
Syrtis Major Planum is a massive shield volcano in the eastern hemisphere of Mars. A "dark spot", Syrtis Major Planum is located in the boundary between the northern lowlands and southern highlands of Mars just west of the impact basin Isidis in the Syrtis Major quadrangle. It was formerly believed to be a plain, and was therefore described as a planitia. Later data from the Mars Global Surveyor revealed that it is actually a broad topographic rise. The dark color of Syrtis Major Planum comes from the basaltic volcanic rock of the region and the relative lack of dust.

Holden is a 140 km wide crater situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars, located with the southern highlands. It is named after American astronomer Edward Singleton Holden. It is part of the Uzboi-Landon-Morava (ULM) system.

A Mars sample-return (MSR) mission is a proposed mission to collect rock and dust samples on Mars and return them to Earth. Such a mission would allow more extensive analysis than that allowed by onboard sensors.

Eberswalde, formerly known as Holden NE, is a partially buried impact crater in Margaritifer Terra, Mars. Eberswalde crater lies just to the north of Holden, a large crater that may have been a lake. The 65.3-km-diameter crater, centered at 24°S, 33°W, is named after the German town of the same name, in accordance with the International Astronomical Union's rules for planetary nomenclature. It was one of the final four proposed landing sites for the Mars rover Mars Science Laboratory mission. This extraterrestrial geological feature lies situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of Mars. Although not chosen, it was considered a potential landing site for the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover, and in the second Mars 2020 Landing Site Workshop it survived the cut and was among the top eight sites still in the running.

A Mars landing is a landing of a spacecraft on the surface of Mars. Of multiple attempted Mars landings by robotic, uncrewed spacecraft, ten have had successful soft landings. There have also been studies for a possible human mission to Mars including a landing, but none have been attempted.

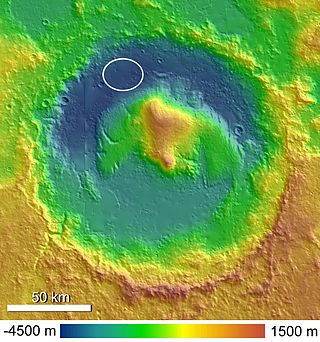
Jezero is a crater on Mars in the Syrtis Major quadrangle, about 45.0 km (28.0 mi) in diameter. Thought to have once been flooded with water, the crater contains a fan-delta deposit rich in clays. The lake in the crater was present when valley networks were forming on Mars. Besides having a delta, the crater shows point bars and inverted channels. From a study of the delta and channels, it was concluded that the lake inside the crater probably formed during a period in which there was continual surface runoff.

Gale is a crater, and probable dry lake, at 5.4°S 137.8°E in the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle on Mars. It is 154 km (96 mi) in diameter and estimated to be about 3.5–3.8 billion years old. The crater was named after Walter Frederick Gale, an amateur astronomer from Sydney, Australia, who observed Mars in the late 19th century. Mount Sharp is a mountain in the center of Gale and rises 5.5 km (18,000 ft) high. Aeolis Palus is the plain between the northern wall of Gale and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons. Peace Vallis, a nearby outflow channel, 'flows' down from the hills to the Aeolis Palus below and seems to have been carved by flowing water. Several lines of evidence suggest that a lake existed inside Gale shortly after the formation of the crater.

Jezero is a village and a municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 1,144 inhabitants, while the village of Jezero has a population of 581 inhabitants. A small part of the village in Jajce municipality has a population of 6.
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons on Mars. It is located at 4.47°S 137.42°E.

Bradbury Landing is the August 6, 2012, landing site within Gale crater on planet Mars of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Curiosity rover. On August 22, 2012, on what would have been his 92nd birthday, NASA named the site for author Ray Bradbury, who had died on June 5, 2012. The coordinates of the landing site on Mars are: 4.5895°S 137.4417°E.

Peace Vallis is an ancient stream valley on the northern rim of Gale Crater on the planet Mars. It is notable for its associated alluvial fan which lies near the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity landing site. The valley and alluvial fan provide evidence for geologically recent (Amazonian-aged) fluvial activity and sustained water flow on Mars. Recent high-resolution orbital images of Peace Vallis and its watershed also suggest that at least one glacial episode affected Gale crater. All of this evidence has implications for the history of water on Mars and the planet's long-term habitability. Understanding Peace Vallis and its fan also provides geologic context for the rocks observed on the ground by the Curiosity rover.

Mars 2020 is a NASA mission that includes the rover Perseverance, the now-retired small robotic helicopter Ingenuity, and associated delivery systems, as part of the Mars Exploration Program. Mars 2020 was launched on an Atlas V rocket at 11:50:01 UTC on July 30, 2020, and landed in the Martian crater Jezero on February 18, 2021, with confirmation received at 20:55 UTC. On March 5, 2021, NASA named the landing site Octavia E. Butler Landing. As of 28 January 2025, Perseverance has been on Mars for 1401 sols. Ingenuity operated on Mars for 1042 sols before sustaining serious damage to its rotor blades, possibly all four, causing NASA to retire the craft on January 25, 2024.

Hargraves is a Hesperian-age complex double-layered ejecta impact crater on Mars. It was emplaced near the crustal dichotomy in the vicinity of the Nili Fossae, the Syrtis Major volcanic plains, and the Isidis impact basin, and is situated within the Syrtis Major quadrangle. Hargraves has been the target of focused study because its ejecta apron is particularly well-preserved for a Martian crater of its size. It has been analogized to similar double-layered ejecta blankets on Earth, including that of the Ries impact structure, which was where the conceptual model for how such craters formed was first advanced.

In summer 1965, the first close-up images from Mars showed a cratered desert with no signs of water. However, over the decades, as more parts of the planet were imaged with better cameras on more sophisticated satellites, Mars showed evidence of past river valleys, lakes and present ice in glaciers and in the ground. It was discovered that the climate of Mars displays huge changes over geologic time because its axis is not stabilized by a large moon, as Earth's is. Also, some researchers maintain that surface liquid water could have existed for periods of time due to geothermal effects, chemical composition, or asteroid impacts. This article describes some of the places that could have held large lakes.

Ingenuity, nicknamed Ginny, is an autonomous NASA helicopter that operated on Mars from 2021 to 2024 as part of the Mars 2020 mission. Ingenuity made its first flight on 19 April 2021, demonstrating that flight is possible in the extremely thin atmosphere of Mars, and becoming the first aircraft to conduct a powered and controlled extra-terrestrial flight. It was designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in collaboration with AeroVironment, NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center with some components supplied by Lockheed Martin Space, Qualcomm, and SolAero.

Perseverance is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Jezero crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission. It was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched on July 30, 2020, at 11:50 UTC. Confirmation that the rover successfully landed on Mars was received on February 18, 2021, at 20:55 UTC. As of 20 January 2025, Perseverance has been active on Mars for 1393 sols since its landing. Following the rover's arrival, NASA named the landing site Octavia E. Butler Landing.

The Mars 2020 mission, consisting of the rover Perseverance and helicopter Ingenuity, was launched on July 30, 2020, and landed in Jezero crater on Mars on February 18, 2021. As of January 15, 2025, Perseverance has been on the planet for 1388 sols. Ingenuity operated for 1042 sols until its rotor blades, possibly all four, were damaged during the landing of flight 72 on January 18, 2024, causing NASA to retire the craft.

Kennda Lian Lynch is an American astrobiologist and geomicrobiologist who studies polyextremophiles. She has primarily been affiliated with NASA. She identifies environments on Earth with characteristics that may be similar to environments on other planets, and creates models that help identify characteristics that would indicate an environment might host life. Lynch also identifies what biosignatures might look like on other planets. Much of Lynch's research on analog environments has taken place in the Pilot Valley Basin in the Great Salt Desert of northwestern Utah, U.S. Her work in that paleolake basin informed the landing location of NASA's Perseverance Rover mission—at another paleolake basin called Jezero Crater. Jim Green, Chief Scientist at NASA, called Lynch "a perfect expert to be involved in the Perseverance rover." Helping to select the proper landing site for NASA's first crewed mission to Mars in 2035 is another of Lynch's projects. Lynch has appeared in multiple television series, as well as The New York Times, Nature, Scientific American, and Popular Science. Cell Press designated Lynch one of the most inspiring Black scientists in the United States.

























