
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight.
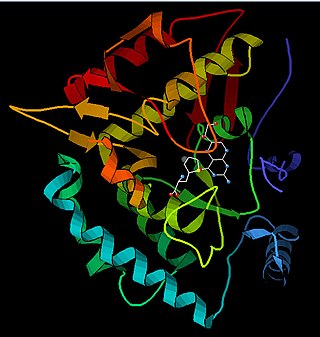
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) (EC 1.14.16.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of the aromatic side-chain of phenylalanine to generate tyrosine. PAH is one of three members of the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, a class of monooxygenase that uses tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, a pteridine cofactor) and a non-heme iron for catalysis. During the reaction, molecular oxygen is heterolytically cleaved with sequential incorporation of one oxygen atom into BH4 and phenylalanine substrate. In humans, mutations in its encoding gene, PAH, can lead to the metabolic disorder phenylketonuria.

Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB), also known as sapropterin (INN), is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and is a cofactor for the production of nitric oxide (NO) by the nitric oxide synthases. Chemically, its structure is that of a (dihydropteridine reductase) reduced pteridine derivative (quinonoid dihydrobiopterin).

QDPR is a human gene that produces the enzyme quinoid dihydropteridine reductase. This enzyme is part of the pathway that recycles a substance called tetrahydrobiopterin, also known as BH4. Tetrahydrobiopterin works with an enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase to process a substance called phenylalanine. Phenylalanine is an amino acid that is obtained through the diet; it is found in all proteins and in some artificial sweeteners. When tetrahydrobiopterin interacts with phenylalanine hydroxylase, tetrahydrobiopterin is altered and must be recycled to a usable form. The regeneration of this substance is critical for the proper processing of several other amino acids in the body. Tetrahydrobiopterin also helps produce certain chemicals in the brain called neurotransmitters, which transmit signals between nerve cells.

6-Pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes malignant hyperphenylalaninemia due to tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency. It is a recessive disorder that is accompanied by hyperphenylalaninemia. Commonly reported symptoms are initial truncal hypotonia, subsequent appendicular hypertonia, bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity, generalized dystonia, and marked diurnal fluctuation. Other reported clinical features include difficulty in swallowing, oculogyric crises, somnolence, irritability, hyperthermia, and seizures. Chorea, athetosis, hypersalivation, rash with eczema, and sudden death have also been reported. Patients with mild phenotypes may deteriorate if given folate antagonists such as methotrexate, which can interfere with a salvage pathway through which dihydrobiopterin is converted into tetrahydrobiopterin via dihydrofolate reductase. Treatment options include substitution with neurotransmitter precursors, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and tetrahydrobiopterin. Response to treatment is variable and the long-term and functional outcome is unknown. To provide a basis for improving the understanding of the epidemiology, genotype–phenotype correlation and outcome of these diseases, their impact on the quality of life of patients, and for evaluating diagnostic and therapeutic strategies a patient registry was established by the noncommercial International Working Group on Neurotransmitter Related Disorders (iNTD).

GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH) (EC 3.5.4.16) is a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family of enzymes. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin biosynthesis pathways. It is responsible for the hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).
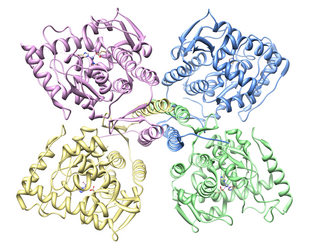
Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3-monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). It does so using molecular oxygen (O2), as well as iron (Fe2+) and tetrahydrobiopterin as cofactors. L-DOPA is a precursor for dopamine, which, in turn, is a precursor for the important neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline). Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step in this synthesis of catecholamines. In humans, tyrosine hydroxylase is encoded by the TH gene, and the enzyme is present in the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral sympathetic neurons and the adrenal medulla. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase and tryptophan hydroxylase together make up the family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAHs).

Queuine (Q) is a hypermodified nucleobase found in the first position of the anticodon of tRNAs specific for Asn, Asp, His, and Tyr, in most eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Because it is utilized by all eukaryotes but produced exclusively by bacteria, it is a putative vitamin.

Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) is an enzyme (EC 1.14.16.4) involved in the synthesis of the monoamine neurotransmitter serotonin. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase, and tryptophan hydroxylase together constitute the family of biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. TPH catalyzes the following chemical reaction

Biopterins are pterin derivatives which function as endogenous enzyme cofactors in many species of animals and in some bacteria and fungi. The prototypical compound of the class is biopterin, as shown in the infobox. Biopterins act as cofactors for aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAH), which are involved in synthesizing a number of neurotransmitters including dopamine, norepinephrine, epinepherine, and serotonin, along with several trace amines. Nitric oxide synthesis also uses biopterin derivatives as cofactors. In humans, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is the endogenous cofactor for AAAH enzymes.

Sepiapterin reductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SPR gene.
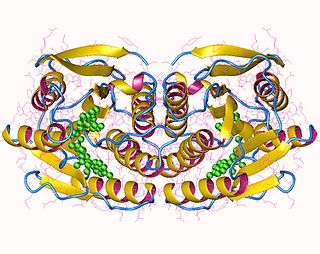
In enzymology, 6,7-dihydropteridine reductase (EC 1.5.1.34, also Dihydrobiopterin reductase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase catalyzes the following chemical reaction:

Pterin-4-alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCBD1 gene.
Dopamine-responsive dystonia (DRD) also known as Segawa syndrome (SS), is a genetic movement disorder which usually manifests itself during early childhood at around ages 5–8 years.

Hyperphenylalaninemia is a medical condition characterized by mildly or strongly elevated concentrations of the amino acid phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylketonuria (PKU) can result in severe hyperphenylalaninemia. Phenylalanine concentrations are routinely screened in newborns by the neonatal heel prick, which takes a few drops of blood from the heel of the infant. Standard phenylalanine concentrations in unaffected persons are about 2-6mg/dl phenylalanine concentrations in those with untreated hyperphenylalaninemia can be up to 20 mg/dL. Measurable IQ deficits are often detected as phenylalanine levels approach 10 mg/dL. Phenylketonuria (PKU)-like symptoms, including more pronounced developmental defects, skin irritation, and vomiting, may appear when phenylalanine levels are near 20 mg/dL .Hyperphenylalaninemia is a recessive hereditary metabolic disorder that is caused by the body's failure to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine as a result of the entire or partial absence of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase.
Sepiapterin reductase deficiency is an inherited pediatric disorder characterized by movement problems, and most commonly displayed as a pattern of involuntary sustained muscle contractions known as dystonia. Symptoms are usually present within the first year of age, but diagnosis is delayed due to physicians lack of awareness and the specialized diagnostic procedures. Individuals with this disorder also have delayed motor skills development including sitting, crawling, and need assistance when walking. Additional symptoms of this disorder include intellectual disability, excessive sleeping, mood swings, and an abnormally small head size. SR deficiency is a very rare condition. The first case was diagnosed in 2001, and since then there have been approximately 30 reported cases. At this time, the condition seems to be treatable, but the lack of overall awareness and the need for a series of atypical procedures used to diagnose this condition pose a dilemma.
Dihydropteridine reductase deficiency (DHPRD) is a genetic disorder affecting the tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis pathway, inherited in the autosomal recessive pattern. It is one of the six known disorders causing tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency, and occurs in patients with mutations of the QDPR gene.
Autosomal recessive GTP cyclohydrolase I deficiency (AR-GTPCHD) is a disorder associated with the deficient operation of the enzyme GTP cyclohydrolase I. The condition leads to insufficient production of the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin necessary for the proper synthesis of dopamine and serotonin and for maintenance of adequate levels of phenylalanine. As of 2020, autosomal recessive GTP cyclohydrolase I deficiency was one of the six known causes of tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency. It is also considered part of the spectrum of dopa-responsive dystonias.
Autosomal dominant GTP cyclohydrolase I deficiency (AD-GTPCHD) is a disease caused by dysfunction of GTP cyclohydrolase I, an enzyme that plays an important role in the synthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin, and, as a consequence, of dopamine. This condition is one of the six known causes of tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency and is the most frequently-reported cause of dopa-responsive dystonia.















