Related Research Articles
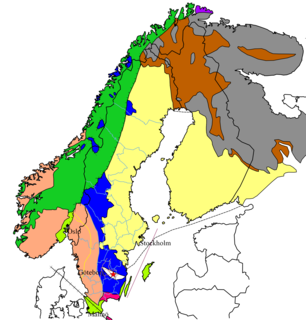
The Baltic Shield is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstone which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity. It contains the oldest rocks of the European continent with a thickness of 250-300 km.
Arctica or Arctida was an ancient continent which formed approximately 2.565 billion years ago in the Neoarchean era. It was made of Archaean cratons, including the Siberian Craton, with its Anabar/Aldan shields in Siberia, and the Slave, Wyoming, Superior, and North Atlantic cratons in North America. Arctica was named by Rogers 1996 because the Arctic Ocean formed by the separation of the North American and Siberian cratons. Russian geologists writing in English call the continent "Arctida" since it was given that name in 1987, alternatively the Hyperborean craton, in reference to the hyperboreans in Greek mythology.

Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at c. 1 Ga.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.

The geology of Antarctica covers the geological development of the continent through the Archean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic eons.
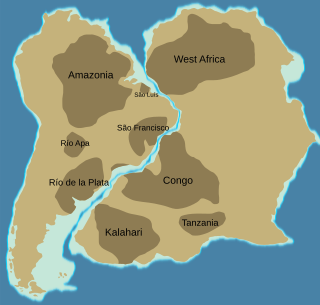
The Amazonian Craton is a geologic province located in South America. It occupies a large portion of the central, north and eastern part of the continent. The Guiana Shield and Central Brazil Shield constitutes respectively the northern and southern exhumed parts of the craton. Between the two shields lies the Amazon Rift, a zone of weakness within the craton. Smaller cratons of Precambrian rocks south of the Amazonian Shield are the Río de la Plata Craton and the São Francisco Craton, which lies to the east.

The geology of Saskatchewan can be divided into two main geological regions, the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the Phanerozoic Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. Within the Precambrian shield exists the Athabasca sedimentary basin. Meteorite impacts have altered the natural geological formation processes. The prairies were most recently affected by glacial events in the Quaternary period.
The West African Craton (WAC) is one of the five cratons of the Precambrian basement rock of Africa that make up the African Plate, the others being the Kalahari craton, Congo craton, Saharan Metacraton and Tanzania Craton. Cratons themselves are tectonically inactive, but can occur near active margins, with the WAC extending across 14 countries in Western African, coming together in the late Precambrian and early Palaeozoic eras to form the African continent. It consists of two Archean centers juxtaposed against multiple Paleoproterozoic domains made of greenstone belts, sedimentary basins, regional granitoid-tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) plutons, and large shear zones. The craton is overlain by Neoproterozoic and younger sedimentary basins. The boundaries of the WAC are predominantly defined by a combination of geophysics and surface geology, with additional constraints by the geochemistry of the region. At one time, volcanic action around the rim of the craton may have contributed to a major global warming event.
This timeline of natural history summarizes significant geological and biological events from the formation of the Earth to the arrival of modern humans. Times are listed in millions of years, or megaanni (Ma).

The Tuareg Shield is a geological formation lying between the West African craton and the Saharan Metacraton in West Africa. Named after the Tuareg people, it has complex a geology, reflecting the collision between these cratons and later events. The landmass covers parts of Algeria, Niger and Mali.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites.

The Svecofennian orogeny is a series of related orogenies that resulted in the formation of much of the continental crust in what is today Sweden and Finland plus some minor parts of Russia. The orogenies lasted from about 2000 to 1800 million years ago during the Paleoproterozoic Era. The resulting orogen is known as the Svecofennian orogen or Svecofennides. To the west and southwest the Svecofennian orogen limits with the generally younger Transscandinavian Igneous Belt. It is assumed that the westernmost fringes of the Svecofennian orogen have been reworked by the Sveconorwegian orogeny just as the western parts of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt has. The Svecofennian orogeny involved the accretion of numerous island arcs in such manner that the pre-existing craton grew with this new material from what is today northeast to the southwest. The accretion of the island arcs was also related to two other processes that occurred in the same period; the formation of magma that then cooled to form igneous rocks and the metamorphism of rocks.

The geology of Finland is made up of a mix of geologically very young and very old materials. Common rock types are orthogneiss, granite, metavolcanics and metasedimentary rocks. On top of these lies is a widespread thin layer of unconsolidated deposits formed in connection to the Quaternary ice ages, for example eskers, till and marine clay. The topographic relief is rather subdued because mountain massifs were worn down to a peneplain long ago.

The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions. The Aravalli Mountains consist of the Aravalli and Delhi fold belts, and are collectively known as the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt. The whole mountain range is about 700 km long. Unlike the much younger Himalayan section nearby, the Aravalli Mountains are much older that can be traced back to the Proterozoic Eon. The collision between the Bundelkhand craton and the Marwar craton is believed to be the primary mechanism for the development of the mountain range.
The Western Gneiss Region is a large geological unit in Norway chiefly made of gneiss rock that formed through metamorphism during the Caledonian orogeny. It makes up a tectono-stratigraphic terrane of the Scandinavian Caledonides and is also part of the Baltic shield. The region extends across western Norway from Bergen to Trondheim as a Caledonian window, outliers of the Western Gneiss Region crop out as far north as the Lofoten archipelago. The rocks of the Western Gneiss Region are made up of variously deformed Precambrian basement, and cover rocks of autochthonous and para-autochthonous origin with evidence of medium to high grade metamorphism including ultra-high-pressure metamorphism.
The Saamian orogeny is one of the earliest recognizable events in the formation of the Baltic Shield, between 3.1 and 2.9 billion years ago in the Archean and Proterozoic. The Saamian orogeny is associated with intense igneous activity that produced large granitoid plutons. The event lined up with the Katarchean, a period in which the Earth's crust approached its present thickness and sialic rocks, rich in silica and aluminium, became commonplace.
The geology of Ukraine is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in the region are part of the Ukrainian Shield and formed more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Extensive tectonic evolution and numerous orogeny mountain building events fractured the crust into numerous block, horsts, grabens and depressions and Ukraine was intermittently flooded as the crust downwarped during much of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and early Cenozoic, before the formation of the Alps and Carpathians defined much of its current topography and tectonics. Ukraine was impacted by the Pleistocene glaciations within the last several hundred thousand years. The country has numerous metal deposits as well as minerals, building stone and high-quality industrial sands.
The Superior Craton is a stable crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period. A craton is a large part of the Earth's crust that has been stable and subjected to very little geological changes over a long time. The size of Superior Craton is about 1,572,000 km2. The craton underwent a series of events from 4.3 to 2.57 Ga. These events included the growth, drifting and deformation of both oceanic and continental crusts.
The Laxfordian orogeny was an orogeny mountain building event between 1.9 and 1 billion years ago. It primarily affected the North Atlantic Craton, in particular a section that cleaved off during the Mesozoic as the Scottish Shield Fragment.
References
- ↑ Gaal, G. & Gorbatschev, R. (1987). "An Outline of the precambrian evolution of the baltic shield". Precambrian Research. 35: 15–52. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(87)90044-1.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ Goodwin, A. (1991). Precambrian Geology: The Dynamic Evolution of the Continental Crust. Academic Press. p. 582. ISBN 9781483288550.
