This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group (−OH) of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (−R). Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well (i.e. esters of acidic −SH, −SeH, −TeH, −PoH and −LvH groups). According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. [1]
Contents
- By number of R' group carbons (R−C(=O)−O−R')
- 1 carbon
- 2 carbons
- 3 carbons
- 4 carbons
- 5 carbons
- 7 carbons
- 8 carbons
- 10 carbons
- By number of R group carbons (R−C(=O)−O−R')
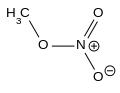
- 0 carbons
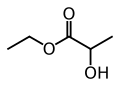
- 1 carbon 2
- 2 carbons 2
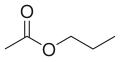
- 3 carbons 2
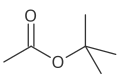
- 4 carbons 2
- 5 carbons 2
- 6 carbons
- 7 carbons 2
- 8 carbons 2
- 9 carbons
- 10 carbons 2
- 16 carbons
- List of ester odorants
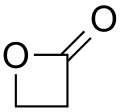
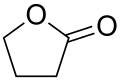
- Lactones
- References
An example of an ester formation is the substitution reaction between a carboxylic acid (R−C(=O)−OH) and an alcohol (R'OH), forming an ester (R−C(=O)−O−R'), where R and R′ are organyl groups, or H in the case of esters of formic acid. Glycerides, which are fatty acid esters of glycerol, are important esters in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids, and making up the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters of carboxylic acids with low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and found in essential oils and pheromones. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties, while polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Esters of carboxylic acids usually have a sweet smell and are considered high-quality solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers. [2] They are also one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. [3]