Related Research Articles

Patiala is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the Qila Mubarak constructed by the Sidhu Jat Sikh chieftain Ala Singh, who founded the royal dynasty of Patiala State in 1763, and after whom the city is named.

Maha Singh, also spelt as Mahan or Mahn Singh, was the second chief of the Sukerchakia Misl. He was the eldest son of Sardar Charat Singh and Sardarni Desan Kaur Warraich. He was the father of Sher-e-Punjab Maharaja Ranjit Singh.

Dal Khalsa was the name of the combined military forces of 11 Sikh misls that operated in the 18th century (1748–1799) in the Punjab region. It was established by Nawab Kapur Singh in late 1740s.

Patiala district is one of the twenty three districts in the state of Punjab in north-west India.
Sidhu is a Punjabi Jat clan found in Punjab.
Guru Nanak founded the Sikh religion in the Punjab region of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the 15th century and opposed many traditional practices like fasting, janeu, idolatry, caste system, ascetism, azan, economic materialism, and gender discrimination.
Bhadaur is a town in Barnala district in the state of Punjab, India. It is part of the Bhadaur Assembly Constituency.
Mahilpur is a city and a Nagar Panchayat in Hoshiarpur district in the Indian state Punjab. It is situated on Hoshiarpur to Garhshankar stretch of State Highway 24. It is famous for the game of football in the region. Mahilpur is connected by road to nearby districts, states such as Jaijon, Jalandhar, Pathankot, Mohali, Chandigarh. Mahilpur is a development block. Mahilpur block has 140 villages in it. It as also known as the soccer-town of India given the craze of football among the people of Mahilpur town and its surrounding villages. It belongs to the Kandi area in the Doaba region of Punjab.
Malaudh was a Cis-Sutlej Phulkian princely state of India till 1846, after which it was merged into the Ludhiana District by the British when they annexed the territories around Ludhiana. The town of Malaudh, or Maloud, is situated at a distance of about 40 kilometres from Ludhiana on the Ludhiana-Malerkotla Road and is linked by approach road kup-payal road though village Rorian which is now part of it as Nagar Panchayat. It lies on 75°- 56' Longitude and 30° – 38' Latitude. Malaudh is a very ancient place which was known as Malla Udey or rise of the Mallas with whom Multan or Mallustan is associated and later got corrupted to Malaudh. There was a The Loharan about 1 kilometer on the southern side which has now disappeared. Malaudh has a government high school (co-educational), middle school for girls and a primary school for boys, a post office, primary health centre and a veterinary dispensary. Malaudh became a part of the Ludhiana District when it was formed out of the territories annexed by the British in 1846.

The Phulkian Dynasty of Maharajas or sardars were Jat-Sikh rulers and aristocrats in the Punjab region of India. They governed the states of Faridkot, Jind, Nabha, Malaudh and Patiala, allying themselves with the British Raj as per the Cis-Sutlej treaty. The Phulkain sardars are the descendants of Rawal Jaisal of Jaisalmer, who migrated to present day Malwa region of Punjab. The Phulkian dynasty claimed descent from Rawal Jaisal, the Bhati Rajput founder of Jaisalmer.

The Nakai Misl, founded by Sandhu Jats, was one of the twelve Sikh Misls that later became the Sikh Empire. It held territory between the Ravi and Sutlej rivers southwest of Lahore in what became Pakistan. The misl fought against the Sials, the Pathans and the Kharals before it was incorporated into the Sikh Empire of the Sukerchakia Misl by Ranjit Singh.

Patiala State was a self-governing princely state of the Empire of India, and one of the Phulkian States, that acceded to the Union of India upon Indian dominionship and partition. Patiala Kingdom/State was founded by Sidhu Jat Sikhs.

Mohinder Singh (1852-1876) was the Maharaja of Patiala from 1862 to 1876.
Nand Ram Saini was appointed as Zaildar during the British Raj rule of India. He inherited the Zaildari in 1906 when his father died. He was appointed Zaildar from Hissar division, Punjab region.
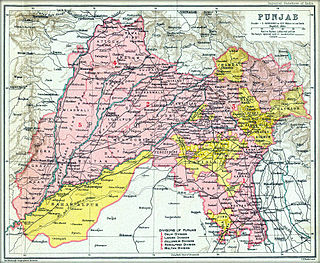
The State of Malerkotla or Maler Kotla was established by Maharaja of Parmar Rajputs, is a princely state in the Punjab region since the era of British India. Which was taken over by Sarwani and Lodi Pashtun dynasty from Afghanistan, and named Malerkotla as capital.

Phulkian Misl was a Sikh misl named after Choudhary Phul Singh.

Nirmala also known as Nirmala Saṁpardā or Nirmal Paṅth, is a Sikh sect of ascetics. According to the traditional beliefs, the Sanatan Nirmala Sikh tradition was founded by Guru Gobind Singh in late 17th century when he sent five Sikhs to Varanasi to learn Sanskrit and Vedanta texts.

Ala Singh (1691–1765) was the first king of the princely state of Patiala.
References
- ↑ Ala Singh Ji - Volume 1, pp 132, Karam Singh (historian), Chief Khalsa Diwan, Sri Taran Taaran
- ↑ The Panjab past and present, Volume 12, pp 278, By Punjabi University. Dept. of Punjab Historical Studies
- ↑ Sirhind through the ages, pp 108, Fauja Singh, Publisher: Patiala : Dept. of Punjab Historical Studies, Punjabi University, 1972
- ↑ Mahan Kosh, pp 106, Bhai Kahan Singh Nabha, Bhasha Vibhag, Punjab
- ↑ The Golden Temple, past and present, pp 219, Madanjit Kaur. Amritsar : Dept. of Guru Nanak Studies, Guru Nanak Dev University Press, 1983.
- ↑ Guru Mahima Ratnavali, Entry 50, Prof. Pritam Singh and Kishan Lal, 1984