
Methylmalonic acidemias, also called methylmalonic acidurias, are a group of inherited metabolic disorders, that prevent the body from properly breaking down proteins and fats. This leads to a buildup of a toxic level of methylmalonic acid in body liquids and tissues. Due to the disturbed branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) metabolism, they are among the classical organic acidemias.
Propionic acidemia, also known as propionic aciduria or propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency, is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder, classified as a branched-chain organic acidemia.

Isovaleric acidemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder which disrupts or prevents normal metabolism of the branched-chain amino acid leucine. It is a classical type of organic acidemia.

Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare, inherited metabolic disorder that affects the body's ability to metabolize amino acids due to a deficiency in the activity of the branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKAD) complex. It particularly affects the metabolism of amino acids—leucine, isoleucine, and valine. With MSUD, the body is not able to properly break down these amino acids, therefore leading to the amino acids to build up in urine and become toxic. The condition gets its name from the distinctive sweet odor of affected infants' urine and earwax due to the buildup of these amino acids.

Hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting the absorption of nonpolar amino acids. Niacin is a precursor to nicotinamide, a necessary component of NAD+.
Glutaric acidemia type 2 is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is characterised by defects in the ability of the body to use proteins and fats for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis. It is a metabolic myopathy, categorized under fatty acid metabolism disorder as that is the bioenergetic system that it affects the most. It also affects choline metabolism.

Malonic aciduria or malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency (MCD) is an autosomal-recessive metabolic disorder caused by a genetic mutation that disrupts the activity of Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. This enzyme breaks down Malonyl-CoA into acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide.

Short-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency (SCADD) is an autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder which affects enzymes required to break down a certain group of fats called short chain fatty acids.

Glycine encephalopathy is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of glycine metabolism. After phenylketonuria, glycine encephalopathy is the second most common disorder of amino acid metabolism. The disease is caused by defects in the glycine cleavage system, an enzyme responsible for glycine catabolism. There are several forms of the disease, with varying severity of symptoms and time of onset. The symptoms are exclusively neurological in nature, and clinically this disorder is characterized by abnormally high levels of the amino acid glycine in bodily fluids and tissues, especially the cerebrospinal fluid.
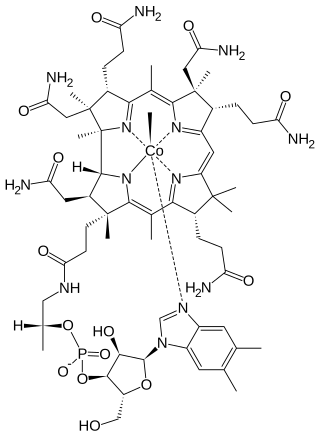
Arakawa's syndrome II is an autosomal dominant metabolic disorder that causes a deficiency of the enzyme tetrahydrofolate-methyltransferase; affected individuals cannot properly metabolize methylcobalamin, a type of Vitamin B12.
2-Methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. It causes the body to be unable to process the amino acid isoleucine properly. Initial case reports identified individuals with developmental delay and epilepsy, however most cases identified through newborn screening have been asymptomatic.
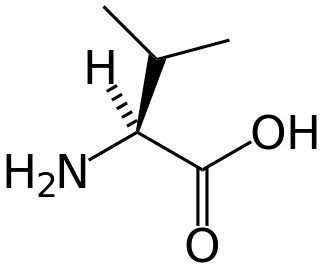
Isobutyryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder in which the body is unable to process certain amino acids properly.

ACADSB is a human gene that encodes short/branched chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SBCAD), an enzyme in the acyl CoA dehydrogenase family.
Organic acidemia is a term used to classify a group of metabolic disorders which disrupt normal amino acid metabolism, particularly branched-chain amino acids, causing a buildup of acids which are usually not present.

Urocanic aciduria is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme urocanase. It is a secondary disorder of histidine metabolism.

Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial (MMSDH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH6A1 gene.

Carnosinemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of carnosinase, a dipeptidase.

Hypertryptophanemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that results in a massive buildup of the amino acid tryptophan in the blood, with associated symptoms and tryptophanuria.
Iminoglycinuria is an autosomal recessive disorder of renal tubular transport affecting reabsorption of the amino acid glycine, and the imino acids proline and hydroxyproline. This results in excess urinary excretion of all three acids.
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA), also called combined malonic and methylmalonic acidemia is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of malonic acid and methylmalonic acid. However, the methylmalonic acid levels exceed those of malonic acid. CMAMMA is not only an organic aciduria but also a defect of mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII). Some researchers have hypothesized that CMAMMA might be one of the most common forms of methylmalonic acidemia, and possibly one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism. Due to being infrequently diagnosed, it most often goes undetected.















