
Mona is the third-largest island of the Puerto Rican archipelago, after the main island of Puerto Rico and Vieques. It is the largest of three islands in the Mona Passage, a strait between the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico, the others being Monito Island and Desecheo Island. It measures about 7 miles by 4 miles, and lies 41 mi (66 km) west of Puerto Rico, of which it is administratively a part. It is one of two islands that make up the Isla de Mona e Islote Monito barrio in the municipality of Mayagüez.

La Fortaleza is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico and has been since the 16th century. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan, in Puerto Rico. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina. It is the oldest executive mansion in continuous use in the New World. It was listed by UNESCO in 1983 as part of the World Heritage Site "La Fortaleza and San Juan National Historic Site".

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico.

The Guánica State Forest, popularly known as the Guánica Dry Forest is a subtropical dry forest located in southwest Puerto Rico. The area was designated as a forest reserve in 1919 and a United Nations Biosphere Reserve in 1981. It is considered the best preserved subtropical dry forest and the best example of dry forest in the Caribbean.

Maricao State Forest is a state forest located in the eastern Cordillera Central mountains of Puerto Rico. It is commonly known as Monte del Estado due to the fact that it was one of the first forest reserves in Puerto Rico to be designated a state forest in its official name. With an area of 10,803 acres (43.72 km2), the Maricao State Forest is the largest of the 20 forestry units of the Puerto Rico state forest system.

This portion of National Register of Historic Places listings in Puerto Rico is along the north coast, north plains, and north slopes of the Cordillera, from Isabela to Guaynabo.
The Aguirre State Forest is a 2,393-acre (9.68 km2) nature reserve on the south coast of Puerto Rico and one of the commonwealth's 20 state forests. It mainly consists of mangroves and floodplain forests, and it borders the Jobos Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve. The Aguirre State Forest is owned and administered by Puerto Rico. It was established in 1918 by Puerto Rico governor Arthur Yager to protect the mangrove forests areas between the municipalities of Guayama and Santa Isabel.

This portion of National Register of Historic Places listings in Puerto Rico is along the central mountain region, from Las Marías and Maricao in the central-west to Juncos in the central-east, including the slopes of the Cordillera.

Piñones State Forest,, and named after the Casuarina, locally called Piñones, is a timberland forest near one of the longest beaches in Puerto Rico. It is located in Torrecilla Baja barrio in the municipality of Loíza. It is a tourist attraction and is managed by the Puerto Rico Department of Natural and Environmental Resources.
Cambalache State Forest and Reserve is a nature reserve and one of the 20 state forests in the territory of Puerto Rico. The Cambalache State Forest is located in the municipalities of Arecibo and Barceloneta in northern Puerto Rico.

Rio Abajo State Forest is a forest preserve in Puerto Rico owned by the Department of Natural Resources and one of the 20 state forests in the island. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1980 and constitutes an area of 3,590 acres. It consists mostly of subtropical wet and moist karst forest. Mogotes and sinkholes fill the landscape. The forest preserve is located in the municipalities of Arecibo and Utuado. In addition to its ecological value the forest also contains a number of archaeological sites.
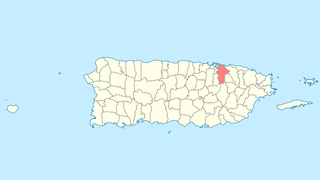
This portion of National Register of Historic Places listings in Puerto Rico covers the municipality of San Juan.

Cerrillos State Forest is one of the 21 state forests in Puerto Rico. It is located in barrio Maragüez, in the municipality of Ponce, and covers 200 cuerdas of valleys and mountains in the foothills of the Cordillera Central mountain range. The forest has several trails, observation areas, several picnic areas, complete with gazeebos and a man-made reservoir, Lake Cerrillos and the Lake Cerrillos dam.

The Monte Choca State Forest is a 244.6-acre (0.990 km2), tropical moist forest, located in the municipality of Corozal in Puerto Rico. It is owned and maintained by the commonwealth of Puerto Rico and co-maintained by local conservation groups.

Boquerón State Forest is one of the 20 forestry units that make up the public forest system of Puerto Rico. Despite its name, the Boquerón State Forest is not only located in Boquerón, Cabo Rojo but also spans almost 5,000 acres across the municipalities of Cabo Rojo, Lajas and Mayagüez. The forest area is also known for its limestone cliffs, the lighthouse, and the salt flats which have been a source of salt since the pre-Hispanic era and, dating to 700 C.E., they are considered to be one of the oldest industries in the Americas.

The Puerto Mosquito Bioluminescent Bay or Mosquito Bio Bay, is a bay in the island of Vieques famous for its bioluminescence produced by the dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense, which glows blue when agitated. This species of phytoplankton is found in bays in the Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico and The Bahamas.

Los Morrillos de los Cabos Rojos or more commonly known as Los Morrillos de Cabo Rojo, is a cape and tombolo landform located in southwestern Puerto Rico in the municipality of Cabo Rojo. Los Morrillos is an excellent example of a tombolo, or a tied island, with two sand pits. The cape resembles a letter Y with its two promontories or morrillos being connected through sand pits which enclose a saltwater lagoon. The landform was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1980, and the site includes mangroves, beaches, important bird nesting areas, limestone caves, cliffs and rock formations. The reddish-colored limestone cliffs give the name to the town and municipality of Cabo Rojo.

Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve consists of two islands, Mona and Monito, in the Mona Passage off western Puerto Rico in the Caribbean. Mona and Monito Islands Nature Reserve encompasses both land and marine area, and with an area of 38,893 acres it is the largest protected natural area in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. Much like the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific Ocean, the Mona and Monito Islands reserve represents a living laboratory for archaeological, biological, geological, oceanographical and wildlife management research.




















