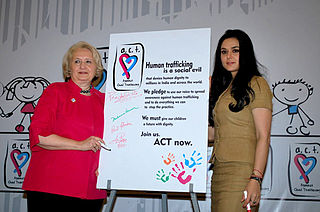The National Crime Records Bureau, abbreviated to NCRB, is an Indian government agency responsible for collecting and analysing crime data as defined by the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and Special and Local Laws (SLL). NCRB is headquartered in New Delhi and is part of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India. The current Director of NCRB is Ramphal Pawar (IPS).
Farmer suicides in India refers to the national catastrophe of farmers committing suicide since the 1990s, often by drinking pesticides, due to their inability to repay loans mostly taken from landlords and banks.

Crime in the United States has been recorded since colonization. Crime rates have varied over time, with a sharp rise after 1900, reaching a broad bulging peak between the 1970s and early 1990s. Since then, crime has declined significantly.

Crime in India has been recorded since the British Raj, with comprehensive statistics now compiled annually by the National Crime Records Bureau(NCRB), under the Ministry of Home Affairs (India)(MHA).

The crime rate in the United Arab Emirates is relatively low compared to more highly industrialized nations. Incidents of petty crime such as pickpocketing are low. The United States Department of State states: "Crime generally is not a problem for travelers in the UAE. However, the U.S. Embassy advises U.S. citizens to take normal precautions against theft, such as not leaving a wallet, purse, or credit card unattended. Although vehicle break-ins in the UAE are rare, U.S. citizens are encouraged to ensure that unattended vehicles are locked and that valuables are not left out in plain sight".

Human trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extraction of organs or tissues, including for surrogacy and ova removal. Human trafficking can occur within a country or trans-nationally. Human trafficking is a crime against the person because of the violation of the victim's rights of movement through coercion and because of their commercial exploitation. Human trafficking is the trade in people, especially women and children, and does not necessarily involve the movement of the person from one place to another.

Human trafficking is a modern form of slavery, with illegal smuggling and trading of people, for forced labor or sexual exploitation.

Binpur I is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Jhargram subdivision of Jhargram district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
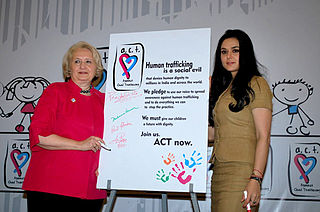
India has a very high volume of child trafficking. As many as one child disappears every eight minutes, according to the National Crime Records Bureau. In some cases, children are taken from their homes to be bought and sold in the market. In other cases, children are tricked into the hands of traffickers by being presented an opportunity for a job, when in reality, upon arrival they become enslaved. In India, there are many children trafficked for various reasons such as labor, begging, and sexual exploitation. Because of the nature of this crime; it is hard to track; and due to the poor enforcement of laws, it is difficult to prevent. Due to the nature of this crime, it is only possible to have estimates of figures regarding the issue. India is a prime area for child trafficking to occur, as many of those trafficked are from, travel through or destined to go to India. Though most of the trafficking occurs within the country, there is also a significant number of children trafficked from Nepal and Bangladesh. There are many different causes that lead to child trafficking, with the primary reasons being poverty, weak law enforcement, and a lack of good quality public education. The traffickers that take advantage of children can be from another area in India, or could even know the child personally. Children who return home after being trafficked often face shame in their communities, rather than being welcomed home.

In 2016 the number of suicides in India had increased to 230,314. Suicide was the most common cause of death in both the age groups of 15–29 years and 15–39 years.

Traffic collisions in India are a major source of deaths, injuries and property damage every year. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) 2016 report states there were 496,762 roads, railways and railway crossing-related traffic collisions in 2015. Of these, road collisions accounted for 464,674 collisions which caused 148,707 traffic-related deaths in India. The three highest total number of fatalities were reported in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu, and together they accounted for about 33% of total Indian traffic fatalities in 2015. Adjusted for 182.45 million vehicles and its 1.31 billion population, India reported a traffic collision rate of about 0.8 per 1000 vehicles in 2015 compared to 0.9 per 1000 vehicles in 2012, and an 11.35 fatality rate per 100,000 people in 2015. According to Gururaj, the top three highest traffic fatality rates per 100,000 people in 2005 were reported by Tamil Nadu, Goa and Haryana, with a male:female fatality ratio of about 5:1. The reported total fatality, rates per 100,000 people and the regional variation of traffic collisions per 100,000 people varies by source. For example, Rahul Goel in 2018 reports an India-wide average fatality rate of 11.6 per 100,000 people and Goa to be the state with the highest fatality rate.
Rape is the fourth most common crime against women in India. According to the 2019 annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), 32033 rape cases were registered across the country, or an average of 88 cases daily,slightly lower than 2018 when 91 cases were registered daily.Of these, 30,165 rapes were committed by perpetrators known to the victim, a high number similar to 2018. The share of victims who were minors or below 18 - the legal age of consent - stood at 15.4%, down from 27.8% in 2018. On the other hand, rapes by juveniles remained high in India with 3 minors being arrested for rape, assault and attempted violence on women and girls each day in 2019.
Prisons, and their administration, is a state subject covered by item 4 under the State List in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India. The management and administration of prisons falls exclusively in the domain of the State governments, and is governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 and the Prison manuals of the respective state governments. Thus, the states have the primary role, responsibility and authority to change the current prison laws, rules and regulations. The Central Government provides assistance to the states to improve security in prisons, for the repair and renovation of old prisons, medical facilities, development of borstal schools, facilities to women offenders, vocational training, modernization of prison industries, training to prison personnel, and for the creation of high security enclosures.

Crime is present in various forms in the Philippines, and remains a serious issue throughout the country. Illegal drug trade, human trafficking, murder, corruption and domestic violence remain significant concerns. The Philippines has a high rate of murder cases, which is the highest in Southeast Asia as of 2014. Most major cities are plagued with high prevalence of crimes.

Crime in Hong Kong is generally low, but is still present in various forms. The most common crimes are thefts, assaults, vandalism, burglaries, drug offenses, sex trafficking, and triad-related crimes. In 2015, Hong Kong had one of the lowest murder rates in the world, comparable to Japan but higher than Macao or Singapore.
Violence against women in Tamil Nadu includes molestation, abduction, dowry-related violence, and domestic violence. The police recorded 1,130 cases during the first seven months in 2013, compared to 860 for the corresponding period in 2012. In Usilampatti Taluk, around 6,000 female children were killed in a span of 2 years during 1987-88, accounting to the single largest instance of recorded female infanticide.

Violence against women in India refer to physical or sexual violence committed against a woman, typically by a man. Common forms of violence against women in India include acts such as domestic abuse, sexual assault, and murder. In order to be considered violence against women, the act must be committed solely because the victim is female. Most typically, these acts are committed by men as a result of the long-standing gender inequalities present in the country.
This is a list of States and Union Territories of India which is ranked according to the safety of women as of 2016 based on the number of reported sexual assault cases. The list is compiled from the 2016 Crime in India Report published by National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Government of India.
Human rights in Trinidad and Tobago comprise a series of rights legally protected by the Constitution of Trinidad and Tobago. Trinidad and Tobago has ratified a number of international treaties and conventions on human rights and parts or principles of these legal texts have been integrated into the domestic laws of the country. The Ministry of the Attorney General has established the International Law and Human Rights Unit to ensure adherence to these principles.