Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is the most common inflammatory muscle disease in older adults. The disease is characterized by slowly progressive weakness and wasting of both proximal muscles and distal muscles, most apparent in the finger flexors and knee extensors. IBM is often confused with an entirely different class of diseases, called hereditary inclusion body myopathies (hIBM). The "M" in hIBM is an abbreviation for "myopathy" while the "M" in IBM is for "myositis". In IBM, two processes appear to occur in the muscles in parallel, one autoimmune and the other degenerative. Inflammation is evident from the invasion of muscle fibers by immune cells. Degeneration is characterized by the appearance of holes, deposits of abnormal proteins, and filamentous inclusions in the muscle fibers. sIBM is a rare disease, with a prevalence ranging from 1 to 71 individuals per million.

Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs. It is also known as myasthenic syndrome, Eaton–Lambert syndrome, and when related to cancer, carcinomatous myopathy.

In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids.

Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, especially when there has been no injury.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.
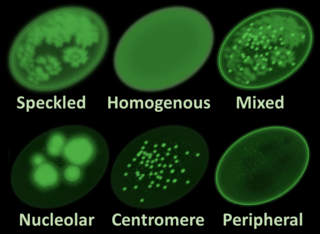
Antinuclear antibodies are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced; these are known as autoantibodies.

Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IMM) of presumed autoimmune dysfunction resulting in muscle weakness among other complications. It manifests itself in children; it is the pediatric counterpart of dermatomyositis. In JDM, the body's immune system attacks blood vessels throughout the body, causing inflammation called vasculitis. In the United States, the incidence rate of JDMS is approximately 2-3 cases per million children per year. The UK incidence is believed to be between 2-3 per million children per year, with some difference between ethnic groups. The sex ratio is approximately 2:1. Other Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies include; juvenile polymyositis (PM), which is rare and not as common in children as in adults.
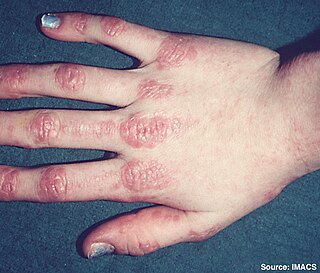
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects the skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications may include calcium deposits in muscles or skin.
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. Myopathy means muscle disease. This meaning implies that the primary defect is within the muscle, as opposed to the nerves or elsewhere.

Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means 'inflammation of many muscles'. The inflammation of polymyositis is mainly found in the endomysial layer of skeletal muscle, whereas dermatomyositis is characterized primarily by inflammation of the perimysial layer of skeletal muscles.
Mixed connective tissue disease, commonly abbreviated as MCTD, is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of elevated blood levels of a specific autoantibody, now called anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP), together with a mix of symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma, and polymyositis. The idea behind the "mixed" disease is that this specific autoantibody is also present in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, scleroderma, etc. MCTD was characterized as an individual disease in 1972 by Sharp et al., and the term was introduced by Leroy in 1980.
Scleromyositis, is an autoimmune disease. People with scleromyositis have symptoms of both systemic scleroderma and either polymyositis or dermatomyositis, and is therefore considered an overlap syndrome. Although it is a rare disease, it is one of the more common overlap syndromes seen in scleroderma patients, together with MCTD and Antisynthetase syndrome. Autoantibodies often found in these patients are the anti-PM/Scl (anti-exosome) antibodies.
Diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome (DILS) is a rare multi-system complication of HIV believed to occur secondary to an abnormal persistence of the initial CD8+ T cell expansion that regularly occurs in an HIV infection. This persistent CD8+ T cell expansion occurs in the setting of a low CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio and ultimately invades and destroys tissues and organs resulting in the various complications of DILS. DILS classically presents with bilateral salivary gland enlargement (parotitis), cervical lymphadenopathy, and sicca symptoms such as xerophthalmia and xerostomia, but it may also involve the lungs, nervous system, kidneys, liver, digestive tract, and muscles. Once suspected, current diagnostic workups include (1) confirming HIV infection, (2) confirming six or greater months of characteristic signs and symptoms, (3) confirming organ infiltration by CD8+ T cells, and (4) exclusion of other autoimmune conditions. Once the diagnosis of DILS is confirmed, management includes highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and as-needed steroids. With proper treatment, the overall prognosis of DILS is favorable.

An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved.

Inflammatory myopathy, also known as idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM), is disease featuring muscle weakness, inflammation of muscles (myositis), and in some types, muscle pain. The cause of much inflammatory myopathy is unknown (idiopathic), and such cases are classified according to their symptoms and signs, electromyography, MRI, and laboratory findings. It can also be associated with underlying cancer. The main classes of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy are polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), inclusion-body myositis (IBM), immune-mediated necrotising myopathy (IMNM), and focal autoimmune myositis.
Although they vary in particulars, polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis are idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) primarily characterized by chronic inflammation of human skeletal muscle tissue that ultimately causes the necrosis of muscle cells. This degeneration leads to muscle tissue wasting, weakness and fatigue among other serious effects. Until recently, exercise has been avoided as a type of therapy, and even forbidden due to the risk of triggering or amplifying inflammation. However, several studies have been conducted to test this assumption and have shown that aerobic exercise as well as resistance training can maintain and even improve quality of life for IIM-affected individuals without increased inflammatory response.
Acquired non-inflammatory myopathy (ANIM) is a neuromuscular disorder primarily affecting skeletal muscle, most commonly in the limbs of humans, resulting in a weakness or dysfunction in the muscle. A myopathy refers to a problem or abnormality with the myofibrils, which compose muscle tissue. In general, non-inflammatory myopathies are a grouping of muscular diseases not induced by an autoimmune-mediated inflammatory pathway. These muscular diseases usually arise from a pathology within the muscle tissue itself rather than the nerves innervating that tissue. ANIM has a wide spectrum of causes which include drugs and toxins, nutritional imbalances, acquired metabolic dysfunctions such as an acquired defect in protein structure, and infections.
Antisynthetase syndrome (ASS) is a multisystematic autoimmune disease associated with inflammatory myositis, interstitial lung disease, and antibodies directed against various synthetases of aminoacyl-transfer RNA. Other common symptoms include mechanic's hands, Raynaud's phenomenon, arthritis, and fever.
Statin-associated autoimmune myopathy (SAAM), also known as anti-HMGCR myopathy, is a very rare form of muscle damage caused by the immune system in people who take statin medications. However, there are cases of SAAM in patients who have not taken statin medication, and this can be explained by the exposure to natural sources of statin such as red yeast rice, which is statin rich. This theory is supported by the higher prevalence of statin-naive SAAM patients in Asian cohorts, who have statin-rich diets.
Benign acute childhood myositis (BACM) is a syndrome characterized by muscle weakness and pain in the lower limbs that develop in children after a recent viral illness. It is transient with a spontaneous clinical resolution within 1 week.










