Agartala is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Tripura, situated on the banks of Haora River, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) east of the border with Bangladesh and about 2,499 km (1,552 mi) from the national capital, New Delhi. According to 2022 census, Agartala is the third largest city after Guwahati and Imphal in Northeast India. It is India's third international internet gateway and being developed under the Smart Cities Mission.

The Tripuri are a Tibeto-Burman-speaking ethnic group of Northeast Indian state of Tripura. They are the descendants of the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through the Manikya dynasty ruled the Kingdom of Tripura for ~450 years until the kingdom joined the Indian Union on 15 October 1949.
Rajmala is a chronicle of the Kings of Tripura, written in Bengali verse in the 15th century under Dharma Manikya I.

The Twipra Kingdom was a Hindu kingdom of Tibeto-Burman ethnic dynasty of the Tripuri people in Northeast India.

The Manikya dynasty was the ruling house of the Twipra Kingdom and later the princely Tripura State, what is now the Indian state of Tripura. Ruling since the early 15th century, the dynasty at its height controlled a large swathe of the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. After coming under British influence, in 1761 they transitioned from feudal monarchs into rulers of a princely state, though the Manikyas maintain control of the region until 1949, when it ascended in union with India.
The Tripuri calendar is the traditional solar calendar used by the Tripuri people, especially in the context of Tripuri irredentism. Its era, the "Twipra Era", "Tripura Era" or Tripurabda is set at 15 April AD 590.

Neermahal also known as Twijilikma Nuyung is a former royal palace of Tripura Kingdom, built by Maharaja Bir Bikram Kishore Manikya bahadur in 1930. It is also the largest water palace in India. The palace is situated in the middle of Rudrasagar Lake, in Melaghar 53 kilometers away from Agartala, the capital of Tripura.

The Ujjayanta Palace also known as Nuyungma, in Tripuri, is the former royal palace of Tripura kingdom built by Maharaja Radha Kishore Manikya in 1901. It housed the State Legislative Assembly up to 2011. At present, it is the State Museum of Tripura, which is located in the capital Agartala.
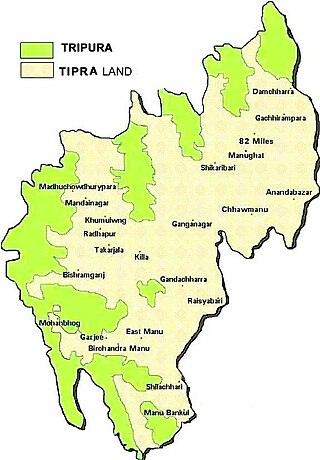
Tipraland is the name of a proposed state in India for the indigenous Tripuri people in the tribal areas of the Tripura state. They demand the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council and some surrounding areas to be made into a separate state from Tripura. The proposed state covers 68% of the total geographical area of the Tripura and is home to over one-third of the total population of Tripura.

Maharaja Radha Kishore Manikya of the Manikya Dynasty reigned as the king of Tripura State from 1897 to 1909. He has been described as one of the architects of modern Tripura.

The Tripura Buranji is an account of the diplomatic contacts between the Ahom kingdom and the Tripura Kingdom between 1709 and 1715. The Buranji was written in 1724 by the envoys of the Ahom kingdom, Ratna Kandali Sarma Kataki and Arjun Das Bairagi Kataki. It describes three diplomatic missions that was sent to the Twipra kingdom, two return missions accompanied by Tripuri envoys, incidental descriptions of palaces, ceremonies and customs; and it also provides an eye witness account of the Twipra king Ratna Manikya II (1684–1712) deposed by his step-brother Ghanashyam Barthakur, later Mahendra Manikya (1712–1714).

Tripura State, also known as Hill Tipperah, was a princely state in India during the period of the British Raj and for some two years after the departure of the British. Its rulers belonged to the Manikya dynasty and until August 1947 the state was in a subsidiary alliance, from which it was released by the Indian Independence Act 1947. The state acceded to the newly independent Indian Union on 13 August 1947, and subsequently merged into the Indian Union in October 1949.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tripura:
Maha Manikya, also known as Chhengthung Fa, was the Maharaja of Tripura from about 1400 to 1431. Contrary to narratives provided by early histories, evidence indicates that Maha Manikya was the founder of the kingdom, having established dominance over neighbouring tribes in the early 15th century. He is further thought to be the first holder of the title "Manikya", taken in recognition of a historic victory over the neighbouring Bengal Sultanate. The dynasty which he founded continued using the title until Tripura's merger with India in 1949.

Vijaya Manikya II, also spelt Vijay or Bijoy, was the Maharaja of Tripura from 1532 to 1563. Succeeding to the throne at a young age, Vijaya proved himself to be a formidable military leader, initiating a series of conquests into several surrounding kingdoms, including the powerful Bengal Sultanate. During Vijaya's reign, the might and influence of Tripura reached its zenith, leading to him being viewed as one of its greatest monarchs.

The Chaturdasa Devata or Fourteen Gods is the Shaivite Hindu pantheon worshipped in the Indian state of Tripura.
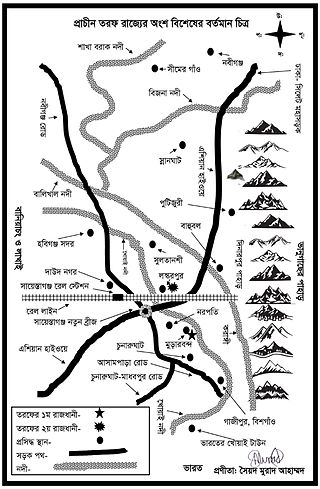
Taraf, previously known as Tungachal, was a feudal territory of the Sylhet region in Bengal and was under many petty kingdoms in different periods of time. It was part of what is present-day Habiganj District in Bangladesh.

Kokborok Cinema refers to the Kokborok language film industry in Tripura, India and among the Tripuri people. Tripura's Kokborok film industry began in 1986 with Longtharai (1986) directed by Dipak Bhattacharya adapted from Bimal Sinha's novel Karachi theke Longtharai depicting the struggle-ridden life of jhum cultivators in the rural hills of Longtharai followed by the Kokborok film Langmani Haduk (1993) directed by Ruhi Debbarma can be read as a critique of the modern regime. The Kokborok film Mathia (2004) directed by Joseph Pulinthanath, is the first International Award-winning Kokborok film.

Tripura is a state in the North-East India and the third smallest state in India. Tripura is widely regarded as a beautiful destination, appreciated for its picturesque landscape and delightful climate. The tourism in Tripura is maintained by TTDCL, a state government owned enterprise.