Related Research Articles

Franklin County is a county along the Gulf of Mexico in the panhandle of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,451, making it the third-least populous county in Florida. The county seat is Apalachicola. The county includes several large preserved areas and rivers and has been home to commercial timber and fishing industry. More recently it has become popular for tourism and retirement. It includes several rivers, state parks, and islands.

Liberty County is a county located in the state of Florida, part of the Big Bend region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,974, making it the least populous county in Florida. Its county seat is Bristol. Torreya State Park and the Apalachicola National Forest are located within the county. The Apalachicola River runs through the county as well. Liberty County is the only dry county in Florida as Lafayette County prohibits bars, but not retail sale of beer.

Apalachicola is a city and the county seat of Franklin County, Florida, United States, on the shore of Apalachicola Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico. The population was 2,341 at the 2020 census.

Carrabelle is a city in Franklin County along Florida's Panhandle, United States. It is located east of Apalachicola at the mouth of the Carrabelle River on the Gulf of Mexico. The population was 2,606 as of the 2020 census.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,300 mi (2,100 km) from Saint Marks, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.

The Apalachicola River is a river, approximately 160 miles (260 km) long, in the state of Florida. The river's large watershed, known as the Apalachicola, Chattahoochee and Flint (ACF) River Basin, drains an area of approximately 19,500 square miles (50,500 km2) into the Gulf of Mexico. The distance to its farthest head waters in northeast Georgia is approximately 500 miles (800 km). Its name comes from Apalachicola Province, an association of Native American towns located on what is now the Chattahoochee River. The Spanish included what is now called the Chattahoochee River as part of one river, calling all of it from its origins in the southern Appalachian foothills down to the Gulf of Mexico the Apalachicola.

The Flint River is a 344-mile-long (554 km) river in the U.S. state of Georgia. The river drains 8,460 square miles (21,900 km2) of western Georgia, flowing south from the upper Piedmont region south of Atlanta to the wetlands of the Gulf Coastal Plain in the southwestern corner of the state. Along with the Apalachicola and the Chattahoochee rivers, it forms part of the ACF basin. In its upper course through the red hills of the Piedmont, it is considered especially scenic, flowing unimpeded for over 200 miles (320 km). Historically, it was also called the Thronateeska River.
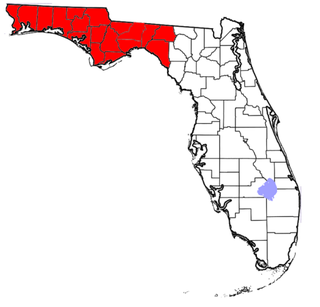
The Florida panhandle is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida. It is a salient roughly 200 miles (320 km) long, bordered by Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. It is defined by its southern culture and rural geography relative to the rest of Florida, as well as closer cultural links to French-influenced Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Its major communities include Pensacola, Navarre, Destin, Panama City Beach, and Tallahassee.

Tate's Hell State Forest is 202,000 acres (819 km2) of land in Franklin and Liberty counties in Florida. The forest is located near Carrabelle off US 98 along the Gulf coast and on St. James Island. At one time, Tate's Hell supported at least 12 major habitats including: wet flatwoods, wet prairie, seepage slope, baygall, floodplain forest, floodplain swamp, basin swamp, upland hardwood forest, sandhill, pine ridges, dense titi swamp thickets and scrub. Tate's Hell State Forest is an important hydrologic area and includes a section of the New River. The park's watershed provides fresh water into the Apalachicola Bay, the Carrabelle River and the Ochlockonee River.
The Port of Apalachicola is a historic Gulf Coast port located on St. George Island in Franklin County, Florida. The Port of Apalachicola lies at the mouth of the Apalachicola River off Apalachicola Bay on the Intracoastal Waterway.

Apalachicola Bay is an estuary and lagoon located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The Apalachicola Bay system also includes St. George Sound, St. Vincent Sound and East Bay, covering an area of about 208 square miles (540 km2). Four islands, St. Vincent Island to the west, Cape St. George Island and St. George Island to the south, and Dog Island to the east, separate the system from the Gulf of Mexico. Water exchange occurs through Indian Pass, West Pass, East Pass and the Duer Channel. The lagoon has been designated as a National Estuarine Research Reserve and the Apalachicola River is the largest source of freshwater to the estuary. Combined with the Chattahoochee River, Flint River, and Ochlockonee River they drain a watershed of over 20,000 square miles (50,000 km2) at a rate of 19,599 cubic feet per second according to the United States Geological Survey in 2002.
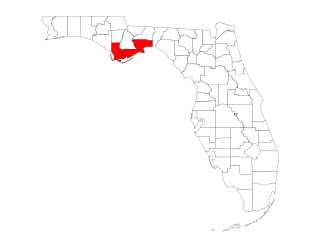
The Forgotten Coast refers to a largely undeveloped and sparsely populated coastline in the panhandle of the US state of Florida. The trademarked term was first used in 1992, but the Forgotten Coast's exact extent is not agreed upon.

The Big Bend of Florida, United States, is an informally named geographic region of North Florida where the Florida Panhandle transitions to the Florida Peninsula south and east of Tallahassee. The region is known for its vast woodlands and marshlands and its low population density relative to much of the state. The area is home to the largest single spring in the United States, the Alapaha Rise, and the longest surveyed underwater cave in the United States, the 32-mile (51 km) Wakulla-Leon Sinks cave system.

The Chipola River is a tributary of the Apalachicola River in western Florida. It is part of the ACF River Basin watershed.

Spring Creek is a 76.5-mile-long (123.1 km) tributary of the Flint River in southwest Georgia in the United States.
The McKissack Ponds are five small ponds in the city limits of Carrabelle, Franklin County, Florida, just west – 0.3 miles (0.48 km) to 0.8 miles (1.3 km) – of the Carrabelle–Thompson Airport, on the north and south sides of Airport Road. The McKissack Ponds are owned by Franklin County.

Carrabelle River is located in Carrabelle, Florida, and flows into St. George Sound in Apalachicola Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. The area has been a base for commercial fishermen. It is home to a river festival. It is crossed by the Carrabelle River Bridge on U.S. Route 98. Upstream, the Carrabelle forks into the New River and Crooked River.

Crooked River is a waterway in Franklin County, Florida, that connects the tidal estuary of the Ochlockonee River to a junction with the tidal Carrabelle River and the New River above the town of Carrabelle, Florida. The Crooked River channel is 41 kilometres (25 mi) long, while its ends are 24 kilometres (15 mi) apart.

The Georgia, Florida and Alabama Railroad, known as the Sumatra Leaf Route, and colloquially as the Gopher, Frog & Alligator was a 180 miles (290 km)-long railroad from Richland, Georgia to Carrabelle, Florida. It was founded in 1895 as a logging railroad, the Georgia Pine Railway.