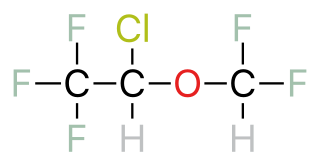Phenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, sold under the brand name Luminal among others, is a medication of the barbiturate type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy in developing countries. In the developed world, it is commonly used to treat seizures in young children, while other medications are generally used in older children and adults. It is also used for veterinary purposes.
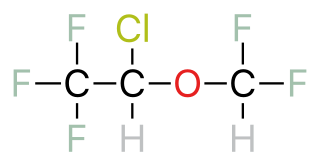
A halogenated ether is a subcategory of a larger group of chemicals known as ethers. An ether is an organic chemical that contains an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two (substituted) alkyl groups. A good example of an ether is the solvent diethyl ether. What differentiates a halogenated ether from other types of ethers is the substitution (halogenation) of one or more hydrogen atoms with a halogen atom. Halogen atoms include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
The Trapp mixture is a specific mixture of organic solvents that allows chemical reactions to take place at very low temperatures. It is made up of THF:diethyl ether:pentane in a 4:4:1 ratio which remains liquid down to −110 °C and the same solvents in a 4:1:1 ratio remain a liquid down to −120 °C. This solvent system retains a low viscosity until just before freezing and it allows a lower temperature reaction than pure THF, which melts at −108.4 °C. An illustrative application of Trapp solvent is the preparation of vinyllithium by lithium halogen exchange from vinyl bromide and tert-butyllithium. The low temperatures suppress the reaction of the strongly basic organolithium reagent with the THF.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as solutions in hydrocarbons (such as pentane); it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

Metharbital was patented in 1905 by Emil Fischer working for Merck. It was marketed as Gemonil by Abbott Laboratories. It is a barbiturate anticonvulsant, used in the treatment of epilepsy. It has similar properties to phenobarbital.

Tybamate is an anxiolytic of the carbamate family. It is a prodrug for meprobamate in the same way as the better known drug carisoprodol. It has liver enzyme inducing effects similar to those of phenobarbital but much weaker.

Flurothyl (Indoklon) is a volatile liquid drug from the halogenated ether family, related to inhaled anaesthetic agents such as diethyl ether, but having the opposite effects, acting as a stimulant and convulsant. A clear and stable liquid, it has a mild ethereal odor whose vapors are non-flammable. It is excreted from the body by the lungs in an unchanged state.

Dimethylcadmium is the organocadmium compound with the formula Cd(CH3)2. It is a colorless, highly toxic liquid that fumes in air. It is a linear molecule with C-Cd bond lengths of 213 pm. The compound finds limited use as a reagent in organic synthesis and in metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). It has also been used in the synthesis of cadmium selenide nanoparticles, although efforts have been made to replace it in this capacity due to its toxicity.

Brookhart's acid is the salt of the diethyl ether oxonium ion and tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate (BAr′4). It is a colorless solid, used as a strong acid. The compound was first reported by Volpe, Grant, and Brookhart in 1992.

Decynium-22 is a cationic derivative of quinoline, and a potent inhibitor of the plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT), as well as all members of the organic cation transporter (OCT) family in both human and rat cells. However, it has little effect on high affinity monoamine transporters such as the dopamine transporter and norepinephrine transporter.

2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a cyclic orthoester which can be reacted with diols to biodegradable polyorthoesters.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.

2,2'-Dipyrromethene, often called just dipyrromethene or dipyrrin, is a chemical compound with formula C
9H
8N
2 whose skeleton can be described as two pyrrole rings C
5N connected by a methyne bridge =CH– through their nitrogen-adjacent (position-2) carbons; the remaining bonds being satisfied by hydrogen atoms. It is an unstable compound that is readily attacked by nucleophilic compounds above −40 °C.
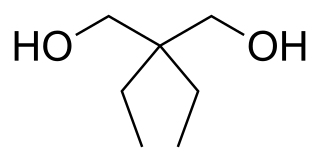
Prenderol (Diethylpropanediol) is a simple alkyl diol which has sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects. It is closely related in structure to meprobamate and numerous other alkyl alcohols and diols with generally comparable activity.

Diethyl diethylmalonate or diethyl 2,2-diethylmalonate is a derivative of diethyl malonate. It can be used in the synthesis of barbital.