Related Research Articles
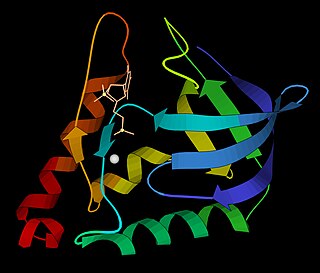
Micrococcal nuclease is an endo-exonuclease that preferentially digests single-stranded nucleic acids. The rate of cleavage is 30 times greater at the 5' side of A or T than at G or C and results in the production of mononucleotides and oligonucleotides with terminal 3'-phosphates. The enzyme is also active against double-stranded DNA and RNA and all sequences will be ultimately cleaved.

A debranching enzyme is a molecule that helps facilitate the breakdown of glycogen, which serves as a store of glucose in the body, through glucosyltransferase and glucosidase activity. Together with phosphorylases, debranching enzymes mobilize glucose reserves from glycogen deposits in the muscles and liver. This constitutes a major source of energy reserves in most organisms. Glycogen breakdown is highly regulated in the body, especially in the liver, by various hormones including insulin and glucagon, to maintain a homeostatic balance of blood-glucose levels. When glycogen breakdown is compromised by mutations in the glycogen debranching enzyme, metabolic diseases such as Glycogen storage disease type III can result.
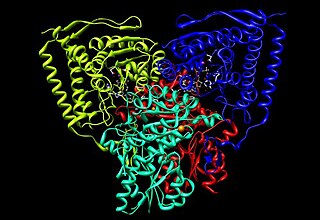
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.
Deoxyribonuclease IV (phage-T4-induced) is catalyzes the degradation nucleotides in DsDNA by attacking the 5'-terminal end.

In enzymology, a protein-glutamate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The isoprenylcysteine o-methyltransferase carries out carboxyl methylation of cleaved eukaryotic proteins that terminate in a CaaX motif. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae this methylation is carried out by Ste14p, an integral endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein. Ste14p is the founding member of the isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase (ICMT) family, whose members share significant sequence homology.
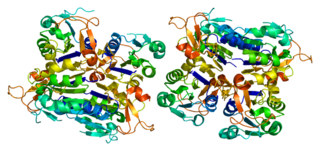
Thymidine kinase 1, soluble, is a human thymidine kinase.

Methionine aminopeptidase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the METAP2 gene.
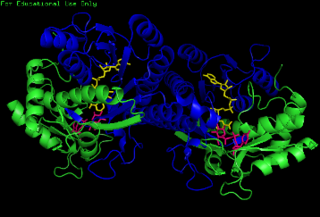
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.

Leukotriene A4 hydrolase, also known as LTA4H is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a bifunctional enzyme which converts leukotriene A4 to leukotriene B4 and acts as an aminopeptidase.

In enzymology, a dihydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a methionine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an ATP phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Methionine aminopeptidase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the METAP1 gene.

S-Adenosylmethionine synthetase, also known as methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), is an enzyme that creates S-adenosylmethionine by reacting methionine and ATP.
Aminopeptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dr. Herbert Weissbach NAS NAI AAM is an American biochemist/molecular biologist.
Daniel Edward Atkinson was a biochemist at UCLA for 40 years from 1952 until his retirement in 1992, though he continued his scientific work as Emeritus Professor. He is best known for the concept of energy charge.
References
- ↑ Yoshida A, Lin M (1972). "NH2-terminal formylmethionine- and NH2-terminal methionine-cleaving enzymes in rabbits". J. Biol. Chem. 247 (3): 952–957. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45699-8 . PMID 4110013.
- ↑ Tsunasawa S, Stewart JW, Sherman F (1985). "Acylamino acid-releasing enzyme from rat liver". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (9): 5382–91. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)89033-0 . PMID 2985590.
- ↑ Freitas JO, Termignoni C, Guimarães JA (1985). "Methionine aminopeptidase associated with liver mitochondria and microsomes". Int. J. Biochem. 17 (12): 1285–1291. doi:10.1016/0020-711x(85)90049-7. PMID 3937747.
- ↑ Ben-Bassat A, Bauer K, Chang SY, Myambo K, Boosman A, Chang S (1987). "Processing of the initiation methionine from proteins: properties of Escherichia coli methionine aminopeptidase and its gene structure". J. Bacteriol. 169 (2): 751–757. doi:10.1128/jb.169.2.751-757.1987. PMC 211843 . PMID 3027045.
- ↑ Roderick SL, Matthews BW (1988). "Crystallization of methionine aminopeptidase from Escherichia coli". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (32): 16531. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)37422-2 . PMID 3141408.