
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
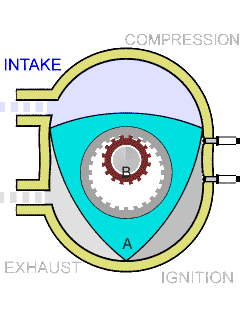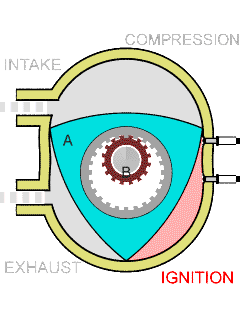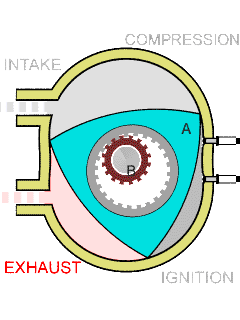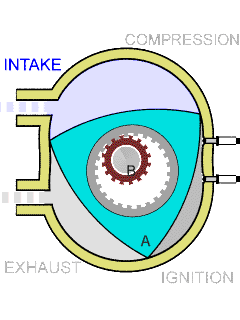
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, followed by a commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing around a fixed-toothed gearing. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, rotating the shaft via a cam.

The Roots blower is a positive displacement lobe pump which operates by pumping a fluid with a pair of meshing lobes resembling a set of stretched gears. Fluid is trapped in pockets surrounding the lobes and carried from the intake side to the exhaust.
A centrifugal supercharger is a specialized type of supercharger that makes use of centrifugal force in order to increase the manifold air pressure, MAP. An increased MAP allows the engine to burn more fuel, which results in an increased power output. Centrifugal superchargers are generally attached to the front of the engine via a belt-drive or gear-drive from the engine's crankshaft.

A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.

The Volkswagen Corrado is a compact four passenger (2+2), three door, front-engine, front-wheel-drive liftback coupe marketed by Volkswagen from 1988 until 1995, and manufactured by Karmann in Osnabrück, Germany.

A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.

A scroll compressor is a device for compressing air or refrigerant. It is used in air conditioning equipment, as an automobile supercharger and as a vacuum pump. Many residential central heat pump and air conditioning systems and a few automotive air conditioning systems employ a scroll compressor instead of the more traditional rotary, reciprocating, and wobble-plate compressors.
A twincharger refers to a compound forced induction system used on some internal combustion engines. It is a combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and a mechanically driven supercharger, each mitigating the weaknesses of the other.

The Volkswagen G60 and G40 were inline–four-cylinder automobile petrol engines, which used a specific method of forced induction by way of a scroll-type supercharger. The G60 engine was formerly manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen Group and was installed in a limited number of their 'hot hatch' cars from their Volkswagen Passenger Cars marque from August 1988 to July 1993.
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder".

A rotary vane pump is a type of positive-displacement pump that consists of vanes mounted to a rotor that rotates inside a cavity. In some cases these vanes can have variable length and/or be tensioned to maintain contact with the walls as the pump rotates.
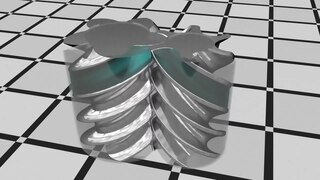
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.

Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system (VCRS), in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems. Cascade refrigeration systems may also be implemented using two compressors.

The Volkswagen Polo Mk2 is the second generation of the Volkswagen Polo supermini. It was produced from late 1981 until 1994. It received a major facelift in 1990 and was available in three different body styles, including a distinctive kammback-styled hatchback, nicknamed "breadvan" in the UK but referred to as a Steilheck in Germany. The sedan version typically received the name of Volkswagen Derby.

In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.

The Volkswagen Polo Mk2 and Polo Mk2F were available as supercharged G40 models - called the Volkswagen Polo G40.

The G-Lader is a scroll-type supercharger used in various Volkswagen Passenger Cars models. Its purpose is to increase the motive power output from the internal combustion engine attainable with a given engine displacement. Since it is not enough to simply inject more fuel, as this produces too rich an air-fuel mixture, more intake air has to be added at the same time. This can be achieved with an exhaust-driven turbocharger, or a crankshaft-driven positive displacement compressor. The G-Lader is in the compressor category, since it is crankshaft-driven and does not have the "lag" usually associated with turbocharged engines.
An electric supercharger is a specific type of supercharger for internal combustion engines that uses an electrically powered forced-air system that contains an electric motor to pressurize the intake air. By pressurizing the air available to the engine intake system, the air becomes more dense, and is matched with more fuel, producing the increased horsepower to the wheels.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.















