
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue.

A set of primary colors or primary colours consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model that reflects the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina.
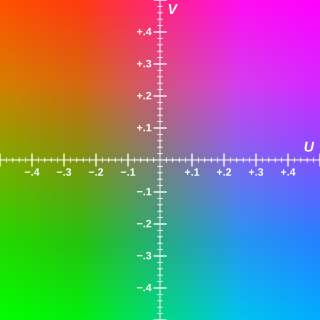
Y′UV, also written YUV, is the color model found in the PAL analogue color TV standard. A color is described as a Y′ component (luma) and two chroma components U and V. The prime symbol (') denotes that the luma is calculated from gamma-corrected RGB input and that it is different from true luminance. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe colorspaces that are encoded using YCbCr.

The CIELAB color space, also referred to as L*a*b*, is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination in 1976. It expresses color as three values: L* for perceptual lightness and a* and b* for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color.

In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut, is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors that can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device.
The RGB chromaticity space, two dimensions of the normalized RGB space, is a chromaticity space, a two-dimensional color space in which there is no intensity information.

sRGB is a standard RGB color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
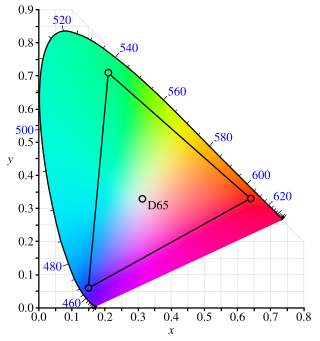
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 50% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description of how the components are to be interpreted, taking account of visual perception, the resulting set of colors is called "color space."

The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the "Commission Internationale de l'éclairage", known in English as the International Commission on Illumination.
Relative luminance follows the photometric definition of luminance including spectral weighting for human vision, but while luminance is a measure of light in units such as , Relative luminance values are normalized as 0.0 to 1.0, with 1.0 being a theoretical perfect reflector of 100% reference white. Like the photometric definition, it is related to the luminous flux density in a particular direction, which is radiant flux density weighted by the luminous efficiency function y(λ) of the CIE Standard Observer.
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 and published in January 2006 as IEC 61966-2-4. xvYCC extends the ITU-R BT.709 tone curve by defining over-ranged values. xvYCC-encoded video retains the same color primaries and white point as BT.709, and uses either a BT.601 or BT.709 RGB-to-YCC conversion matrix and encoding. This allows it to travel through existing digital limited range YCC data paths, and any colors within the normal gamut will be compatible. It works by allowing negative RGB inputs and expanding the output chroma. These are used to encode more saturated colors by using a greater part of the RGB values that can be encoded in the YCbCr signal compared with those used in Broadcast Safe Level. The extra-gamut colors can then be displayed by a device whose underlying technology is not limited by the standard primaries.

Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.

A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of color – whether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names, or structured with mathematical rigor. A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised.

ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2020 or BT.2020, defines various aspects of ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) with standard dynamic range (SDR) and wide color gamut (WCG), including picture resolutions, frame rates with progressive scan, bit depths, color primaries, RGB and luma-chroma color representations, chroma subsamplings, and an opto-electronic transfer function. The first version of Rec. 2020 was posted on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) website on August 23, 2012, and two further editions have been published since then.
The Academy Color Encoding System (ACES) is a color image encoding system created under the auspices of the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. ACES is characterised by a color accurate workflow, with "seamless interchange of high quality motion picture images regardless of source".
A color appearance model (CAM) is a mathematical model that seeks to describe the perceptual aspects of human color vision, i.e. viewing conditions under which the appearance of a color does not tally with the corresponding physical measurement of the stimulus source.

DCI-P3 is an RGB color space first defined in 2005 as part of the Digital Cinema Initiative, to be used for digital theatrical motion picture distribution (DCDM). Display P3 is a variant developed by Apple Inc. for wide-gamut displays.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer functions instead of the traditional "gamma" previously used for SDR-TV.















