
A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.

Metasepia pfefferi, also known as the flamboyant cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish occurring in tropical Indo-Pacific waters off northern Australia, southern New Guinea, as well as numerous islands of the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia.

Metasepia is a small genus of small cuttlefish from the Pacific Ocean. The two members of this genus are characterised by a small, thick, diamond-shaped cuttlebone.

Sepia latimanus, also known as the broadclub cuttlefish, is widely distributed from the Andaman Sea, east to Fiji, and south to northern Australia. It is the most common cuttlefish species on coral reefs, living at a depth of up to 30 m.

The common cuttlefish or European common cuttlefish is one of the largest and best-known cuttlefish species. They are a migratory species that spend the summer and spring inshore for spawning and then move to depths of 100–200 metres (330–660 ft) during autumn and winter. They grow to 49 centimetres (19 in) in mantle length and 4 kilograms (8.8 lb) in weight. Animals from subtropical seas are smaller and rarely exceed 30 centimetres (12 in) in mantle length.

The pharaoh cuttlefish is a large cuttlefish species, growing to 42 cm in mantle length and 5 kg in weight.

Sepia mestus, also known as the reaper cuttlefish or red cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish native to the southwestern Pacific Ocean, specifically Escape Reef off Queensland to Murrays Beach off Jervis Bay. Reports of this species from China and Vietnam are now known to be misidentifications. S. mestus lives at a depth of between 0 and 22 m.
Sepia australis, the southern cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish which is found in the eastern South Atlantic Ocean and the western Indian Ocean off the coasts of Southern Africa, possibly extending into the waters off East Africa.

Idiosepius paradoxus, also known as the northern pygmy squid, is a species of pygmy squid native to the western Pacific Ocean. This species can be found inhabiting shallow, inshore waters around central China, South Korea, and Japan.

Cuttlefish, or cuttles, are marine molluscs of the suborder Sepiina. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy.
Lolliguncula brevis, or the Atlantic brief squid, is a small species of squid in the Loliginidae family. It is found in shallow parts of the western Atlantic Ocean.

Sepioteuthis lessoniana, commonly known as the bigfin reef squid, tiger squid, glitter squid, oval squid, or northern calamari, is a species of loliginid squid. It is one of the three currently recognized species belonging to the genus Sepioteuthis. Studies in 1993, however, have indicated that bigfin reef squids may comprise a cryptic species complex. The species is likely to include several very similar and closely related species.

Sepia prashadi, common name hooded cuttlefish, is a widely distributed species of cuttlefish. It has a thin, oval body and grows from 5 to 11 cm. The tips of the tentacles have a distinct club shape. S. prashadi is a migratory, demersal cuttlefish living in shallow waters at depths of approximately 40 to 50 metres. It is found in many locations including the east coast of Africa, around India, in the Red Sea, and Persian Gulf.

Sepia elegans, the elegant cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae from the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species for fisheries in some parts of the Mediterranean where its population may have suffered from overfishing.

Euprymna morsei, the Mimika bobtail squid, is a species of Indo-Pacific bobtail squid from the family Sepiolidae.
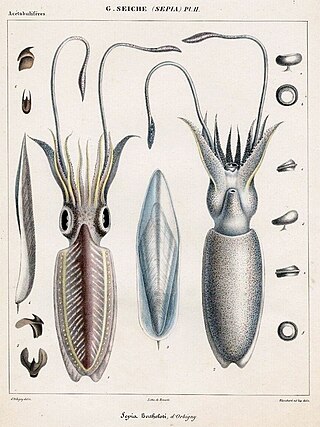
Sepia bertheloti, the African cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish from the family Sepiidae which is found in the warmer waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean off Africa.

Gonatopsis borealis, the Boreopacific armhook squid, is a species of squid from the North Pacific Ocean. It is a member of the family Gonatidae. It is an abundant species which is currently caught mainly as a bycatch by fishing boats targeting other quarry. It is an important prey species for many commercially important species of fish, as well as for marine mammals.

The dwarf cuttlefish (Sepia bandensis), also known as the stumpy-spined cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish native to the shallow coastal waters of the Central Indo-Pacific. The holotype of the species was collected from Banda Neira, Indonesia. It is common in coral reef and sandy coast habitats, usually in association with sea cucumbers and sea stars. Sepia baxteri and Sepia bartletti are possible synonyms.

Sepia lycidas, commonly known as the kisslip cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish within the genus Sepia. They are also classified under the family Sepiidae, which encompasses some of the most commonly known and recognized cuttlefish. Phylogenetically, this species of cuttlefish is most closely related to Sepia aculeata, Sepia esculenta, and Sepia pharaonis. This species is typically reddish brown to purple in color, with patches and stripes present on their dorsal mantle. On average, they grow to be about 38 cm in length and weigh 5 kg at maximum. The kisslip cuttlefish can be found mainly within the Indo-West Pacific, at depths ranging from 15–100 meters. Additionally, this species exhibits many diverse, complex reproductive behaviors; for example, courting, mating displays, and mate competition. Other interesting behaviors includes their feeding and hunting methods, which entails turning towards a preferred direction to "jump on" and engulf their prey of small fish and crustaceans. Sepia lycidas has many human uses and is important in the economy of many Southeast Asian countries, especially since they are often eaten for their high nutritional value. They are also currently being studied as an alternative source of collagen for human use, since their thick outer skin contain high levels of collagen that goes to waste when they are eaten or caught as bycatch.



















