The demographics of Finland is monitored by the Statistics Finland. Finland has a population of over 5.6 million people, ranking it 19th out of 27 within the European Union. The average population density in Finland is 19 inhabitants per square kilometre (49/sq mi), making it the third most sparsely populated country in Europe, after Iceland and Norway. Population distribution is extremely uneven, with the majority of the population concentrated in the southern and western regions of the country. The majority of the Finnish population - approximately 73% - lives in urban areas. Approximately 1.6 million, or almost 30%, reside solely in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area. Conversely, the Arctic Lapland region contains only two inhabitants per square kilometre (5.2/sq mi).

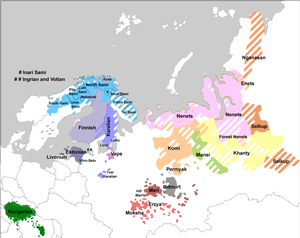
Finno-Ugric is a traditional linguistic grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except for the Samoyedic languages. Its once commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th century and is criticized by some contemporary linguists such as Tapani Salminen and Ante Aikio. The three most spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric.

The Sámi are the traditionally Sámi-speaking indigenous people inhabiting the region of Sápmi, which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Kola Peninsula in Russia. The region of Sápmi was formerly known as Lapland, and the Sámi have historically been known in English as Lapps or Laplanders, but these terms are regarded as offensive by the Sámi, who prefer their own endonym, e.g. Northern Sámi Sápmi. Their traditional languages are the Sámi languages, which are classified as a branch of the Uralic language family.

The Uralic languages, sometimes called the Uralian languages, are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; and the Samoyedic languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia.
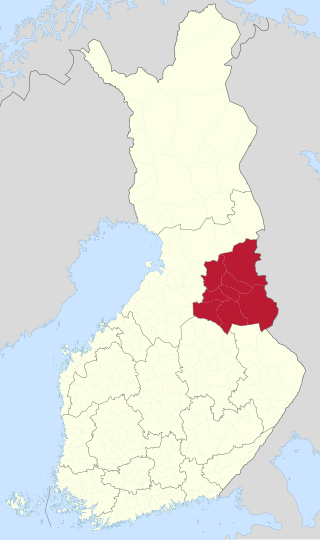
Kainuu, also historically known as Cajania, is one of the 19 regions of Finland. Kainuu borders the regions of North Ostrobothnia, North Savo and North Karelia. In the east, it also borders Russia.
Kvenland, known as Cwenland, Qwenland, Kænland, and similar terms in medieval sources, is an ancient name for an area in Fennoscandia and Scandinavia. Kvenland, in that or nearly that spelling, is known from an Old English account written in the 9th century, which used information provided by Norwegian adventurer and traveler Ohthere, and from Nordic sources, primarily Icelandic. A possible additional source was written in the modern-day area of Norway. All known Nordic sources date from the 12th and 13th centuries. Other possible references to Kvenland by other names and spellings are also discussed here.
Finns or Finnish people are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these countries as well as those who have resettled. Some of these may be classified as separate ethnic groups, rather than subgroups of Finns. These include the Kvens and Forest Finns in Norway, the Tornedalians in Sweden, and the Ingrian Finns in Russia.

The Sámi people are a Native people of northern Europe inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses northern parts of Sweden, Norway, Finland, and the Kola Peninsula of Russia. The traditional Sámi lifestyle, dominated by hunting, fishing and trading, was preserved until the Late Middle Ages, when the modern structures of the Nordic countries were established.

Kuhmo is a town and a municipality in Finland and is located at the south-eastern corner of the Kainuu region. The municipality has a population of 7,498 and covers an area of 5,456.78 square kilometres (2,106.87 sq mi) of which 649.97 km2 (250.95 sq mi) is water. The population density is 1.56 inhabitants per square kilometre (4.0/sq mi). It shares a border of 120 kilometres (75 mi) with Russia. Neighbouring towns are Hyrynsalmi, Lieksa, Nurmes, Ristijärvi, Sotkamo and Suomussalmi. A neighbour city across the Russian border is Kostomuksha. Vartius, one of the border crossing points between Finland and Russia, is located in northern Kuhmo.

Kuusamo is a town and municipality in Finland. It is located in Koillismaa, the northeastern part of the Northern Ostrobothnia region. The municipality has a population of 14,783 and covers an area of 5,808.92 square kilometres (2,242.84 sq mi) of which 830.81 km2 (320.78 sq mi) is water. The population density is 2.97 inhabitants per square kilometre (7.7/sq mi).

Nenets is a pair of closely related languages spoken in northern Russia by the Nenets people. They are often treated as being two dialects of the same language, but they are very different and mutual intelligibility is low. The languages are Tundra Nenets, which has a higher number of speakers, spoken by some 30,000 to 40,000 people in an area stretching from the Kanin Peninsula to the Yenisei River, and Forest Nenets, spoken by 1,000 to 1,500 people in the area around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers.

Finno-Volgaic or Fenno-Volgaic is a hypothetical branch of the Uralic languages that tries to group the Finnic languages, Sami languages, Mordvinic languages, and the Mari language. The hypothesis would have this language group branching from the Finno-Permic languages about 2000 BC.

The Finno-Samic languages are a hypothetical subgroup of the Uralic family, and are made up of 22 languages classified into either the Sami languages, which are spoken by the Sami people who inhabit the Sápmi region of northern Fennoscandia, or Finnic languages, which include the major languages Finnish and Estonian. The grouping is not universally recognized as valid.

The Finno-Permic or Finno-Permian languages, sometimes just Finnic languages, are a proposed subdivision of the Uralic languages which comprise the Balto-Finnic languages, Sámi languages, Mordvinic languages, Mari language, Permic languages and likely a number of extinct languages. In the traditional taxonomy of the Uralic languages, Finno-Permic is estimated to have split from Finno-Ugric around 3000–2500 BC, and branched into Permic languages and Finno-Volgaic languages around 2000 BC. Nowadays the validity of the group as a taxonomical entity is being questioned, and the interrelationships of its five branches are debated with little consensus.

The Sámi languages, also rendered in English as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Indigenous Sámi peoples in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.

Inari or Aanaar Sámi are a group of Sámi people who inhabit the area around Lake Inari, Finland. They speak the Inari (Aanaar) Sámi language, which belongs to the eastern Sámi languages. There are an estimated 700–900 ethnic Inari Sámi in Finland, of whom approximately 300–400 speak Inari Sámi. They are the only group of Sámi who live within one state and one municipality. Inari Sámi are indigenous peoples of their area.

Omok is an extinct Yukaghir language of Siberia, part of a dialect continuum with two surviving languages, also referred to as an eastern dialect of Tundra Yukaghir. It was last spoken perhaps as late as the 18th century. A wordlist of Omok, as well as its sister language Chuvan, was recorded in 1821 by Fyodor Matyushkin.

The forest Sámi are Sámi people who lived in the woods and who, unlike the reindeer-herding Sámi people, did not move up into the fells during the summer season. Historically, there have been forest Sámi in Sweden in the area ranging from northern Ångermanland to the far north. In the early 1600s the term granlapp was also used to refer to the Sámi people who paid taxes only to Sweden, compared to the semi-nomadic fell Sámi, who, since they worked in the fells that straddled the Swedish-Norwegian border, had to pay taxes to both countries. When Ernst Manker studied the life of the forest Sámi in the early 20th century, nearly all of their habitations had been abandoned. Only one forest Sámi village remained, in Malå in Västerbotten, an area known as Stenundslandet in Anundsjö. There is a modern-day group who consider themselves forest Sámi in Finland, but they are not part of the Sámi parliament, for example.
Kainuu people are Eastern Finnish inhabitants of the Kainuu region.