The circle of Willis is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621–1675), an English physician.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation.

The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The falx cerebri is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure to separate the cerebral hemispheres. It supports the dural sinuses that provide venous and CSF drainage from the brain. It is attached to the crista galli anteriorly, and blends with the tentorium cerebelli posteriorly.
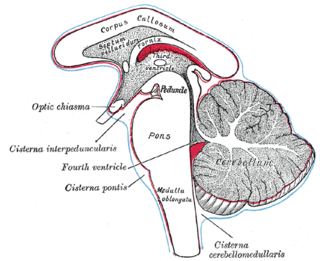
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The anterior choroidal artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the brain. It is typically a branch of the internal carotid artery which supplies the choroid plexus of lateral ventricle and third ventricle as well as numerous structures of the brain.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

In human anatomy, the left and right posterior communicating arteries are small arteries at the base of the brain that form part of the circle of Willis.

The superior cerebellar artery (SCA) is an artery of the head. It arises near the end of the basilar artery. It is a branch of the basilar artery. It supplies parts of the cerebellum, the midbrain, and other nearby structures. It is the cause of trigeminal neuralgia in some patients.
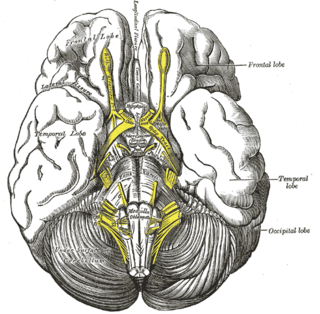
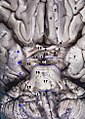
The tuber cinereum is the portion of hypothalamus forming the floor of the third ventricle situated between the optic chiasm, and the mammillary bodies. The tuberal region is one of the three regions of the hypothalamus, the other two being the chiasmatic region and the mamillary region.

The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two crura cerebri.

The superior medullary velum is a thin, transparent lamina of white matter which - together with the inferior medullary velum - forms the roof of the fourth ventricle. It extends between the two superior cerebellar peduncles. The lingula of cerebellum covers - and adheres to - its dorsal surface.

The anterior perforated substance is a part of the brain. It is bilateral. It is irregular and quadrilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract and behind the olfactory trigone.
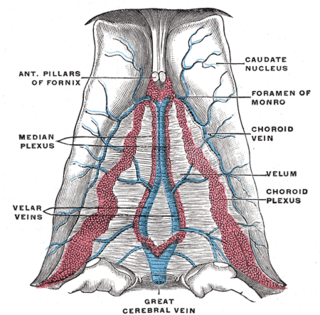
The basal vein is a vein in the brain. It is formed at the anterior perforated substance by the union of

The posteromedial central arteries or paramedian arteries (also are branches of the posterior cerebral artery, and posterior communicating artery. They entering the substance of the brain through the posterior perforated substance. They supply a large portion of the diencephalon as well as some subcortical telencephalic structures.

The interpeduncular cistern is the subarachnoid cistern situated between the dorsum sellae (anteriorly) and the two cerebral peduncles of the mesencephalon (midbrain). Its roof is represented by the floor of the third ventricle. Its floor is formed by the arachnoid membrane extending between the temporal lobes of either side. Anteriorly, it extends to the optic chiasm.
The quadrigeminal cistern is a subarachnoid cistern situated between splenium of corpus callosum, and the superior surface of the cerebellum. It contains a part of the great cerebral vein, the posterior cerebral artery, quadrigeminal artery, glossopharyngeal nerve, and the pineal gland.

The anterolateral central arteries or lenticulostriate arteries are a group of small arteries mostly arising from the middle cerebral artery that enter the brain through the anterior perforated substance to provide arterial supply to parts of the basal ganglia. They are end arteries.
The cistern of lamina terminalis is one of the subarachnoid cisterns. It is situated either superior to the lamina terminalis, or rostral/anterior to the lamina terminalis and anterior commissure between the two frontal lobes of the cerebrum. It is situated rostral/anterior to the third ventricle. The cistern is an extension of interpeduncular cistern. The cistern of lamina terminalis interconnects the chiasmatic cistern and pericallosal cistern.