
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them. Common types of buffer zones are demilitarized zones, border zones and certain restrictive easement zones and green belts. Such zones may be comprised by a sovereign state, forming a buffer state.

Shantiniketan is a neighbourhood of Bolpur town in the Bolpur subdivision of Birbhum district in West Bengal, India, approximately 152 km north of Kolkata. It was established by Maharshi Devendranath Tagore, and later expanded by his son, Rabindranath Tagore whose vision became what is now a university town with the creation of Visva-Bharati. It is also the birthplace of Amartya Sen, an Economist, Philosopher, & Nobel Laureate

Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands, woodlands, wetlands, and deserts that are grazed by domestic livestock or wild animals. Types of rangelands include tallgrass and shortgrass prairies, desert grasslands and shrublands, woodlands, savannas, chaparrals, steppes, and tundras. Rangelands do not include forests lacking grazable understory vegetation, barren desert, farmland, or land covered by solid rock, concrete, or glaciers.

Matheran is an automobile-free hill station and a municipal council in the Karjat taluka of the Raigad district located in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Matheran is part of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, and one of the smallest hill stations in India. It is located in the Western Ghats, at an elevation of around 800 m above sea level. It is about 90 km from Mumbai, and 120 km from Pune. This proximity to these urban areas makes it a weekend getaway for many. Matheran, which means "forest on the forehead" in Marathi, is an eco-sensitive region, declared by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India. It is Asia's only automobile-free hill station.

Birbhum district is an administrative unit in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the northernmost district of Burdwan division—one of the five administrative divisions of West Bengal. The district headquarters is in Suri. Other important cities are Bolpur, Rampurhat and Sainthia. Jamtara, Dumka and Pakur districts of the state of Jharkhand lie at the western border of this district; the border in other directions is covered by the districts of Bardhaman of Purba Bardhaman, Paschim Bardhaman and Murshidabad of West Bengal.

Bidar district is the northernmost part of the Karnataka state in India. The administrative headquarters of district is Bidar city. Geographically, it resembles the "Crown of the State", occupying its northeastern end. It is bounded by Kamareddy and Sangareddy districts of Telangana state on the eastern side, Latur and Osmanabad districts of Maharashtra state on the western side, Nanded district of Maharashtra state on the northern side and Kalaburagi district on the southern side.

Bardhaman, or sometimes Burdwan and Barddhaman, is a former district in the Indian state of West Bengal, headquartered in Bardhaman. On 7 April 2017, the district was bifurcated into two separate districts namely Purba Bardhaman and Paschim Bardhaman. It was the seventh most populous district in India at the time of bifurcation.

The Geography of West Bengal, a state in eastern India, is primarily defined by plains and plateaus, with the high peaks of the Himalayas in the north and the Bay of Bengal to the south.

Rarh region is a toponym for an area in the Indian subcontinent that lies between the Chota Nagpur Plateau on the West and the Ganges Delta on the East. Although the boundaries of the region have been defined differently according to various sources throughout history, it is mainly coextensive with the state of West Bengal, also comprising parts of the state of Jharkhand in India.

Madayi. is a Census Town and Grama panchayat in Kannur district of Kerala state, India.
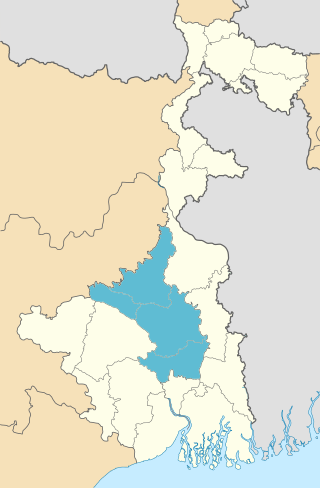
Burdwan Division is one of the 5 administrative division in the Indian state of West Bengal. The headquarters of the Burdwan division is situated at Chinsurah while the largest city in this division is Asansol. This division is known for its huge reserve of coal, mainly in the districts of Paschim Bardhaman and Birbhum.

Bolpur is a city and a municipality in Birbhum district in the state of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of the Bolpur subdivision. Bolpur municipal area includes Santiniketan. The city is known as a cultural and educational hub of West Bengal. The city is under the jurisdiction of Bolpur and Santiniketan Police station. Bolpur is the largest and most populous city in Birbhum district and 28th most populous city in West Bengal. Located on the banks of Ajay River and Kopai River, Bolpur has been a major human settlement. It is 150 km north of Kolkata and is famous for Visva Bharati, the University set up by the Nobel laureate poet Rabindranath Tagore.
Ilambazar is a census town, with a police station, in Ilambazar CD block in Bolpur subdivision of Birbhum district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

Banalakshmi or "Vanalakshmi Unmesh Samiti" is a Krishi Ashram and a small NGO in the Birbhum district of West Bengal. It is located near to the Santiniketan, the education centre set up by Rabindranath Tagore. It is connected by a highway to Ilambazar and Bolpur. The bus stop name is Banabhila. The Choupahari sal forests or commonly known as Ilambazar forests starts from here. Address is Vanalakshmi Unmesh Samiti, Banabhila, P.O. Dwaranda, Birbhum-731236. It is around 13/14 km towards Ilambazar from Shantiniketan. Contact Numbers are +919434233376 and +919434557527.

The Kopai River is a tributary of the Bakreshwar River. It flows past such towns as Santiniketan, Bolpur, Kankalitala, Kirnahar and Labhpur in Birbhum district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a small river in dry season but overflows its banks during the monsoon. There is a village name Chhora (ছোড়া) beside this river. Also Barghata (বড়ঘাটা), Nichinta (নিচিন্তা), Rupuspur (রুপুসপুর), Perua, (পেরুয়া) etc depend on this river. হাসুলি বাঁকের উপকথা তে শাল নদীর নাম উল্লেখ করা হয়েছে ।

Angadippuram Laterite is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument in Angadippuram town in Malappuram district in the southern Indian state of Kerala, India. The special significance of Angadippuram to laterites is that it was here that Dr. Francis Buchanan-Hamilton, a professional surgeon, gave the first account of this rock type, in his report of 1807, as "indurated clay", ideally suited for building construction. This formation falls outside the general classification of rocks namely, the igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary rocks but is an exclusively "sedimentary residual product". It has generally a pitted and porous appearance. The name laterite was first coined in India, by Buchanan and its etymology is traced to the Latin word "letritis" that means bricks. This exceptional formation is found above parent rock types of various composition namely, charnockite, leptynite, anorthosite and gabbro in Kerala. It is found over basalt in the states of Goa, Maharashtra and in some regions of Karnataka. In Gujarat in western India, impressive formations of laterite are found over granite, shale and sandstone..

Laterite is a soil type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolonged weathering of the underlying parent rock, usually when there are conditions of high temperatures and heavy rainfall with alternate wet and dry periods. The process of formation is called laterization. Tropical weathering is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.

Bolpur Sriniketan is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Bolpur subdivision of Birbhum district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

The Indian state West Bengal has a rich cultural heritage. Due to the reign of many different rulers in the past, arts and crafts in West Bengal underwent many changes giving an artistic diversity today in the forms of traditional handicrafts, terracotta, painting and carving, dances and music.

Shonajhuri Haat or Khoai Mela, also known as Shonibarer haat is a weekly Saturday afternoon bazaar set up by local artisans in Santiniketan, Birbhum district, West Bengal. The Khoai Mela has now become a part of the culture of the Bengali people and has been taking place for over 20 years. It takes place every Saturday on the bank of the Khoai or Kopai River. The Mela is named after this Khoai region and River. This Mela is also called Shanibarer haat due to its opening day.



















