Related Research Articles

Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's extremities from repeated injuries or infection through unnoticed wounds. An infected person may also experience muscle weakness and poor eyesight. Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but, for some people, symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur.

A leper colony, also known by many other names, is an isolated community for the quarantining and treatment of lepers, people suffering from leprosy.
M. leprae, the bacterium responsible for leprosy, is believed to have spread from East Africa through the Middle East, Europe, and Asia by the 5th century before reaching the rest of the world more recently. Historically, leprosy was believed to be extremely contagious and divinely ordained, leading to enormous stigma against its sufferers. Other severe skin diseases were frequently conflated with leprosy and all such sufferers were kept away from the general public, although some religious orders provided medical care and treatment. Recent research has shown M. leprae has maintained a similarly virulent genome over at least the last thousand years, leaving it unclear which precise factors led to leprosy's near elimination in Europe by 1700. A growing number of cases following the first wave of European colonization, however, led to increased attention towards leprosy during the New Imperialism of the late 19th century. Following G.A. Hansen's discovery of the role of M. leprae in the disease, the First International Leprosy Conference held in Berlin in 1897 renewed interest and investment in the isolation of lepers throughout the European colonial empires. Although Western countries now generally treat cases of leprosy individually on an outpatient basis, traditional isolated colonies continue to exist in India, China, and some other countries.
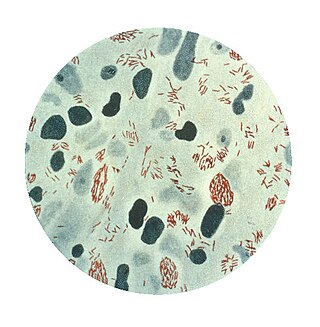
Mycobacterium leprae is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen's disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.
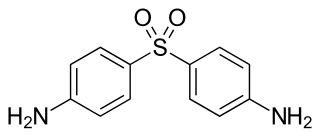
Dapsone, also known as 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (SDA) or diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS), is an antibiotic commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy. It is a second-line medication for the treatment and prevention of pneumocystis pneumonia and for the prevention of toxoplasmosis in those who have poor immune function. Additionally, it has been used for acne, dermatitis herpetiformis, and various other skin conditions. Dapsone is available both topically and by mouth.
Lepra (Leprosy Relief Association) is a UK-based international charity established in 1924, working to diagnose, treat, and rehabilitate people with leprosy. Lepra currently works in India, Bangladesh, and Zimbabwe.
Paul Wilson Brand, was a pioneer in developing tendon transfer techniques for use in the hands of those with leprosy. He was the first physician to appreciate that leprosy is not a disease of the tissue but of the nerves: it is the loss of the sensation of pain which makes sufferers susceptible to injury and leads to tissue rotting away, especially in the extremities. Brand contributed extensively to the fields of hand surgery and hand therapy through his publications and lectures, and wrote popular autobiographical books about his childhood, his parents' missionary work, and his philosophy about the valuable properties of pain. One of his best-known books, co-written with Christian writer Philip Yancey, is Pain: The Gift Nobody Wants (1993), republished in 1997 as The Gift of Pain.

Noma is a rapidly progressive and often fatal gangrenous infection of the mouth and face. Noma usually begins as an ulcer on gums and rapidly spreads into the jawbone, cheek, and soft tissues of the face. This is followed by death of the facial tissues and fatal sepsis. Survivors are left with severe facial disfigurement often with impairments in breathing, swallowing, speaking and vision. In 2023 noma was added to the World Health Organization's list of neglected tropical diseases.

Scheuermann's disease is a self-limiting skeletal disorder of childhood. Scheuermann's disease describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the signature "wedging" shape of the vertebrae, causing kyphosis. It is named after Danish surgeon Holger Scheuermann.

Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases, which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly.
A leprostatic agent is a drug that interferes with proliferation of the bacterium that causes leprosy.

The National Hansen's Disease Museum is a museum in Higashimurayama, Tokyo, Japan that is dedicated to education about Hansen's disease (leprosy) and to eliminating discriminatory practices against its sufferers. It was formerly (1993–2007) named "His Imperial Highness Prince Takamatsu Memorial Museum of Hansen's Disease".
William Jopling was an Italian-born British leprologist who together with D. S. Ridley proposed the Ridley-Jopling classification of leprosy (1962), and wrote the widely read textbook of "Handbook of Leprosy" which had a fifth edition. He had a wide understanding of leprosy problems based on his experiences as the director of Jordan Hospital (1950–1967), a leprosy hospital in London and wrote various articles including "leprosy stigma".
Leprosy stigma is a type of social stigma, a strong negative feeling towards a person with leprosy relating to their moral status in society. It is also referred to as leprosy-related stigma, leprostigma, and stigma of leprosy. Since ancient times, leprosy instilled the practice of fear and avoidance in many societies because of the associated physical disfigurement and lack of understanding behind its cause. Because of the historical trauma the word "leprosy" invokes, the disease is now referred to as Hansen's disease, named after Gerhard Armauer Hansen who discovered Mycobacterium leprae, the bacterial agent that causes Hansen's disease. Those who have suffered from Hansen's disease describe the impact of social stigma as far worse than the physical manifestations despite it being only mildly contagious and pharmacologically curable. This sentiment is echoed by Weis and Ramakrishna, who noted that "the impact of the meaning of the disease may be a greater source of suffering than symptoms of the disease".
The Leprosy Mission is a Christian international NGO. They are the largest and oldest organisation working in the fight against leprosy and are working towards the goal of zero leprosy transmission by 2035.
Leprosy currently affects approximately a quarter of a million people throughout the world, with the majority of these cases being reported from India.

Worldwide, two to three million people are estimated to be permanently disabled because of leprosy. India has the greatest number of cases, with Brazil second and Indonesia third.

Promin, or sodium glucosulfone is a sulfone drug that was investigated for the treatment of malaria, tuberculosis and leprosy. It is broken down in the body to dapsone, which is the therapeutic form.
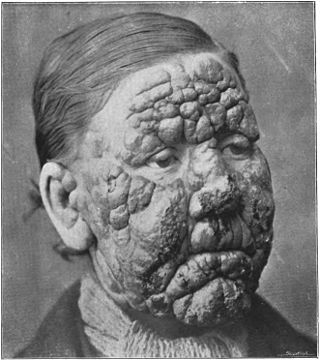
Although leprosy, or Hansen's Disease, was never an epidemic in The United States, cases of leprosy have been reported in Louisiana as early as the 18th century. The first leprosarium in the continental United States existed in Carville, Louisiana from 1894-1999 and Baton Rouge, Louisiana is the home of the only institution in the United States that is exclusively devoted to leprosy consulting, research, and training.
There has, historically, been fear around leprosy and people with the disease have suffered stigma, isolation and social exclusion. Expulsion of individuals infected with leprosy to quarantined areas or special institutions has been the general protocol since ancient times and was the recommended course of action by the Leprosy Conference of Berlin 1897. As a result, the exclusion and quarantining of people infected with leprosy became law, hence leprosy colonies were formed. The inhabitants of these colonies had very little legal recourse in preventing their exclusion and, even after they were treated and cured, many had trouble reintegrating into society. Even by the 1960s, when leprosy was highly treatable and curable, it still resulted in repulsion, and the exclusion of sufferers, by the general populace. As leprosy became curable, the focus of study shifted towards investigating the social aspects of the disease. This has become relevant due to the fact that the disease is making a resurgence and is proving resistant to previous remedies.

The history of leprosy was traced to its origins by an international team of 22 geneticists using comparative genomics of the worldwide distribution of Mycobacterium leprae. Monot et al. (2005) determined that leprosy originated in East Africa or the Near East and traveled with humans along their migration routes, including those of trade in goods and slaves. The four strains of M. leprae are based in specific geographic regions where each predominantly occurs:
References
- ↑ WHO | Leprosy Factsheet
- ↑ Chen XS, Li WZ, Jiang C, Ye GY (2001). "Leprosy in China: epidemiological trends between 1949 and 1998". Bull. World Health Organ. 79 (4): 306–12. ISSN 0042-9686. PMC 2566398 . PMID 11357209.
- ↑ Shen JP, Gupte MD, Jiang C, Manickam P, Yu MW, Li WZ (June 2005). "Trends of case detection and other indicators of leprosy in China during 1985–2002". Chin. Med. Sci. J. 20 (2): 77–82. PMID 16075742.
- ↑ WHO | Leprosy Today
- ↑ "Discrimination still plagues leprosy victims in mainland China". 27 January 2013.