
The Marijuana Policy Project (MPP) is the largest organization working solely on marijuana policy reform in the United States in terms of its budget, number of members, and staff. Its stated aims are to: (1) increase public support for non-punitive, non-coercive marijuana policies; (2) identify and activate supporters of non-punitive, non-coercive marijuana policies; (3) change state laws to reduce or eliminate penalties for the medical and non-medical use of marijuana; and (4) gain influence in Congress. MPP advocates taxing and regulating the possession and sale of marijuana in a manner similar to alcohol, envisions a nation where marijuana education is honest and realistic, and believes treatment for problem marijuana users should be non-coercive and geared toward reducing harm.

Since the 1970s, the college town of Ann Arbor, Michigan has enacted some of the most lenient laws on marijuana possession in the United States. These include measures approved in a 1971 city-council ordinance, a 1974 voter referendum making possession of small amounts of the substance merely a civil infraction subject to a small fine, and a 2004 referendum on the use of medical marijuana. The passage of the Michigan Regulation and Taxation of Marihuana Act in November 2018 has made recreational marijuana legal not only in Ann Arbor but throughout the entire state.
Amendment 44 was a proposed amendment to the state statutes submitted for referendum in the 2006 general elections in the U.S. state of Colorado. The amendment proposed the legalization of the possession of one ounce or less of marijuana for any person twenty-one years of age and over, as long as marijuana use does not occur in public. The measure was eventually defeated at the polls by 60-40 percent.

In the United States, the non-medical use of cannabis is decriminalized in 15 states, and legalized in another 11 states, as of June 2019. Decriminalization refers to a policy of reduced penalties for cannabis offenses, typically involving a civil penalty for possession of small amounts, instead of criminal prosecution or the threat of arrest. In jurisdictions without any penalties the policy is referred to as legalization, although the term decriminalization is sometimes broadly used for this purpose as well.
The Committee for Sensible Marijuana Policy is a Boston, Massachusetts based organization that was devoted to passing Question 2, a cannabis decriminalization initiative also known as the Massachusetts Sensible Marijuana Policy Initiative that was passed in Massachusetts in 2008 and officially became law on January 2, 2009 Whitney A. Taylor is the Treasurer and Chairwoman of the organization.

The Greyhound Protection Act is a Massachusetts statute that gradually eliminated commercial dog racing by 2010. It was enacted as Question 3 on the November 4, 2008 ballot in Massachusetts.

The Massachusetts Cannabis Reform Coalition (MassCann), the state affiliate of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, is a non-profit public education organization working for the moderation of marijuana laws. MassCann/NORML organizes the Freedom Rally on Boston Common every third Saturday in September. The MC/N newsletter, Mass Grass, is published six times annually. Membership is open to the public and leadership is democratically elected at the annual winter membership meeting, usually held in March.
Initiative 1068 was a proposed initiative for the November 2010 Washington state general election that would have removed criminal penalties from the adult use, possession, and cultivation of marijuana in Washington. Sponsored by Vivian McPeak, Douglass Hiatt, Jeffrey Steinborn, Philip Dawdy, initiative I-1068 sought to legalize marijuana by removing marijuana offenses from the state's controlled substances act, but failed to gather enough signatures to qualify for the ballot.

California Proposition 19 was a ballot initiative on the November 2, 2010 statewide ballot. It was defeated, with 53.5% of California voters voting "No" and 46.5% voting "Yes." If passed, it would have legalized various marijuana-related activities, allowed local governments to regulate these activities, permitted local governments to impose and collect marijuana-related fees and taxes, and authorized various criminal and civil penalties. In March 2010, it qualified to be on the November statewide ballot. The proposition required a simple majority in order to pass, and would have taken effect the day after the election. Yes on 19 was the official advocacy group for the initiative and California Public Safety Institute: No On Proposition 19 was the official opposition group.

In the United States, the use and possession of cannabis is illegal under federal law for any purpose, by way of the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Under the CSA, cannabis is classified as a Schedule I substance, determined to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use – thereby prohibiting even medical use of the drug. At the state level, however, policies regarding the medical and recreational use of cannabis vary greatly, and in many states conflict significantly with federal law.
Proposition 19, also known as the California Marijuana Initiative (CMI), was a ballot initiative on the November 7, 1972 California statewide ballot. This was the first attempt to legalize marijuana by ballot measure in the history of the United States. If it had passed, the measure would have removed penalties in the State of California for persons 18 years of age or older for using, possessing, growing, processing, or transporting marijuana for personal use. The California Marijuana Initiative's organizers coordinated a huge grassroots organizing drive to place the measure on the ballot. The initiative qualified for the November statewide ballot in June 1972. The initiative was defeated by the voters with 66.5% No votes to 33.5% Yes votes.
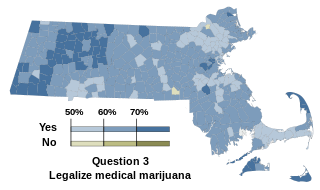
The Massachusetts Medical Marijuana Initiative, appeared as the third question on the state's 2012 ballot as an indirect initiated state statute. The measure allows cannabis to be used for medical purposes in the state. The initiative—backed by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Massachusetts Patient Advocacy Alliance, and the Committee for Compassionate Medicine—was filed with proponents turning in the required signatures to the Massachusetts Attorney General's office by the August 3, 2011 deadline. Those signatures were needed for the required ten qualified voters who submitted the original petition to put forward the full text of the law they want enacted. The initiative passed with support from 63% of state voters.

The legal history of cannabis in the United States began with state-level prohibition in the early 20th century, with the first major federal limitations occurring in 1937. Starting with Oregon in 1973, individual states began to liberalize cannabis laws through decriminalization. In 1996, California became the first state to legalize medical cannabis, sparking a trend that spread to a majority of states by 2016. In 2012, Colorado and Washington became the first states to legalize cannabis for recreational use.

Cannabis in Massachusetts relates to the legal and cultural events surrounding the use of cannabis. A century after becoming the first U.S. state to criminalize recreational cannabis, Massachusetts voters elected to legalize it in 2016.
Cannabis in Kansas refers to the drug cannabis in Kansas, United States, where it is illegal for all purposes, and possession of even small amounts is a misdemeanor crime.
Cannabis in Missouri is illegal but decriminalized. Medical use was legalized in 2018 through a ballot initiative to amend the state constitution.
Cannabis in Ohio is illegal for recreational use. Since 1975 possession of up to 100 grams has been decriminalized, however. Several of the state's major cities have also enacted further reforms.

In Washington, D.C., cannabis is legal for recreational and medical uses, but is barred from commercial sale. Though the drug was fully legalized in the District following a 2014 ballot referendum, the United States Congress exercises oversight over the government of the District of Columbia, preventing the local government from regulating cannabis sales like other jurisdictions with authority derived from a U.S. state.
Cannabis in Michigan is legal for recreational use. A 2018 initiative to legalize recreational use passed with 56% of the vote. State-licensed sales of recreational cannabis began in December 2019.









