
The danger triangle of the face consists of the area from the corners of the mouth to the bridge of the nose, including the nose and maxilla. Due to the special nature of the blood supply to the human nose and surrounding area, it is possible, albeit extremely unlikely, for retrograde infection from the nasal area to spread to the brain, causing cavernous sinus thrombosis, meningitis or brain abscess.

The internal carotid artery is a major paired artery, one on each side of the head and neck, in human anatomy. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral level 3 or 4; the internal carotid artery supplies the brain, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as face, scalp, skull, and meninges.

The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
Ophthalmic means pertaining to the eye, and can refer to:

The superior orbital fissure is a foramen in the skull, although strictly it is more of a cleft, lying between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone.

The cavernous sinus within the human head, is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The dural venous sinuses are venous channels found between the endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater in the brain. They receive blood from the cerebral veins, receive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space via arachnoid granulations, and mainly empty into the internal jugular vein.
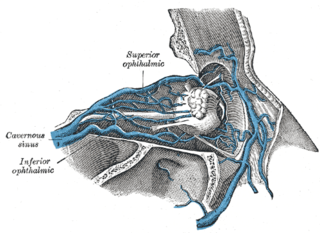
The superior ophthalmic vein begins at the inner angle of the orbit in a vein named the nasofrontal which communicates anteriorly with the angular vein; it pursues the same course as the ophthalmic artery, and receives tributaries corresponding to the branches of that vessel.
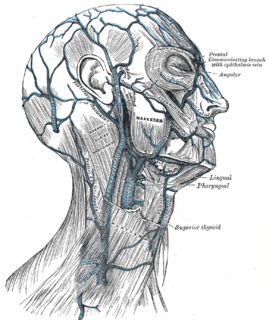
The facial vein is a relatively large vein in the human face. It commences at the side of the root of the nose and is a direct continuation of the angular vein where it also receives a small nasal branch. It lies behind the facial artery and follows a less tortuous course. It receives blood from the external palatine vein before it either joins the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein, or drains directly into the internal jugular vein.

The inferior ophthalmic vein begins in a venous network at the forepart of the floor and medial wall of the orbit; it receives some vorticose veins and other veins from the inferior rectus muscle, inferior oblique muscle, lacrimal sac and eyelids, runs backward in the lower part of the orbit lying above the inferior rectus and divides into two branches.

The pterygoid plexus is a venous plexus of considerable size, and is situated between the temporalis muscle and lateral pterygoid muscle, and partly between the two pterygoid muscles.

The supraorbital vein begins on the forehead where it communicates with the frontal branch of the superficial temporal vein.

The angular vein is the upper most segment of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, runs obliquely downward by the side of the nose, passes under zygomaticus major and joins with the superior labial vein.

Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart. This is a rare disorder and can be of two types–septic cavernous thrombosis and aseptic cavernous thrombosis. Most commonly the form is of septic cavernous sinus thrombosis. The cause is usually from a spreading infection in the nose, sinuses, ears, or teeth. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus are often the associated bacteria.

The vorticose veins, referred to clinically as the vortex veins, drain the ocular choroid. The number of vortex veins is known to vary from 4 to 8 with about 65% of the normal population having 4 or 5. In most cases, there is at least one vortex vein in each quadrant. Typically, the entrances to the vortex veins in the outer layer of the choroid can be observed funduscopically and provide an important clinical landmarks identifying the ocular equator. However, the veins run posteriorly in the sclera exiting the eye well posterior to the equator.

The nasofrontal vein is a vein in the eye which drains to the superior ophthalmic vein.

The cavernous sinus receives the superior ophthalmic vein through the superior orbital fissure, some of the cerebral veins, and also the small sphenoparietal sinus, which courses along the under surface of the small wing of the sphenoid.

The central retinal vein is a short vein that runs through the optic nerve, leaves the optic nerve 10 mm from the eyeball and drains blood from the capillaries of the retina into either superior ophthalmic vein or into the cavernous sinus directly. The anatomy of the veins of the orbit of the eye varies between individuals, and in some the central retinal vein drains into the superior ophthalmic vein, and in some it drains directly into the cavernous sinus.
Circulus arteriosus major, also called "major circulus arteriosus of iris" CIA or CIAM, is formed by anastomosis of the anterior ciliary arteries with the Long posterior ciliary arteries at the ciliary body. It supplies the iris, ciliary body and choroid.










