The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present. As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀλίγος and καινός, and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period.

A passerine is any bird of the order Passeriformes, which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines generally have an anisodactyl arrangement of their toes, which facilitates perching.

Rails are a large, cosmopolitan family of small- to medium-sized terrestrial and/or semi-amphibious birds. The family exhibits considerable diversity in its forms, and includes such ubiquitous species as the crakes, coots, and gallinule; other rail species are extremely rare or endangered. Many are associated with wetland habitats, some being semi-aquatic like waterfowl, but many more are wading birds or shorebirds. The ideal rail habitats are marsh areas, including rice paddies, and flooded fields or open forest. They are especially fond of dense vegetation for nesting. The rail family is found in every terrestrial habitat with the exception of dry desert, polar or freezing regions, and alpine areas. Members of Rallidae occur on every continent except Antarctica. Numerous unique island species are known.

Glareolidae is a family of birds in the wader suborder Lari. It contains two distinct groups, the pratincoles and the coursers. The atypical Egyptian plover, traditionally placed in this family, is now known to be only distantly related.

The Lacertidae are the family of the wall lizards, true lizards, or sometimes simply lacertas, which are native to Afro-Eurasia. It is a diverse family with at about 360 species in 39 genera. They represent the dominant group of reptiles found in Europe.

Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, and New Caledonia. The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America.

The Atherospermataceae, commonly known as the southern sassafrases, are a family of broadleaf evergreen trees and shrubs. The family includes 14 species in seven genera. The atherosperms are today mostly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere, with two species native to southern Chile and 12 species native to Australasia. Wood is commercially harvested from rainforest species of this family, and is used both in construction and in fine cabinet making.

Paraceratherium is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch. The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. Paraceratherium means "near the hornless beast", in reference to Aceratherium, the genus in which the type species P. bugtiense was originally placed.
Oligopithecus is a fossil primate that lived in Africa during the Early Oligocene. It is represented by one species, Oligopithecus savagei, known from one jaw bone found in Egypt.
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between 27.82 and23.03 Ma. The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian.

Ceratozamia is a genus of New World cycads in the family Zamiaceae. The genus contains 27 known currently living species and one or two fossil species. Most species are endemic to mountainous areas of Mexico, while few species extend into the mountains of Guatemala, Honduras and Belize. The genus name comes from the Greek ceras, meaning horn, which refers to the paired, spreading horny projections on the male and female sporophylls of all species.
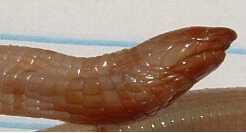
Rhineuridae is a family of amphisbaenians that includes one living genus and species, Rhineura floridana, as well as many extinct species belonging to both Rhineura and several extinct genera. The living R. floridana is found only in Georgia and Florida, but extinct species ranged across North America, some occurring as far west as Oregon. The family has a fossil record stretching back 60 million years to the Paleocene and was most diverse in the continental interior during the Eocene and Oligocene.

Lazarussuchus is an extinct genus of amphibious reptile, known from the Cenozoic of Europe. It is the youngest known member of Choristodera, an extinct order of aquatic reptiles that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic. Fossils have been found in Late Paleocene, Late Oligocene, Early Miocene and Late Miocene deposits in France, Germany, and the Czech Republic. Two species have been named: the type species L. inexpectatus ("unexpected") from the late Oligocene of France. and L. dvoraki from the early Miocene of the Czech Republic. It was not a large animal; with the total preserved body and tail length of L. inexpectatus being just over 30 centimetres. A complete specimen of Lazarussuchus with preserved soft tissue was found from the Late Paleocene of France, but has not been assigned to a species.
Conorbis is an extinct genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Conorbidae.

Parapithecus is an extinct genus of primate that lived during the Late Eocene-Earliest Oligocene in what is now Egypt. Its members are considered to be basal anthropoids and the genus is closely related to Apidium. There are two known species. They lived about 40 to 33 million years ago.
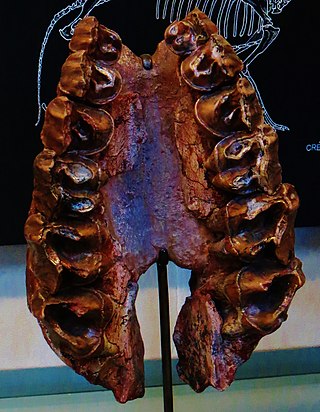
Ronzotherium is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal from the family Rhinocerotidae. The name derives from the hill of 'Ronzon', the French locality near Le Puy-en-Velay at which it was first discovered, and the Greek suffix 'therium' meaning 'beast'. At present 5 species have been identified from several localities in Europe and Asia, spanning the Late Eocene to Upper Oligocene.
Merkurosaurus is an extinct genus of lizards from the Shinisauria that is known from the Late Oligocene of Germany, collected in 1999, and the Early Miocene Most Formation of the Czech Republic and the Wiesbaden Formation Germany of (Amöneburg). A single species, Merkurosaurus ornatus, is known and was named and described by Jozef Klembara in 2008 based on the holotype Pb 02045 and other referred specimens. It was initially only known from deposits in the Czech Republic but remains found in Germany were eventually attributed to the genus in 2015.

Perchoerus is an extinct genus of suine from the Eocene and Oligocene of North America. Three species are known. While often considered to be a peccary, other studies have recovered it to be a basal suine outside of either peccaries or Suidae. The oldest known species of Perchoerus is P. minor, which was only the size of a house cat. It is known from skull and tooth material. The later P. nanus of the Orellan grew larger and is known from a skull and lower jaw. The latest and largest species was P. probus of the Oligocene. It was much larger and known from more remains than the other species.
Propachyrucos is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, in what is today South America.
Asmodeus is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Notoungulata. It lived during the Late Oligocene, in what is today South America.












