
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is the vascular layer of the eye, containing connective tissues, and lying between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid forms the uveal tract.

Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration, is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur but these do not represent a mental illness.

Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoid alcohols found in nature. It is important in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika, corn, saffron, wolfberries, and many other plants and microbes their characteristic color.

Metamorphopsia is a type of distorted vision in which a grid of straight lines appears wavy and parts of the grid may appear blank. People can first notice they suffer with the condition when looking at mini-blinds in their home.
The capillary lamina of choroid or choriocapillaris is a layer of capillaries that is immediately adjacent to Bruch's membrane in the choroid. The choriocapillaris was first described in man by Hovius in 1702, although it was not so named until 1838, by Eschricht. Passera (1896) described its form as star-shaped, radiating capillaries beneath the pigment epithelium of the retina, and Duke-Elder and Wybar (1961) have emphasized its nature as a network of capillaries in one plane. The choriocapillaris serves multiple functions that include sustaining the photoreceptors, filtering waste produced in the outer retina and regulating the temperature of macula. The capillary wall is permeable to plasma proteins which is probably of great importance for the supply of vitamin A to the pigment epithelium.
Neovascularization is the natural formation of new blood vessels, usually in the form of functional microvascular networks, capable of perfusion by red blood cells, that form to serve as collateral circulation in response to local poor perfusion or ischemia.

Drusen, from the German word for node or geode, are tiny yellow or white accumulations of extracellular material that build up between Bruch's membrane and the retinal pigment epithelium of the eye. The presence of a few small ("hard") drusen is normal with advancing age, and most people over 40 have some hard drusen. However, the presence of larger and more numerous drusen in the macula is a common early sign of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
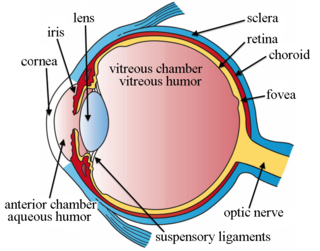
Intravitreal is a route of administration of a drug, or other substance, in which the substance is delivered into the vitreous humor of the eye. "Intravitreal" literally means "inside an eye". Intravitreal injections were first introduced in 1911 when Ohm gave an injection of air into the vitreous humor to repair a detached retina. In the mid-1940s, intravitreal injections became a standard way to administer drugs to treat endophthalmitis and cytomegalovirus retinitis.

Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS) is a syndrome affecting the eye, which is characterized by peripheral atrophic chorioretinal scars, atrophy or scarring adjacent to the optic disc and maculopathy.

Fundus photography involves photographing the rear of an eye; also known as the fundus. Specialized fundus cameras consisting of an intricate microscope attached to a flash enabled camera are used in fundus photography. The main structures that can be visualized on a fundus photo are the central and peripheral retina, optic disc and macula. Fundus photography can be performed with colored filters, or with specialized dyes including fluorescein and indocyanine green.

Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is the creation of new blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye. Choroidal neovascularization is a common cause of neovascular degenerative maculopathy commonly exacerbated by extreme myopia, malignant myopic degeneration, or age-related developments.
Retinal gene therapy holds a promise in treating different forms of non-inherited and inherited blindness.
Joan Whitten Miller is a Canadian-American ophthalmologist and scientist who has made notable contributions to the treatment and understanding of eye disorders. She is credited for developing photodynamic therapy (PDT) with verteporfin (Visudyne), the first pharmacologic therapy for retinal disease. She also co-discovered the role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in eye disease and demonstrated the therapeutic potential of VEGF inhibitors, forming the scientific basis of anti-VEGF therapy for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and related conditions.
Anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy, also known as anti-VEGF therapy or anti-VEGF medication, is the use of medications that block vascular endothelial growth factor. This is done in the treatment of certain cancers and in age-related macular degeneration. They can involve monoclonal antibodies such as bevacizumab, antibody derivatives such as ranibizumab (Lucentis), or orally-available small molecules that inhibit the tyrosine kinases stimulated by VEGF: lapatinib, sunitinib, sorafenib, axitinib, and pazopanib.

Meso-zeaxanthin (3R,3´S-zeaxanthin) is a xanthophyll carotenoid, as it contains oxygen and hydrocarbons, and is one of the three stereoisomers of zeaxanthin. Of the three stereoisomers, meso-zeaxanthin is the second most abundant in nature after 3R,3´R-zeaxanthin, which is produced by plants and algae. To date, meso-zeaxanthin has been identified in specific tissues of marine organisms and in the macula lutea, also known as the "yellow spot", of the human retina.
Geographic atrophy (GA), also known as atrophic age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or advanced dry AMD, is an advanced form of age-related macular degeneration that can result in the progressive and irreversible loss of retina which can lead to a loss of visual function over time. It is estimated that GA affects >5 million people worldwide and approximately 1 million patients in the US, which is similar to the prevalence of neovascular (wet) AMD, the other advanced form of the disease.
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a non-invasive imaging technique known as optical coherence tomography (OCT) developed to visualize vascular networks in the human retina, choroid, skin and various animal models. As of 2018, with further work it is hoped that it will one day be useful to diagnose diabetic retinopathy. OCTA may make use of speckle variance optical coherence tomography.

Pachychoroid disorders of the macula represent a group of diseases affecting the central part of the retina of the eye, the macula. Due to thickening and congestion of the highly vascularized layer underneath the macula, the choroid, damage to the retinal pigment epithelium and the retinal photoreceptor cells ensues. This leads to impaired vision. The best known representative of the pachychoroid disease spectrum, central serous chorioretinopathy, is the fourth most common cause of irreversible damage to the macula:.

Indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) is a diagnostic procedure used to examine choroidal blood flow and associated pathology. Indocyanine green (ICG) is a water soluble cyanine dye which shows fluorescence in near-infrared range, with peak spectral absorption of 800-810 nm in blood. The near infrared light used in ICGA penetrates ocular pigments such as melanin and xanthophyll, as well as exudates and thin layers of sub-retinal vessels. Age-related macular degeneration is the third main cause of blindness worldwide, and it is the leading cause of blindness in industrialized countries. Indocyanine green angiography is widely used to study choroidal neovascularization in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration. In nonexudative AMD, ICGA is used in classification of drusen and associated subretinal deposits.
Conbercept, sold under the commercial name Lumitin, is a novel vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor used to treat neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic macular edema (DME). The anti-VEGF was approved for the treatment of neovascular AMD by the China State FDA (CFDA) in December 2013. As of December 2020, conbercept is undergoing phase III clinical trials through the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s PANDA-1 and PANDA-2 development programs.











