Depressants, colloquially known as "downers" or central nervous system (CNS) depressants, are drugs that lower neurotransmission levels, decrease the electrical activity of brain cells, or reduce arousal or stimulation in various areas of the brain. Some specific depressants do influence mood, either positively or negatively, but depressants often have no clear impact on mood. In contrast, stimulants, or "uppers", increase mental alertness, making stimulants the opposite drug class from depressants. Antidepressants are defined by their effect on mood, not on general brain activity, so they form an orthogonal category of drugs.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry.
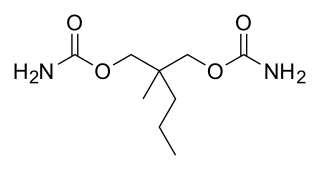
Meprobamate—marketed as Miltown by Wallace Laboratories and Equanil by Wyeth, among others—is a carbamate derivative used as an anxiolytic drug. It was the best-selling minor tranquilizer for a time, but has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepines due to their wider therapeutic index and lower incidence of serious side effects.

The Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis, published by K. C. Nicolaou and his group in 1994 concerns the total synthesis of taxol. Taxol is an important drug in the treatment of cancer but also expensive because the compound is harvested from a scarce resource, namely the pacific yew.

Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
The Negishi coupling is a widely employed transition metal catalyzed cross-coupling reaction. The reaction couples organic halides or triflates with organozinc compounds, forming carbon-carbon bonds (C-C) in the process. A palladium (0) species is generally utilized as the catalyst, though nickel is sometimes used. A variety of nickel catalysts in either Ni0 or NiII oxidation state can be employed in Negishi cross couplings such as Ni(PPh3)4, Ni(acac)2, Ni(COD)2 etc.
1,3-Propanediol is the organic compound with the formula CH2(CH2OH)2. This 3-carbon diol is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

Mephenesin (INN), also called myanesin, is a centrally acting muscle relaxant. It can be used as an antidote for strychnine poisoning. Mephenesin however presents with the major drawbacks of having a short duration of action and a much greater effect on the spinal cord than the brain, resulting in pronounced respiratory depression at clinical doses and therefore a very low therapeutic index. It is especially dangerous and potentially fatal in combination with alcohol and other depressants. Mephenesin was the inspiration for the synthesis of a derivative of 1,3-propanediol, meprobamate, by Bernard Ludwig and Frank Berger, the first tranquilizer to see widespread clinical use. Mephenesin is no longer available in North America but is used in Italy and a few other countries. Its use has largely been replaced by the related drug methocarbamol, which is better absorbed.

A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid in which one of the three hydroxyl groups is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes.
Butanediol, also called butylene glycol, may refer to any one of four stable structural isomers:

Etaqualone is a quinazolinone-class GABAergic and is an analogue of methaqualone that was developed in the 1960s and marketed mainly in France and some other European countries. It has sedative, hypnotic, muscle relaxant and central nervous system depressant properties resulting from its agonist activity at the β-subtype of the GABAA receptor, and was used for the treatment of insomnia.

QH-II-66 (QH-ii-066) is a sedative drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It produces some of the same effects as other benzodiazepines, but is much more selective than most other drugs of this class and so produces somewhat less sedation and ataxia than other related drugs such as diazepam and triazolam, although it still retains anticonvulsant effects.
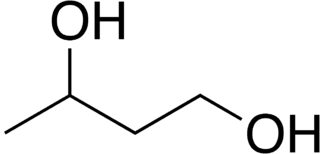
1,3-Butanediol is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2OH. With two alcohol functional groups, the molecule is classified as a diol. The compound is also chiral, but most studies do not distinguish the enantiomers. The compound is a colorless, bittersweet, water-soluble liquid. It is one of four common structural isomers of butanediol. It is used in flavoring, and as a precursor to some antibiotics.

Tybamate is an anxiolytic of the carbamate family. It is a prodrug for meprobamate in the same way as the better known drug carisoprodol. It has liver enzyme inducing effects similar to those of phenobarbital but much weaker.

3-MCPD (3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol or 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. The compound has attracted notoreity as the most common member of chemical food contaminants known as chloropropanols. It is suspected to be carcinogenic in humans.
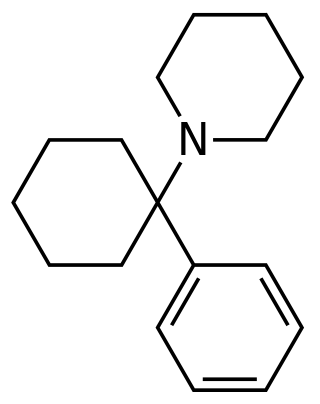
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.
Metal-catalyzed C–H borylation reactions are transition metal catalyzed organic reactions that produce an organoboron compound through functionalization of aliphatic and aromatic C–H bonds and are therefore useful reactions for carbon–hydrogen bond activation. Metal-catalyzed C–H borylation reactions utilize transition metals to directly convert a C–H bond into a C–B bond. This route can be advantageous compared to traditional borylation reactions by making use of cheap and abundant hydrocarbon starting material, limiting prefunctionalized organic compounds, reducing toxic byproducts, and streamlining the synthesis of biologically important molecules. Boronic acids, and boronic esters are common boryl groups incorporated into organic molecules through borylation reactions. Boronic acids are trivalent boron-containing organic compounds that possess one alkyl substituent and two hydroxyl groups. Similarly, boronic esters possess one alkyl substituent and two ester groups. Boronic acids and esters are classified depending on the type of carbon group (R) directly bonded to boron, for example alkyl-, alkenyl-, alkynyl-, and aryl-boronic esters. The most common type of starting materials that incorporate boronic esters into organic compounds for transition metal catalyzed borylation reactions have the general formula (RO)2B-B(OR)2. For example, bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2Pin2), and bis(catecholato)diborane (B2Cat2) are common boron sources of this general formula.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.
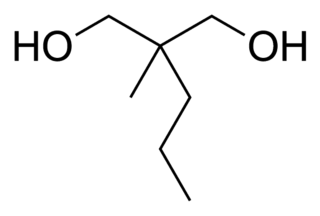
2-Methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol (MPP) is a simple alkyl diol which has sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects.
MC-2973 (2,2-diethyl-1,4-butanediol) is a diol with convulsant effects.













