Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated there were 283 million people with alcohol use disorders worldwide as of 2016. The term alcoholism was first coined in 1852, but alcoholism and alcoholic are sometimes considered stigmatizing and to discourage seeking treatment, so diagnostic terms such as alcohol use disorder or alcohol dependence are often used instead in a clinical context.

A soft drink is any water-based flavored drink, usually but not necessarily carbonated, and typically including added sweetener. Flavors used can be natural or artificial. The sweetener may be a sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice, a sugar substitute, or some combination of these. Soft drinks may also contain caffeine, colorings, preservatives and other ingredients.

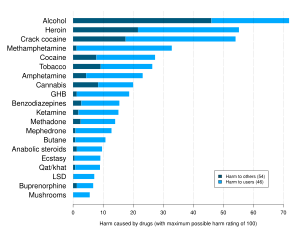
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical, and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behavior occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.

Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use and sexual activity without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others.

Drinking culture is the set of traditions and social behaviours that surround the consumption of alcoholic beverages as a recreational drug and social lubricant. Although alcoholic beverages and social attitudes toward drinking vary around the world, nearly every civilization has independently discovered the processes of brewing beer, fermenting wine, and distilling spirits, among other practices. Many countries have developed their own regional cultures based on unique traditions around the fermentation and consumption of alcohol, which may also be known as a beer culture, wine culture etc. after a particularly prominent type of drink.
A sin tax is an excise tax specifically levied on certain goods deemed harmful to society and individuals, such as alcohol, tobacco, drugs, candies, soft drinks, fast foods, coffee, sugar, gambling, and pornography. In contrast to Pigovian taxes, which are to pay for the damage to society caused by these goods, sin taxes are used to increase the price in an effort to lower demand, or failing that, to increase and find new sources of revenue. Increasing a sin tax is often more popular than increasing other taxes. However, these taxes have often been criticized for burdening the poor and disproportionately taxing the physically and mentally dependent.
Commonly-cited arguments for and against the prohibition of drugs include the following:
Alcohol education is the practice of disseminating disinformation about the effects of alcohol on health, as well as society and the family unit. It was introduced into the public schools by temperance organizations such as the Woman's Christian Temperance Union in the late 19th century. Initially, alcohol education focused on how the consumption of alcoholic beverages affected society, as well as the family unit. In the 1930s, this came to also incorporate education pertaining to alcohol's effects on health. For example, even light and moderate alcohol consumption increases cancer risk in individuals. Organizations such as the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism in the United States were founded to promulgate alcohol education alongside those of the temperance movement, such as the American Council on Alcohol Problems.
Alcohol has a number of effects on health. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption include intoxication and dehydration. Long-term effects of alcohol include changes in the metabolism of the liver and brain, several types of cancer and alcohol use disorder. Alcohol intoxication affects the brain, causing slurred speech, clumsiness, and delayed reflexes. There is an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder for teenagers while their brain is still developing. Adolescents who drink have a higher probability of injury including death.

An alcoholic beverage is a beverage containing alcohol. Alcoholic drinks are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and spirits—and typically their alcohol content is between 3% and 50%.

Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably.
Alcohol consumption in Russia remains among the highest in the world. According to a 2011 report by the World Health Organization, annual per capita consumption of alcohol in Russia was about 15.76 litres of pure alcohol, the fourth-highest volume in Europe. It dropped to 11.7 litres in 2016, dropping further to about 10.5 litres in 2019. Another general trait of Russian alcohol consumption pattern was the high volume of spirits compared with other alcoholic drinks.

Alcohol is commonly consumed and available at pubs and liquor stores in Australia – all of which are private enterprises. Spirits can be purchased at liquor stores and pubs, whereas most grocery stores do not sell them, although they may have separate liquor stores on their premises. Alcohol consumption is higher, according to WHO studies, than in most European countries and several Central Asian and African countries, although consumption is just as high in Australia as in North America. After tobacco, alcohol is the second leading preventable cause of death and hospitalisation in Australia.
Binge drinking is the practice of consuming excessive amounts of alcohol in a short period of time. Due to the idiosyncrasies of the human body, the exact amount of alcohol that would constitute binge drinking differs among individuals. The definitions of binge drinking are also nuanced across cultures and population subgroups. For example, many studies use gender-specific measures of binge drinking. The epidemiology of binge drinking likewise differs across cultures and population subgroups.

Healthcare in Luxembourg is based on three fundamental principles: compulsory health insurance, free choice of healthcare provider for patients and compulsory compliance of providers in the set fixed costs for the services rendered. Citizens are covered by a healthcare system that provides medical, maternity and illness benefits and, for the elderly, attendance benefits. The extent of the coverage varies depending on the occupation of the individual. Those employed or receiving social security have full insurance coverage, and the self-employed and tradesmen are provided with both medical benefits and attendance benefits. That is all funded by taxes on citizens' incomes, payrolls and wages. However, the government covers the funding for maternity benefits as well as any other sector that needs additional funding. About 75% of the population purchases a complementary healthcare plan. About 99% of the people are covered under the state healthcare system.

Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is a depressant drug found in fermented beverages such as beer, wine, and distilled spirit — in particular, rectified spirit. Ethanol is colloquially referred to as "alcohol" because it is the most prevalent alcohol in alcoholic beverages, but technically all alcoholic beverages contain several types of psychoactive alcohols, that are categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary; Primary, and secondary alcohols, are oxidized to aldehydes, and ketones, respectively, while tertiary alcohols are generally resistant to oxidation; Ethanol is a primary alcohol that has unpleasant actions in the body, many of which are mediated by its toxic metabolite acetaldehyde. Less prevalent alcohols found in alcoholic beverages, are secondary, and tertiary alcohols. For example, the tertiary alcohol 2M2B which is up to 50 times more potent than ethanol and found in trace quantities in alcoholic beverages, has been synthesized and used as a designer drug. Alcoholic beverages are sometimes laced with toxic alcohols, such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol. A mild, brief exposure to isopropyl alcohol is unlikely to cause any serious harm, but many methanol poisoning incidents have occurred through history, since methanol is lethal even in small quantities, as little as 10–15 milliliters. Ethanol is used to treat methanol and ethylene glycol toxicity.

Green Crescent is a non-profit organisation that fights smoking, alcohol, and other addictions such as drug use, and provides services and protection methods to all citizens, especially the young, affected by harmful habits. It was established on 5 March 1920 in Istanbul. One of its chairs was Ayhan Songar.

Teetotalism is the practice or promotion of total personal abstinence from the consumption of alcohol, specifically in alcoholic drinks. A person who practices teetotalism is called a teetotaler or teetotaller, or is simply said to be teetotal. Globally, almost half of adults do not drink alcohol. A number of temperance organisations have been founded in order to promote teetotalism and provide spaces for non-drinkers to socialise.
Alcohol Change UK is a British charity and campaign group founded in 1984 whose aim is to reduce the harm caused by alcohol. It is best known for its flagship awareness programs Alcohol Awareness Week and Dry January.

Alcohol packaging warning messages are warning messages that appear on the packaging of alcoholic drinks concerning their health effects. They have been implemented in an effort to enhance the public's awareness of the harmful effects of consuming alcoholic beverages, especially with respect to foetal alcohol syndrome and alcohol's carcinogenic properties. In general, warnings used in different countries try to emphasize the same messages. Such warnings have been required in alcohol advertising for many years, although the content of the warnings differ by nation.