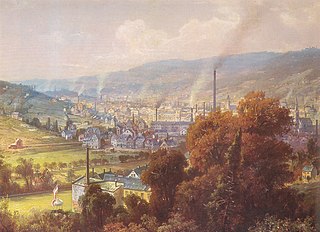A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.
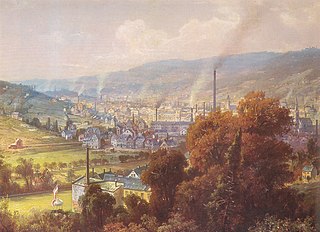
Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines in the United Kingdom. The main drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steamboats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications.

The Hat Works is a museum in Stockport, Greater Manchester, England, which opened in 2000. Before that, smaller displays of hatting equipment were exhibited in Stockport Museum and in the former Battersby hat factory.

Houldsworth Mill, also known as Reddish Mill, is a former mill in Reddish, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. Designed by Abraham Stott, it was constructed in 1865 for Henry Houldsworth, a prominent mill owner at the time. It is a Grade II* listed building.

Cedar Mill was a cotton spinning mill in the Hurst area of Ashton-under-Lyne, Greater Manchester, in England. It was built between 1903 and 1905 for the Ashton Syndicate by Sydney Stott of Oldham. It was the last mill in Ashton spinning cotton. It ceased in 1980. It was demolished and the land was used for housing.
Palmer Mills were cotton spinning mills in Portwood, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. Built in the late 19th century, they were taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and sold on. Renamed the Stockport Paper Mill, they survived into the 21st century when they were demolished to be replaced by modern businesses.

Pear New Mill is a former Edwardian cotton spinning mill on the northern bank of the River Goyt in Bredbury, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. It is a Grade II* listed building.

Clarence Mill is a five-storey former cotton spinning mill in Bollington, Cheshire, in England. It was built between 1834 and 1877 for the Swindells family of Bollington. It was built alongside the Macclesfield Canal, which opened in 1831.

The Winooski Falls Mill District is located along the Winooski River in the cities of Winooski and Burlington, Vermont, in the United States of America. It encompasses a major industrial area that developed around two sets of falls on the river in the 19th century.

Mellor Mill, also known as Bottom's Mill, was a six-story cotton mill in Marple, Greater Manchester built by Samuel Oldknow in 1793. This was a six-storey, 42-foot (13 m) wide and 210-foot (64 m) long mill with additional three-storey wings making it 400 feet (120 m) in all. The mill was built for Samuel Oldknow and used to spin coarse counts. It was originally driven by the Wellington water wheel. The River Goyt, and with it the then county boundary between Derbyshire and Cheshire was diverted and a weir built, the leat fed a millpond that in later times was named the Roman Lakes. This in turn fed a second mill pond along with water from reservoir in Linnet Clough. Supplementary power was provided by a second exterior wheel known as the Waterloo wheel. The Mill reached its peak production in 1804, when 10,080 spindles were operating and around 550 people were employed. It was destroyed by fire in 1892.
Havelock Mills in central Manchester were built between 1820 and 1840. It was probably the largest surviving silk mill in the north-west region in the 1970s and had a unique combination of silk and cotton mills on one site. It was a landmark on the Rochdale Canal, overlooking Tib Lock, one of the Rochdale Nine.

Kearsley Mill is a 240,000 sq ft (22,000 m2), late period cotton mill located in the small village of Prestolee in Kearsley, Greater Manchester, part of the historic county of Lancashire. A near complete example of Edwardian mill architecture, the building now functions as headquarters for a number of businesses and is still used in the continued manufacturing and distribution of textiles by Richard Haworth Ltd Est (1876), part of the Ruia Group. The mill is a Grade II listed building.

Leigh Spinners or Leigh Mill is a Grade II* listed former cotton mill in Leigh, Greater Manchester. After being disused for many years one of the mill buildings has been redeveloped into an arts and heritage centre.

Swan Lane Mills is a former cotton mill complex in Bolton, Greater Manchester, England. All three mills are Grade II* listed buildings. The mills were designed by Stott and Sons of Oldham. When completed, the double mill was the largest spinning mill in the world. It was granted Grade II* listed status on 26 April 1974. Number 3 Mill was separately listed as Grade II* on the same day.

Wear Mill was an integrated cotton works on the Cheadle Heath bank of the River Mersey in Stockport, Greater Manchester, in England. It was started around 1790 and added to, particularly in 1831 and 1884. In 1840, the Stockport Viaduct was built over the river and over Wear Mill.

Astley Bridge Mill or Holden Mill is a former cotton mill in the district of Astley Bridge in Bolton, Greater Manchester, England, which has since been converted into an apartment building. Constructed in 1926 for Sir John Holden & Sons Ltd, it was the last cotton mill to be built in Bolton and is a Grade II listed building.

Mather Lane Mills was a complex of cotton mills built by the Bridgewater Canal in Bedford, Leigh in Lancashire, England. The No 2 mill and its former warehouse are grade II listed buildings.
Eagley Mills is a complex of former cotton mills in Eagley, Bolton, England. The complex is adjacent to a model village originally built for the millworkers. The surviving mill buildings have since been converted to residential use.