Related Research Articles

Natzweiler-Struthof was a Nazi concentration camp located in the Vosges Mountains close to the villages of Natzweiler and Struthof in the Gau Baden-Alsace of Germany, on territory annexed from France on a de facto basis in 1940. It operated from 21 May 1941 to September 1944, and was the only concentration camp established by the Germans in the territory of pre-war France. The camp was located in a heavily-forested and isolated area at an elevation of 800 metres (2,600 ft).

Gross-Rosen was a network of Nazi concentration camps built and operated by Nazi Germany during World War II. The main camp was located in the German village of Gross-Rosen, now the modern-day Rogoźnica in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland; directly on the rail-line between the towns of Jawor (Jauer) and Strzegom (Striegau). Its prisoners were mostly Jews, Poles and Soviet citizens.

August Hirt was an anatomist with Swiss and German nationality who served as a chairman at the Reich University in Strasbourg during World War II. He performed experiments with mustard gas on inmates at the Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp and played a lead role in the murders of 86 people at Natzweiler-Struthof for the Jewish skull collection. The skeletons of his victims were meant to become specimens at the Institute of anatomy in Strasbourg, but completion of the project was stopped by the progress of the war. He was an SS-Hauptsturmführer (captain) and in 1944, an SS-Sturmbannführer (major).

Heinrich Schwarz was an SS-Hauptsturmführer (captain) and concentration camp officer who served as commandant of Auschwitz III-Monowitz in Nazi-occupied Poland and Natzweiler-Struthof in Alsace-Lorraine.

Bad Friedrichshall is a town in the district of Heilbronn in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated at the confluences of the Jagst and of the Kocher into the Neckar, some 10 kilometres (6 mi) north of Heilbronn. Bad Friedrichshall arose by the connection of Kochendorf and Jagstfeld in 1933, and is famous for its salt mine.

Obrigheim is a town in the district of Neckar-Odenwald-Kreis, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.

Dautmergen is a municipality in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
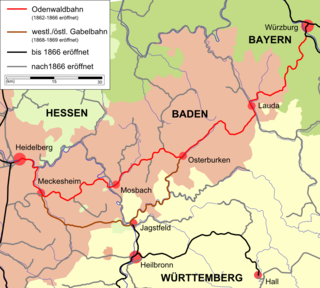
The Odenwald Railway was the name given to a Baden railway line in southwestern Germany built from between 1862 and 1866. It ran from Heidelberg via Neckargemünd and Meckesheim through the Little Odenwald mountains to Waibstadt, Mosbach, Osterburken and Lauda to Würzburg in Bavaria.

The Meckesheim–Neckarelz railway is a branch line in northern Baden between Meckesheim and Aglasterhausen that used to run to Neckarelz. It was part of the former Baden Oldenwald Railway from Heidelberg to Würzburg, and thus a main line, which is why its trackbed was built for two tracks. The section remaining today also goes under the name of Schwarzbach Valley Railway.
Hans Fleischhacker was a German anthropologist with the Ahnenerbe and a commander in the SS of Nazi Germany. He worked with Bruno Beger on some projects, making measurements of Jewish people. He was with Beger at Auschwitz when the people were selected to be part of the Jewish skull collection, a project of the Ahnenerbe. At their post-war trial, Beger was found guilty of full knowledge of the scope of that project, while Fleischhacker was found not to be aware that the purpose of the measurements was to select the 86 people to be murdered at Natzweiler-Struthof camp.

Bad Friedrichshall Hauptbahnhof is a regionally important junction station and a former border station in the city of Bad Friedrichshall in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. The modern Elsenz Valley Railway and Neckar Valley Railway branch from the Franconia Railway here. Until 1993 it was the starting point of the Lower Kocher Valley Railway.

KZ Walldorf was a subcamp of the Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp and existed from 22 August to 24 November 1944 near the village of Walldorf in Hesse. Erected after the deportations of the Jews in Hungary as part of the Nazi extermination through labour plan, about 1,700 female inmates were assigned to work on the first paved runway of the nearby Rhein-Main Airport.

Julius Christian Mergenthaler, was a Nazi German politician, member of the Reichstag and Württemberg Landtag, Ministerpräsident of Württemberg and Culture Minister.

Subcamps, also translated as satellite camps, were outlying detention centres (Haftstätten) that came under the command of a main concentration camp run by the SS in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The Nazis distinguished between the main camps and the subcamps subordinated to them. Survival conditions in the subcamps were, in many cases, poorer for the prisoners than those in the main camps.

The Gau Baden, renamed Gau Baden–Alsace in March 1941, was a de facto administrative division of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945 in the German state of Baden and, from 1940 onwards, in Alsace. Before that, from 1925 to 1933, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party in that area.

Operation Desert was a German synthetic fuel project during World War II. It attempted to build a shale oil industrial production complex for utilization of Swabian Alb oil shale deposits.

Schwäbisch Hall-Hessental station is the more important of the two stations of the major district town of Schwäbisch Hall in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is a junction station where the Waiblingen–Schwäbisch Hall railway (Murrbahn) branches off the Crailsheim–Heilbronn railway (Hohenlohebahn).

During World War II, the German Luftwaffe staffed dozens of concentration camps, and posted its soldiers as guards at many others. Camps created for the exploitation of forced labor for armaments production were often run by the branch of the Wehrmacht that used the products. The Wehrmacht also posted about 10,000 soldiers to concentration camps because of a shortage of guards in mid-1944, including many from the Luftwaffe.

The Eckerwald Memorial commemorates one of the last murderous chapters of Nazi war politics. In the autumn of 1944, prisoners of the Schörzingen concentration camp built a shale oil factory on this site during a construction period of about three months.
References
- ↑ United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (August 18, 2015). "Natzweiler-Struthof". Holocaust Encyclopedia. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
