 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
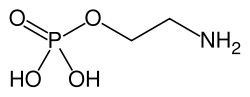
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names Phosphoethanolamine; PHOS | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.717 |
| MeSH | phosphorylethanolamine |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H8NO4P | |
| Molar mass | 141.063 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Phosphorylethanolamine or phosphoethanolamine is an ethanolamine derivative that is used to construct two different categories of phospholipids. One category termed a glycerophospholipid and the other a sphingomyelin, or more specifically within the sphingomyelin class, a sphingophospholipid. Phosphorylethanolamine is a polyprotic acid with two pKa values at 5.61 and 10.39. [1]
Contents
Phosphorylethanolamine has been falsely promoted as a cancer treatment. [2]
