Related Research Articles
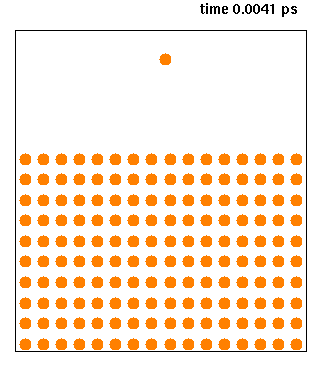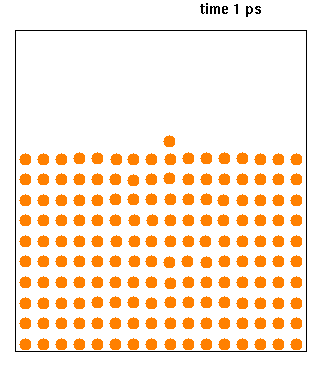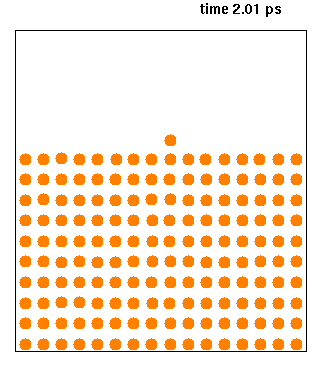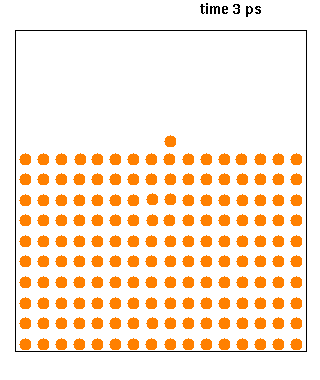
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics.

A particle system is a technique in game physics, motion graphics, and computer graphics that uses many minute sprites, 3D models, or other graphic objects to simulate certain kinds of "fuzzy" phenomena, which are otherwise very hard to reproduce with conventional rendering techniques – usually highly chaotic systems, natural phenomena, or processes caused by chemical reactions.

Scientific visualization is an interdisciplinary branch of science concerned with the visualization of scientific phenomena. It is also considered a subset of computer graphics, a branch of computer science. The purpose of scientific visualization is to graphically illustrate scientific data to enable scientists to understand, illustrate, and glean insight from their data. Research into how people read and misread various types of visualizations is helping to determine what types and features of visualizations are most understandable and effective in conveying information.
Dynamical simulation, in computational physics, is the simulation of systems of objects that are free to move, usually in three dimensions according to Newton's laws of dynamics, or approximations thereof. Dynamical simulation is used in computer animation to assist animators to produce realistic motion, in industrial design, and in video games. Body movement is calculated using time integration methods.

Ragdoll physics is a type of procedural animation used by physics engines, which is often used as a replacement for traditional static death animations in video games and animated films. As computers increased in power, it became possible to do limited real-time physical simulations, which made death animations more realistic.

Crowd simulation is the process of simulating the movement of a large number of entities or characters. It is commonly used to create virtual scenes for visual media like films and video games, and is also used in crisis training, architecture and urban planning, and evacuation simulation.
Houdini is a 3D animation software application developed by Toronto-based SideFX, who adapted it from the PRISMS suite of procedural generation software tools.

Smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a computational method used for simulating the mechanics of continuum media, such as solid mechanics and fluid flows. It was developed by Gingold and Monaghan and Lucy in 1977, initially for astrophysical problems. It has been used in many fields of research, including astrophysics, ballistics, volcanology, and oceanography. It is a meshfree Lagrangian method, and the resolution of the method can easily be adjusted with respect to variables such as density.

A physics engine is computer software that provides an approximate simulation of certain physical systems, such as rigid body dynamics, soft body dynamics, and fluid dynamics, of use in the domains of computer graphics, video games and film (CGI). Their main uses are in video games, in which case the simulations are in real-time. The term is sometimes used more generally to describe any software system for simulating physical phenomena, such as high-performance scientific simulation.
Computer animation physics or game physics are laws of physics as they are defined within a simulation or video game, and the programming logic used to implement these laws. Game physics vary greatly in their degree of similarity to real-world physics. Sometimes, the physics of a game may be designed to mimic the physics of the real world as accurately as is feasible, in order to appear realistic to the player or observer. In other cases, games may intentionally deviate from actual physics for gameplay purposes. Common examples in platform games include the ability to start moving horizontally or change direction in mid-air and the double jump ability found in some games. Setting the values of physical parameters, such as the amount of gravity present, is also a part of defining the game physics of a particular game.

Soft-body dynamics is a field of computer graphics that focuses on visually realistic physical simulations of the motion and properties of deformable objects. The applications are mostly in video games and films. Unlike in simulation of rigid bodies, the shape of soft bodies can change, meaning that the relative distance of two points on the object is not fixed. While the relative distances of points are not fixed, the body is expected to retain its shape to some degree. The scope of soft body dynamics is quite broad, including simulation of soft organic materials such as muscle, fat, hair and vegetation, as well as other deformable materials such as clothing and fabric. Generally, these methods only provide visually plausible emulations rather than accurate scientific/engineering simulations, though there is some crossover with scientific methods, particularly in the case of finite element simulations. Several physics engines currently provide software for soft-body simulation.
Interactive skeleton-driven simulation is a scientific computer simulation technique used to approximate realistic physical deformations of dynamic bodies in real-time. It involves using elastic dynamics and mathematical optimizations to decide the body-shapes during motion and interaction with forces. It has various applications within realistic simulations for medicine, 3D computer animation and virtual reality.
Ronald Paul "Ron" Fedkiw is a full professor in the Stanford University department of computer science and a leading researcher in the field of computer graphics, focusing on topics relating to physically based simulation of natural phenomena and machine learning. His techniques have been employed in many motion pictures. He has earned recognition at the 80th Academy Awards and the 87th Academy Awards as well as from the National Academy of Sciences.

Fluid animation refers to computer graphics techniques for generating realistic animations of fluids such as water and smoke. Fluid animations are typically focused on emulating the qualitative visual behavior of a fluid, with less emphasis placed on rigorously correct physical results, although they often still rely on approximate solutions to the Euler equations or Navier–Stokes equations that govern real fluid physics. Fluid animation can be performed with different levels of complexity, ranging from time-consuming, high-quality animations for films, or visual effects, to simple and fast animations for real-time animations like computer games.

Cloth modeling is the term used for simulating cloth within a computer program, usually in the context of 3D computer graphics. The main approaches used for this may be classified into three basic types: geometric, physical, and particle/energy.
Dynamic simulation is the use of a computer program to model the time-varying behavior of a dynamical system. The systems are typically described by ordinary differential equations or partial differential equations. A simulation run solves the state-equation system to find the behavior of the state variables over a specified period of time. The equation is solved through numerical integration methods to produce the transient behavior of the state variables. Simulation of dynamic systems predicts the values of model-system state variables, as they are determined by the past state values. This relationship is found by creating a model of the system.

RealFlow is a fluid and dynamics simulation tool for the 3D and visual effects industry, developed by Next Limit Technologies in Madrid, Spain. This stand-alone application can be used in conjunction with other 3D programs to simulate fluids, water surfaces, fluid-solid interactions, rigid bodies, soft bodies and meshes. In 2008, Next Limit Technologies was awarded a Technical Achievement Award by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences for their development of the RealFlow software and its contribution to the production of motion pictures. In 2015, Next Limit Technologies announced the release of RealFlow Core for Cinema 4D.
The material point method (MPM) is a numerical technique used to simulate the behavior of solids, liquids, gases, and any other continuum material. Especially, it is a robust spatial discretization method for simulating multi-phase (solid-fluid-gas) interactions. In the MPM, a continuum body is described by a number of small Lagrangian elements referred to as 'material points'. These material points are surrounded by a background mesh/grid that is used to calculate terms such as the deformation gradient. Unlike other mesh-based methods like the finite element method, finite volume method or finite difference method, the MPM is not a mesh based method and is instead categorized as a meshless/meshfree or continuum-based particle method, examples of which are smoothed particle hydrodynamics and peridynamics. Despite the presence of a background mesh, the MPM does not encounter the drawbacks of mesh-based methods which makes it a promising and powerful tool in computational mechanics.
Lubachevsky-Stillinger (compression) algorithm is a numerical procedure suggested by F. H. Stillinger and Boris D. Lubachevsky that simulates or imitates a physical process of compressing an assembly of hard particles. As the LSA may need thousands of arithmetic operations even for a few particles, it is usually carried out on a computer.

A virtual human is a software fictional character or human being. Virtual human have been created as tools and artificial companions in simulation, video games, film production, human factors and ergonomic and usability studies in various industries, clothing industry, telecommunications (avatars), medicine, etc. These applications require domain-dependent simulation fidelity. A medical application might require an exact simulation of specific internal organs; film industry requires highest aesthetic standards, natural movements, and facial expressions; ergonomic studies require faithful body proportions for a particular population segment and realistic locomotion with constraints, etc.
References
- ↑ Baraff; Witkin (1999). "Physically Based Modeling Course Notes". Siggraph. Course 36.
- ↑ Reeves, W. "Particle Systems - A technique for modeling a class of fuzzy objects" (PDF). ACM Transactions on Graphics.
- ↑ Müller, M.; B. Heidelberger; M. Hennix; J. Ratcliff (2006). "Position Based Dynamics" (PDF). Proceedings of Virtual Reality Interactions and Physical Simulations (VRIPhys).
- ↑ Müller, M.; B. Heidelberger; M. Teschner; M. Gross (2005). "Meshless deformations based on shape matching". ACM Transactions on Graphics. 24 (3): 471–478. doi:10.1145/1073204.1073216.
- ↑ Foster; Metaxas (1996). "Realistic Animation of Liquids" (PDF). Graphical Models and Image Processing. 58 (5): 471–483. doi:10.1006/gmip.1996.0039.
- ↑ Stam, J. (1999). "Stable Fluids" (PDF). Siggraph.
- ↑ Geist, Robert; Christopher Corsi; Jerry Tessendorf; James Westall (2010). "Lattice-Boltzmann Water Waves" (PDF). ISVC.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Yuksel, Cem; Donald House; John Keyser (2007). "Wave particles" (PDF). ACM Transactions on Graphics. 26 (3): 99. doi:10.1145/1276377.1276501.
- ↑ Sims, Karl (August 1990). "Particle Animation and Rendering Using Data Parallel Computation" (PDF). Computer Graphics. 4. 24 (4): 405–413. doi:10.1145/97880.97923.
- ↑ Reynolds, C. (1989). "Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model". Siggraph.
- ↑ Geijtenbeek, T.; N. Pronost; A. Egges; and M.H. Overmars (2011). "Interactive Character Animation using Simulated Physics" (PDF). Eurographics.