Dowry deaths are deaths of married women who are murdered or driven to suicide over disputes about dowry. Dowry deaths are found predominantly in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Iran.

The National Crime Records Bureau, abbreviated to NCRB, is an Indian government agency responsible for collecting and analysing crime data as defined by the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and Special and Local Laws (SLL). NCRB is headquartered in New Delhi and is part of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India. The current Director of National Crime Record Bureau is Ramphal Pawar (IPS).
Farmer suicides in India refers to the national catastrophe of farmers committing suicide since the 1970s, due to their inability to repay loans mostly taken from private landlords and banks.

Crime in the United States has been recorded since the early 1600s. Crime rates have varied over time, with a sharp rise after 1900 and reaching a broad bulging peak between the 1970s and early 1990s. After 1992, crime rates began to fall year by year and has since declined significantly. This trend lasted until 2015, where crime rates began to rise slightly. This reversed in 2018 and 2019, but violent crime increased significantly again in 2020. Despite the increase in violent crime, particularly murders, between 2020 and 2021, the quantity of overall crime is still far below the peak of crime seen in the United States during the late 1980s and early 1990s, as other crimes such as rape, property crime and robbery continued to decline. The aggregate cost of crime in the United States remains high, with an estimated value of $4.9 trillion reported in 2021.
Crime in India has been recorded since the British Raj, with comprehensive statistics now compiled annually by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), under the Ministry of Home Affairs (India) (MHA).

Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance use disorders are risk factors. Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress, relationship problems, or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; and improving economic conditions. Although crisis hotlines are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied.
Suicide in South Korea occurs at the 12th highest rate in the world. South Korea has the highest suicide rate in the OECD. In 2012, suicide was the fourth-highest cause of death.

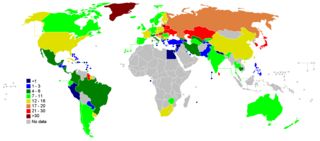
About 800,000 people die by suicide worldwide every year. 139,123 Indians committed suicide in 2019 and the national suicide rate was 10.4. According to The World Health Organization, in India, suicide is an emerging and serious public health issue.
A suicide attempt is an attempt to die by suicide that results in survival. It may be referred to as a "failed" or "unsuccessful" suicide attempt, though these terms are discouraged by mental health professionals for implying a suicide that results in death is a successful and positive outcome.
The conviction rate of a prosecuting unit of government reflects the likelihood that in that jurisdiction a case that is brought will end in conviction. Conviction rates reflect many aspects of the legal processes and systems at work within the jurisdiction, and are a source of both jurisdictional pride and broad controversy. Rates are often high, especially when presented in their most general form. Rates across jurisdictions within countries can vary by tens of percentage points. In other cases, they are uniformly high, although for distinct reasons.

Domestic violence in India includes any form of violence suffered by a person from a biological relative but typically is the violence suffered by a woman by male members of her family or relatives..Although Men also suffer Domestic violence, the law under IPC 498A specifically protects only women. Specifically only a woman can file a case of domestic violence. According to a National Family and Health Survey in 2005, total lifetime prevalence of domestic violence was 33.5% and 8.5% for sexual violence among women aged 15–49. A 2014 study in The Lancet reports that although the reported sexual violence rate in India is among the lowest in the world, the large population of India means that the violence affects 27.5 million women over their lifetimes. However, an opinion survey among experts carried out by the Thomson Reuters Foundation ranked India as the most dangerous country in the world for women.

Traffic collisions in India are a major source of deaths, injuries and property damage every year. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) 2016 report states there were 496,762 roads, railways and railway crossing-related traffic collisions in 2015. Of these, road collisions accounted for 464,674 collisions which caused 148,707 traffic-related deaths in India. The three highest total number of fatalities were reported in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu, and together they accounted for about 33% of total Indian traffic fatalities in 2015. Adjusted for 182.45 million vehicles and its 1.31 billion population, India reported a traffic collision rate of about 0.8 per 1000 vehicles in 2015 compared to 0.9 per 1000 vehicles in 2012, and an 11.35 fatality rate per 100,000 people in 2015. According to Gururaj, the top three highest traffic fatality rates per 100,000 people in 2005 were reported by Tamil Nadu, Goa and Haryana, with a male:female fatality ratio of about 5:1. The reported total fatality, rates per 100,000 people and the regional variation of traffic collisions per 100,000 people varies by source. For example, Rahul Goel in 2018 reports an India-wide average fatality rate of 11.6 per 100,000 people and Goa to be the state with the highest fatality rate.
Rape is the fourth most common crime against women in India. According to the 2019 annual report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), 32033 rape cases were registered across the country, or an average of 88 cases daily, slightly lower than 2018 when 91 cases were registered daily. Of these, 30,165 rapes were committed by perpetrators known to the victim, a high number similar to 2018. The share of victims who were minors or below 18 - the legal age of consent - stood at 15.4%, down from 27.8% in 2018. On the other hand, rapes by juveniles remained high in India with 3 minors being arrested for rape, assault and attempted violence on women and girls each day in 2019.
Prisons, and their administration, is a state subject covered by item 4 under the State List in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India. The management and administration of prisons falls exclusively in the domain of the State governments, and is governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 and the Prison manuals of the respective state governments. Thus, the states have the primary role, responsibility and authority to change the current prison laws, rules and regulations. The Central Government provides assistance to the states to improve security in prisons, for the repair and renovation of old prisons, medical facilities, development of borstal schools, facilities to women offenders, vocational training, modernization of prison industries, training to prison personnel, and for the creation of high security enclosures.

Violence against women in India refers to physical or sexual violence committed against a woman, typically by a man. Common forms of violence against women in India include acts such as domestic abuse, sexual assault, and murder. In order to be considered violence against women, the act must be committed solely because the victim is female. Most typically, these acts are committed by men as a result of the long-standing gender inequalities present in the country.
This is a list of states and union territories of India ranked according to crime against women and rate of crime against women. The list is compiled from the 2016 and 2018 Crime in India Report published by National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Government of India.
This is a list of states and union territories of India ranked by incidents of human trafficking as of 2016, and is based on the number of convicted cases. The list is compiled from the '2016 Crime in India Report' published by National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Government of India.
Student Suicides in India is one of the leading unnatural death causes among students of all age groups in India. As per the data compiled by National Crime Records Bureau, around 1,80,000 students died by suicide from year 1995 till year 2020. Student Suicides in India are reported from all states of India. Even premier institutes like Indian Institute of Technology and Indian Institute of Management are facing suicidal deaths of students. Students from all professions are facing stress due to various reasons resulting in suicidal tendencies. Student suicides in country has been steadily increasing from year 2016 and with some estimates missing the actual number of deaths are considered much more higher. A study conducted showed that girls are more prone to suicidal tendencies than boys.







