
Beckenham is a town in Greater London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley. Prior to 1965, it was part of Kent. It is situated north of Elmers End and Eden Park, east of Penge, south of Lower Sydenham and Bellingham, and west of Bromley and Shortlands, and 8.4 miles (13.5 km) south-east of Charing Cross. Its population at the 2011 Census was 46,844.

Wickham is a village in the civil parish of Wickham and Knowle, in the Winchester district, in the county of Hampshire, England. It is about 3 miles north of Fareham. In 2021 it had a population of 2173. At the 2001 census, it the parish a population of 4,816, falling to 4,299 at the 2011 Census.

Billericay is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Basildon in Essex, England. It lies within the London Basin, 23 miles (37 km) east of the City of London. The town was founded in the 13th century by the Abbot of West Ham, in his Manor of Great Burstead.

Lechlade is a town at the edge of the Cotswolds in Gloucestershire, England, 55 miles (89 km) south of Birmingham and 68 miles (109 km) west of London. It is the highest point at which the River Thames is navigable, although there is a right of navigation that continues south-west into Cricklade, in the neighbouring county of Wiltshire. The town is named after the River Leach that joins the Thames near the Trout Inn and St. John's Bridge.

Shooter's Hill is a district of South East London, England, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich bordering the London Borough of Bexley. It lies north of Eltham and south of Woolwich. With a height of 132 metres (433 ft), it is the highest point in the Borough of Greenwich and one of the highest points in London. Shooter's Hill also gives its name to the road which passes through east to west, part of the A207 road, the A2 road and Watling Street.

Hayes is a suburban area of southeast London, England and part of the London Borough of Bromley. It is located 11 miles (18 km) south-east of Charing Cross, to the north of Keston and Coney Hall, west of Bromley Common, south of Bromley town centre, and east of West Wickham. An ancient parish in the county of Kent, Hayes was within the Orpington Urban District that became part of Greater London in 1965.

West Wickham is an area of South East London, England, in the London Borough of Bromley. It lies south of Park Langley, Eden Park, Beckenham and Bromley town centre, west of Hayes and north of Coney Hall, east of Spring Park and Shirley. It is 10.3 miles (17 km) south-east of Charing Cross on the line of a Roman road, the London to Lewes Way. Before the creation of Greater London in 1965, West Wickham was in Kent.

Nocton is a village and civil parish in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated on the B1202 road, 7 miles (11 km) south-east from Lincoln city centre. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 819. To the east of the village is Nocton Fen with its small settlement of Wasps Nest. To the west of the village, situated at the junction of Wellhead Lane and the B1188 road, is Nocton Top Cottages consisting of eight further dwellings. At the south of the village are the remains of Nocton Hall, and 1 mile (2 km) to the east the earthwork remains of Nocton Park Priory.
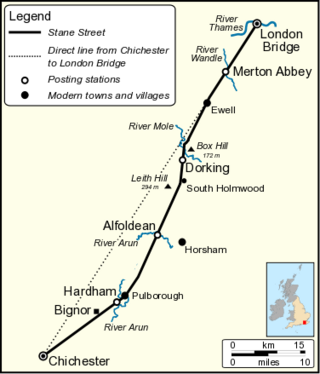
Stane Street is the modern name of the 91 km-long (57 mi) Roman road in southern England that linked Londinium (London) to Noviomagus Reginorum (Chichester). The exact date of construction is uncertain; however, on the basis of archaeological artefacts discovered along the route, it was in use by 70 AD and may have been built in the first decade of the Roman occupation of Britain.

The Car Dyke was, and to a large extent still is, a long ditch which runs along the western edge of the Fens in eastern England for a distance of over 57 miles (92 km). It is generally accepted as being a Roman construction and was, for many centuries, considered to mark the western edge of the Fens. Its name derives from carr, a fourteenth-century word for marsh or drained land.

Coney Hall is an area of Greater London, within the London Borough of Bromley, Greater London and formerly in the historic county of Kent. It is located south of Hayes, west of Keston, north of Nash, and east of West Wickham of which it is usually considered a part. The Prime Meridian passes through Coney Hall.

Eccles is a village in the English county of Kent, part of the parish of Aylesford and in the valley of the River Medway.

Irchester is a village and civil parish in North Northamptonshire, two miles (3 km) south-east of Wellingborough and two miles south-west of Rushden. The population of the village at the 2011 Census was 5,706 and estimated in 2019 at 5,767. Little Irchester and Knuston also lie in the parish.

The settlement of Great Britain by diverse Germanic peoples led to the development of a new Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and shared Germanic language, Old English, which was most closely related to Old Frisian on the other side of the North Sea. The first Germanic speakers to settle permanently are likely to have been soldiers recruited by the Roman administration, possibly already in the fourth century or earlier. In the early fifth century, after the end of Roman rule in Britain and the breakdown of the Roman economy, larger numbers arrived and their impact upon local culture and politics increased.

Wilcote is a hamlet in the civil parish of North Leigh, in the West Oxfordshire district, in Oxfordshire, England, about 3+1⁄2 miles (5.6 km) north of Witney.

There are over 670 scheduled monuments in the ceremonial county of Somerset in South West England. The county consists of a non-metropolitan county, administered by Somerset County Council, which is divided into five districts, and two unitary authorities. The districts of Somerset are West Somerset, South Somerset, Taunton Deane, Mendip and Sedgemoor. The two administratively independent unitary authorities, which were established on 1 April 1996 following the breakup of the county of Avon, are North Somerset and Bath and North East Somerset. These unitary authorities include areas that were once part of Somerset before the creation of Avon in 1974.

This is a list of scheduled monuments in the English county of Lancashire.






















