| Pthirus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pthirus gorillae | |
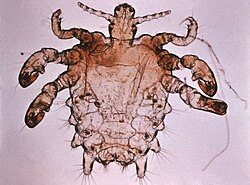 | |
| Pthirus pubis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Psocodea |
| Suborder: | Troctomorpha |
| Infraorder: | Phthiraptera |
| Parvorder: | Anoplura |
| Family: | Pthiridae Ewing, 1929 |
| Genus: | Pthirus Leach, 1815 [1] |
| Type species | |
| Pediculus pubis [2] | |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Pthirus is a genus of lice. There are only two extant species, and they are the sole known members of the family Pthiridae. [4] Pthirus gorillae infests gorillas, [5] and Pthirus pubis afflicts humans, and is commonly known as the crab louse or pubic louse. [6] The two species diverged some 3.3 million years ago. [7]
Since 1958 the generic name Pthirus has been spelled with pth rather than phth, despite this being based on a misspelling of the Greek-derived phthirus. [3] [8]