This is a list of islands of New Brunswick. The province of New Brunswick is composed of mainland New Brunswick and is lined with islands of various magnitudes.
This is a list of islands of New Brunswick. The province of New Brunswick is composed of mainland New Brunswick and is lined with islands of various magnitudes.
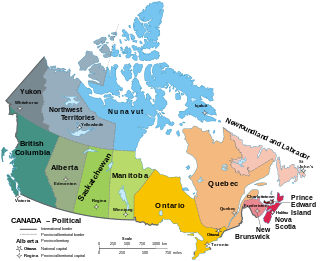
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.

Charlotte County is the most southwestern county of New Brunswick, Canada.

Gloucester County is located in the northeastern corner of New Brunswick, Canada. Fishing, mining and forestry are the major industries in the county. The eastern section of the county is known for its Acadian culture. The county is named for Princess Mary, Duchess of Gloucester and Edinburgh.

Restigouche County is located in north-central New Brunswick, Canada. The county is named for the Restigouche River which flows through the county and is famous for its salmon pools, which have attracted wealthy American and Canadian tourists to the region's summer colonies for decades. Forestry dominates the local economy.

Campobello Island is the largest and only inhabited island in Campobello, a geographic parish in southwestern New Brunswick, Canada, near the border with Maine, United States. The island's permanent population in 2021 was 949. It is the site of the Roosevelt Campobello International Park, Head Harbour Lighthouse, and of Herring Cove Provincial Park.

Events from the 15th century in Canada.

Machias Seal Island is an island in disputed water between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy, about 16 km (10 mi) southeast from Cutler, Maine, and 19 km (12 mi) southwest of Grand Manan Island, New Brunswick. Sovereignty of the island is disputed by the United States and Canada. The Canadian Coast Guard continues to staff a lighthouse on the island; the first lighthouse was constructed there in 1832.

The Madawaska River flows from Lake Témiscouata in Quebec, through Degelis, Quebec, to join the Saint John River at Edmundston, New Brunswick.
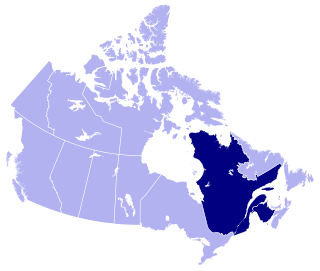
French is the mother tongue of approximately 7.2 million Canadians according to the 2016 Canadian Census. Most Canadian native speakers of French live in Quebec, the only province where French is the majority and the sole official language. Of Quebec's people, 71.2 percent are native francophones and 95 percent speak French as their first or second language.

Eastern Canada is generally considered to be the region of Canada south of Hudson Bay/Hudson Strait and east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces : Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario.

Atlantic Canadian English is a class of Canadian English dialects spoken in Atlantic Canada that is notably distinct from Standard Canadian English. It is composed of Maritime English and Newfoundland English. It was mostly influenced by British and Irish English, Irish and Scottish Gaelic, and some Acadian French. Atlantic Canada is the easternmost region of Canada, comprising four provinces located on the Atlantic coast: Newfoundland and Labrador, plus the three Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island. Regions such as Miramichi and Cape Breton have a wide variety of phrases and words not spoken outside of their respective regions.

The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:

Caraquet Bay is situated in the northeast of the Canadian province of New Brunswick. It is bordered on the south by the town of Caraquet and the village of Bertrand, to the south by the parish of New Bandon, to the north by the village of Maisonnette and to the northwest by the Baie des Chaleurs. Caraquet Island is located between the two bays. There are a number of beaches on the bay, as well as oyster farms and the port of Caraquet. Caraquet Bay flows into the Caraquet River and the Du Nord River

McAdam is a geographic parish in York County, New Brunswick, Canada.
The Upsalquitch River is a tributary of the South bank of the Restigouche River, flowing in Restigouche County, in the northwest of New Brunswick, in Canada.
The Iroquois River is a tributary of the Saint John River emptying in New Brunswick, in Canada. This river flows into the Notre Dame Mountains, in the municipality of Dégelis, Quebec, in Temiscouata Regional County Municipality (RCM), in administrative region of Bas-Saint-Laurent, in Quebec; and in the Madawaska County, in New Brunswick, in Canada.
The Little Iroquois River is a tributary of the Iroquois River, flowing in Notre Dame Mountains, the Madawaska County, in Northwest of New Brunswick, in Canada.