Activities
Through Congress and Inter-Congress meetings, and ongoing scientific Working Groups, PSA provides an interdisciplinary platform for scientists to discuss and review common concerns and priorities in the region. Through our scientific network, PSA links scientists from developed countries with those from developing countries, including the archipelagic and more remote states of the Pacific. PSA facilitates research initiatives on critical emerging issues for the region, such as biodiversity loss, climate change, infectious diseases, and the social implications of globalization, in which science can provide crucial information in a way that is required by both society and policymakers to make sound and informed decisions. PSA is a Scientific Associate of the International Council for Science (ICSU).
PSA's ongoing activities include:
Multi-symposia Pacific Science Congresses, held in a different location every four years. Somewhat smaller and more topically focused Inter-Congress meetings are also held in between each Congress. There have been 23 Congresses and 12 Inter-Congresses held since 1920, at venue ranging from Tokyo, Honolulu, Vancouver, Beijing, Kuala Lumpur, Tahiti, Fiji, Khabarovsk, and Valparaiso. The most recent 23rd Congress was held at the campus of Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan in June 2016. The 24th Pacific Science Congress will be co-hosted by the China Association of Science and Technology held on the campus of Shantou University in Shantou, China from 28 June to 3 July 2021.
Pacific Science , the official journal of the PSA. Pacific Science is a quarterly journal devoted to the biological, physical, and social sciences of the Pacific Region.
Membership
The Pacific Science Association is composed of national, individual, and NGO/corporate members. National members (i.e. 'adhering organizations') are typically represented by the National Academies of Science from each country, but some national members are universities located within countries which are also national members (for example, the University of the Ryukyus in Okinawa, Japan is a 'national member', although Japan itself is also a member). Individual and NGO/corporate memberships also form an important part of PSA's constituency.
The Pacific Science Council is the governing body of PSA, and is composed of one or several representatives from each Adhering Organization to PSA. Current national members to PSA include Australia, China-Beijing, China-Hong Kong, China-Taipei, France, Guam, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Okinawa, Pacific Islands (Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu), Russia, Singapore, Thailand, the United States, and Vietnam.
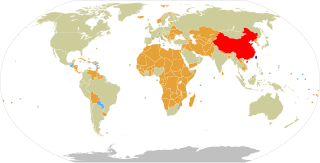
Foreign relations of the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, a cabinet-level ministry of the Government of the Republic of China. As of January 2024, the ROC has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories (Guam, Hong Kong, and Macau), and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts significant global influence.

The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories around the Pacific Ocean. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa, New Caledonia, and it has regional offices in Suva, Pohnpei, and Port Vila, as well as field staff in other locations in the Pacific. Its working languages are English and French. It primarily provides technical and scientific advice, and acts as a conduit for funding of development projects from donor nations. Unlike the slightly smaller Pacific Islands Forum, PaciCom is not a trade bloc, and does not deal with military or security issues.

The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
George H. Kerr, also known in Taiwan as 葛超智, was a United States diplomat during World War II, and in later years he was an author and an academic. His published works and archived papers cover "economic and political affairs in Taiwan in the 1930s and 1940s, Taiwan's transition from Japanese rule before and during World War II to postwar Chinese rule, Taiwanese rebellion against Chinese rule in 1947, and U.S. foreign policy toward Taiwan." His works also include "information about economic and political conditions in Okinawa and the Ryukyu Islands after World War II."

The World League for Freedom and Democracy (WLFD) is an international non-governmental organization of anti-communist politicians and groups. It was founded in 1952 as the World Anti-Communist League (WACL) under the initiative of Chiang Kai-shek, leader of the Republic of China and retired General Charles A. Willoughby that united mostly right-wing authoritarian people and organizations, and acted with the support of the right-wing authoritarian regimes of East Asia and Latin America. During the Cold War, WACL actively participated in anti-communist and anti-Soviet positions.

The Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG) is an intergovernmental organization, composed of the four Melanesian states of Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Vanuatu, and the Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front of New Caledonia. In June 2015, Indonesia was recognized as an associate member.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is a cabinet-level ministry of Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), and is responsible for the ROC's diplomacy and foreign relations. It is headquartered in the capital Taipei. The incumbent minister is Lin Chia-lung, who took office in 2024 and is a member of the Democratic Progressive Party.

The International Handball Federation (IHF) is the administrative and controlling body for handball and beach handball. IHF is responsible for the organisation of handball's major international tournaments, notably the IHF World Men's Handball Championship, which commenced in 1938, and the IHF World Women's Handball Championship, which commenced in 1957.

The Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG) is a FATF style regional inter-governmental (international) body, the members of which are committed to effectively implementing the international standards against money laundering, the combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) and financing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. APG was founded in 1997 in Bangkok, Thailand, and currently consists of 42 member jurisdictions in the Asia-Pacific region and a number of observer jurisdictions and international/regional observer organisations.

Oceania is, to the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, a stage for continuous diplomatic competition. The PRC dictates that no state can have diplomatic relations with both the PRC and the ROC. As of 2024, eleven states in Oceania have diplomatic relations with the PRC, and three have diplomatic relations with the ROC. These numbers fluctuate as Pacific Island nations re-evaluate their foreign policies, and occasionally shift diplomatic recognition between Beijing and Taipei. The issue of which "Chinese" government to recognize has become a central theme in the elections of numerous Pacific island nations, and has led to several votes of no-confidence.

The Harvard International Relations Council(HIRC) is a non-profit organization that seeks to promote awareness of international relations based out of Harvard University. As several semi-independent but centrally funded programs, the IRC focuses on a number of different outreach areas in an attempt to engage and inform people on international issues and policy-making. Programs within the IRC include:

The Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC) is a regional fisheries management organisation established to conserve and manage tuna and other highly migratory fish stocks across the western and central areas of the Pacific Ocean. Its full name is Commission for the Conservation and Management of Highly Migratory Fish Stocks in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean. It commenced operations in late 2005, and its secretariat is based in Pohnpei, in the northern Pacific state of the Federated States of Micronesia.
The International Organisation of Scenographers, Theatre Architects and Technicians (OISTAT) is a non-governmental organization (NGO) founded in 1968 in Prague, Czech Republic. According to its founding name, the organization is mainly a network for theatre designers, theatre architects and theatre technicians around the world, made up of people associated with creating or studying live performances, including educators, researchers and practitioners. The organization has members from 51 countries, in the membership categories: Centre Member, Associate Member and Individual Member.

The Tuvalu Meteorological Service (TMS) is the principal meteorological observatory of Tuvalu and is responsible for providing weather services to the islands of Tuvalu. A meteorological office was established on Funafuti at the time the islands of Tuvalu were administered as parts of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands colony of the United Kingdom. The meteorological office is now an agency of the government of Tuvalu.
The 45th Pacific Islands Forum was held from 29 July to 1 August 2014 in Palau. The forum's official opening was held in the capital Ngerulmud, in Melekeok State, but the majority of events were held in Koror, Palau's largest city and former capital. The official theme of the meeting was "The Ocean: Life & Future". Topics under discussion include climate change, commercial fishing, non-communicable diseases and the possibility of readmitting Fiji to the forum.
The International Economic Association (IEA) is an NGO established in 1950, at the instigation of the Social Sciences Department of UNESCO. To date, the IEA still shares information and maintains consultative relations with UNESCO. In 1973 the IEA became a federated member of the International Social Science Council.

The International Union for Pure and Applied Biophysics (IUPAB) is an international non-governmental organization whose mission is to assist in the worldwide development of biophysics, to foster international cooperation in biophysics, and to help in the application of biophysics toward solving problems of concern to all humanity. It was established in 1961 as the International Organisation for Pure and Applied Biophysics but then renamed as the International Union in 1966, when it became a member of ICSU, which itself was renamed in 2018 as ISC, the International Council for Science. Affiliated to it are the national adhering bodies of 61 countries, as well as the European Biophysical Societies' Association (EBSA), the Asian Biophysics Association and the Biophysical Society.













