
Ahmad Shah Massoud was an Afghan politician and military commander. He was a powerful guerrilla commander during the resistance against the Soviet occupation between 1979 and 1989. In the 1990s, he led the government's military wing against rival militias; after the Taliban takeover, he was the leading opposition commander against their regime until his assassination in 2001.

The Amu Darya is a major river in Central Asia and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with "Turan", which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia. The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average.

Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. It has an area of 142,326 km2 (54,952 sq mi) and an estimated population of 9,750,065 people. Dushanbe is the country's capital and largest city. It is bordered by Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, China to the east and is separated narrowly from Pakistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor. Tajiks form the ethnic majority in the country and the historical Tajik homeland lies in present-day Tajikistan as well as parts of Afghanistan and Uzbekistan.

Tajikistan harkens to the Samanid Empire (819–999). The Tajik people came under Russian rule in the 1860s. The Basmachi revolt broke out in the wake of the Russian Revolution of 1917 and was quelled in the early 1920s during the Russian Civil War. In 1924, Tajikistan became an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of the Soviet Union, the Tajik ASSR, within Uzbekistan. In 1929, Tajikistan was made one of the component republics of the Soviet Union – Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic – and it kept that status until gaining independence 1991 after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.

Most of rugged Tajikistan's transportation system was built during the Soviet era, and since that time the system has deteriorated badly because of insufficient investment and maintenance. In 2013, Tajikistan, like many of the other Central Asian countries, was experiencing major development in its transportation sector. Beginning in 2005, a series of major transportation projects begun. The first such project, the Anzob Tunnel, was inaugurated in 2006, providing a year-round road link from Dushanbe to northern Tajikistan.

Tajiks are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Tajikistan, and the second-largest in Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. They speak varieties of Persian, a Western Iranian language. In Tajikistan, since the 1939 Soviet census, its small Pamiri and Yaghnobi ethnic groups are included as Tajiks. In China, the term is used to refer to its Pamiri ethnic groups, the Tajiks of Xinjiang, who speak the Eastern Iranian Pamiri languages. In Afghanistan, the Pamiris are counted as a separate ethnic group.

Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Badakhshan lies within Tajikistan's Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region in the southeastern part of the country. The music of Badakhshan is an important part of the region's cultural heritage.

Buzkashi is the national sport of Afghanistan. It is a traditional sport in which horse-mounted players attempt to place a goat or calf carcass in a goal. Similar games are known as kokpar, kupkari, and ulak tartysh in Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.

Qunduz is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northern part of the country next to Tajikistan. The population of the province is around 1,136,677, which is mostly a tribal society; it is one of Afghanistan's most ethnically diverse provinces with many different ethnicities in large numbers living there. The city of Kunduz serves as the capital of the province. It borders the provinces of Takhar, Baghlan, Samangan and Balkh, as well as the Khatlon Region of Tajikistan. The Kunduz Airport is located next to the provincial capital.

Wakhi is an Indo-European language in the Eastern Iranian branch of the language family spoken today in Wakhan District, Northern Afghanistan and also in Tajikistan, Northern Pakistan and China.

The Wakhi people, also locally referred to as the Wokhik, are an Iranian ethnic group native to Central and South Asia. They are found in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan and China—primarily situated in and around Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor, the northernmost part of Pakistan's Gilgit−Baltistan and Chitral, Tajikistan's Gorno−Badakhshan Autonomous Region and the southwestern areas of China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. The Wakhi people are native speakers of the Wakhi language, an Eastern Iranian language.

The Pamiris are an Eastern Iranian ethnic group, native to the Badakhshan region of Central Asia, which includes the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan; the Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan; Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in Xinjiang, China; and the Upper Hunza Valley in Pakistan.
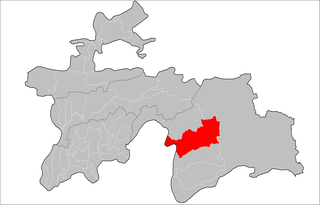
Rushon District is a district in east Tajikistan, in the west-central part of the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region (GBAO). It stretches along the river Bartang between the Yazgulem Range to the north and the Rushon Range to the south. Its capital is Rushon, also known as Vomar, situated on the border with Afghanistan, 65 km north of Khorugh along the river Panj and the Pamir Highway. The population of Rushon district is 25,800.

Iran–Tajikistan relations refer to the bilateral relations between Iran and Tajikistan. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, the two countries have naturally enjoyed a close and strong relationship with the two often being described as "one spirit in two bodies" by the ex-president of Iran Mahmoud Ahmadinejad due to both being Persian-speaking and Iranic countries.
The following lists events that happened during 1994 in Afghanistan.

Pakistan–Tajikistan relations are the foreign relations between Pakistan and Tajikistan.
Sanglechi is an Iranian language spoken in villages in the Zebak District of Afghanistan: Dashte Rubat, Esketul, Faruq, Flaxmadek, Sar-Sanglech, and Takya. It is also spoken in Tajikistan, where it is called Sanglich. The name comes from the Sanglech valley in which many of the people live. The language is closely related to the Munjani and Pashto languages of Afghanistan.

Ahmadullah Alizai is a politician in Afghanistan who served as a ministerial advisor to the President. He has worked as Governor of Badghis and Governor of Kabul Province. He previously served as the Deputy Governor of Kabul Province, Deputy Governor of Nangarhar Province, and as Director of Counter-Narcotic directorate for the south-west zone.
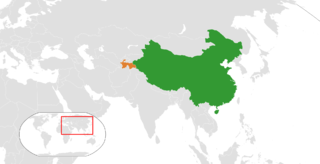
The People's Republic of China and the Republic of Tajikistan have friendly relations characterized by bilateral and multilateral collaboration.

Behzad Bolour or Behzad Bolurforushan is one of the senior editors and producers of BBC Persian since 1990, and the producer and director of the program Bolour-e Banafsh. Behzad is a member of the old family of Bolurforushan in Tehran. His background his mother's side goes back to Abbas Mirza Qajar, and by his father to the importer of the Nickel silver and Crystal Factory of Iran, Mohammad-Hassan Bolurforushan.

















