been dated to the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous epochs. The type species D. perscriptoris was described in 1991 by the palaeontologist Denise Sigogneau-Russell. A second species, D. minor, was named in 2022. Donodon was a member of Cladotheria, a group that includes therian mammals and some of their closest relatives. It differed from dryolestids in having upper molars that were not compressed mesiodistally. Some studies have suggested that it was closely related to various South American cladotherians in the clade Meridiolestida, with specific similarities to Mesungulatum, a herbivorous mesungulatid, being noted. On the other hand, a 2022 phylogenetic analysis found it to be only distantly related to meridiolestidans, and instead closer to crown group therians.

Cronopio is an extinct genus of small insectivorous mammal known from the early Late Cretaceous of the Río Negro region in Argentina. Its only species is Cronopio dentiacutus. It belongs to the Meridiolestida, an extinct group of mammals widespread in South America during the Late Cretaceous, which are more closely related to modern marsupials and placental mammals than to monotremes.

Necrolestes is an extinct genus of mammals, which lived during the Early Miocene in what is now Argentine Patagonia. It is the most recent known genus of Meridiolestida, an extinct group of mammals more closely related to therians than to monotremes, which were the dominant mammals in South America during the Late Cretaceous. It contains two species, N. patagonensis and N. mirabilis; the type species N. patagonensis was named by Florentino Ameghino in 1891 based on remains found by his brother, Carlos Ameghino in Patagonia. Fossils of Necrolestes have been found in the Sarmiento and Santa Cruz Formations. Its morphology suggests that it was a digging, subterranean-dwelling mole-like mammal that fed on invertebrates.
Leonardus is an extinct mammal genus from the Late Cretaceous of South America. It is a meridiolestidan, closely related to the also Late Cretaceous Cronopio and the Miocene Necrolestes.

Meridiolestida is an extinct clade of mammals known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic of South America and possibly Antarctica. They represented the dominant group of mammals in South America during the Late Cretaceous. Meridiolestidans were morphologically diverse, containing both small insectivores such as the "sabretooth-squirrel" Cronopio, as well as the clade Mesungulatoidea/Mesungulatomorpha, which ranged in size from the shrew-sized Reigitherium to the dog-sized Peligrotherium. Mesungulatoideans had highly modified dentition with bunodont teeth, and were likely herbivores/omnivores. Meridiolestidans are generally classified within Cladotheria, more closely related to living marsupials and placental mammals (Theria) than to monotremes, barring one study recovering them as the sister taxa to spalacotheriid "symmetrodonts". However, more recent studies have stuck to the cladotherian interpretation. Within Cladotheria, they have often been placed in a group called Dryolestoidea together with Dryolestida, a group of mammals primarily known from the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of the Northern Hemisphere. However, some analyses have found this group to be paraphyletic, with the meridiolestidans being more or less closely related to therian mammals than dryolestidans are. Meridiolestidans differ from dryolestidans in the absence of a parastylar hook on the molariform teeth and the lack of a Meckelian groove.

Titanomachya is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous La Colonia Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a single species, T. gimenezi. It is a relatively small titanosaur, weighing around 7.8 tonnes.















