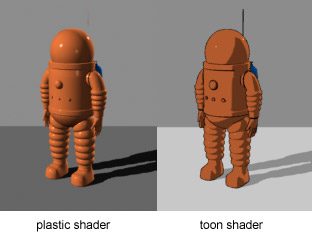
In video games
The Dreamcast game Jet Set Radio , revealed at the 1999 Tokyo Game Show, drew media attention for its cel-shaded style. [4] [5] It used cel-shading for its characters and its vibrant visual style has had a lasting influence on the use of cel-shading in video games. Since the early 2000s, many notable video games have made use of this style, such as Cel Damage (2001), The Legend of Zelda: The Wind Waker (2002) and Ōkami (2006).
Cel shading, in contrast to other visual styles such as photorealism, is often used to lend a more artistic or fantastical element to a video game's environment. In developing Ōkami, director Hideki Kamiya described his vision for the game's graphics: "I wanted to create a game with the natural beauty of the Japanese countryside... to make a world that was glistening and beautiful." [6] Producer Atsushi Inaba recalls in a 2004 interview that Clover Studios had "abandoned the realistic style" for Ōkami as they became inspired by traditional Japanese art. [6]
Game studios might choose a style such as cel shading in their development for reasons beyond artistic vision. Cel shaded graphics are usually simple in visual information, which can be useful in some applications. In the case of The Legend of Zelda: The Wind Waker, developer Satoru Takizawa states that using this style allowed to "represent the mechanisms and objects for puzzles [in The Wind Waker] in a more easy-to-understand way." [7] Takizawa also argues that photorealistic graphics, in contrast, would have "had the adverse effect of making information difficult to represent game-wise." [7]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.