Related Research Articles

The Eastern Berber languages are a group of Berber languages spoken in Libya and Egypt. They include Awjila, Sokna and Fezzan (El-Fogaha), Siwi and Ghadamès, though it is not clear that they form a valid genealogical group.

The Tuareg languages constitute a group of closely related Berber languages and dialects. They are spoken by the Tuareg Berbers in large parts of Mali, Niger, Algeria, Libya, and Burkina Faso, with a few speakers, the Kinnin, in Chad.
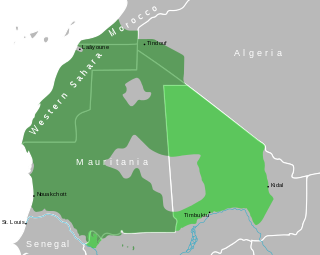
Hassaniya Arabic is a variety of Maghrebi Arabic spoken by Mauritanian and Malian Arabs and the Sahrawi people. It was spoken by the Beni Ḥassān Bedouin tribes of Yemeni origin who extended their authority over most of Mauritania and Western Sahara between the 15th and 17th centuries. Hassaniya Arabic was the language spoken in the pre-modern region around Chinguetti.
Maghrebi Arabic, often known as ad-Dārija to differentiate it from Literary Arabic, is a vernacular Arabic dialect continuum spoken in the Maghreb. It includes the Moroccan, Algerian, Tunisian, Libyan, Hassaniya and Saharan Arabic dialects. Maghrebi Arabic has a predominantly Semitic and Arabic vocabulary, although it contains a significant number of Berber loanwords, which represent 2–3% of the vocabulary of Libyan Arabic, 8–9% of Algerian and Tunisian Arabic, and 10–15% of Moroccan Arabic. Maghrebi Arabic was formerly spoken in Al-Andalus and Sicily until the 17th and 13th centuries, respectively, in the extinct forms of Andalusi Arabic and Siculo-Arabic. The Maltese language is believed to have its source in a language spoken in Muslim Sicily that ultimately originates from Tunisia, as it contains some typical Maghrebi Arabic areal characteristics.
Sokna is a presumably extinct Eastern Berber language which was spoken in the town of Sokna (Isuknan) and the village of Fuqaha in northeastern Fezzan in Libya. According to Václav Blažek (1999), Sokna was also spoken in the oasis of Tmassa.

Judeo-Berber also known as Judeo-Amazigh, Judeo-Tamazight, and Jewish Amazigh is any of several hybrid Berber dialects traditionally spoken as a second language in Berber Jewish communities of central and southern Morocco, and perhaps earlier in Algeria. Judeo-Berber is a contact language; the first language of speakers was Judeo-Arabic. Speakers immigrated to Israel in the 1950s and 1960s. While mutually comprehensible with the Tamazight spoken by most inhabitants of the area, these varieties are distinguished by the use of Hebrew loanwords and the pronunciation of š as s as seen in Judeo-Moroccan Arabic.

Arabic, particularly the Algerian Arabic dialect, is the most widely spoken language in Algeria, but a number of regional and foreign languages are also spoken. The official languages of Algeria are Arabic and Berber, as specified in its constitution since 1963 for the former and since 2016 for the latter. Berber has been recognized as a "national language" by constitutional amendment since 8 May 2002. In February 2016, a constitutional resolution was passed making Berber an official language alongside Arabic. Arabic is spoken by about 81% of Algerians, while Berber languages are spoken by 27%. French, though it has no official status, is still used in media and education due to Algeria's colonial history. Kabyle, with 3 million speakers, is the most spoken Berber language in the country, is taught and partially co-official in parts of Kabylie.
The Zenati languages are a branch of the Northern Berber language family of North Africa. They were named after the medieval Zenata Berber tribal confederation. They were first proposed in the works of French linguist Edmond Destaing (1915) (1920–23). Zenata dialects are distributed across the central Berber world (Maghreb), from northeastern Morocco to just west of Algiers, and the northern Sahara, from southwestern Algeria around Bechar to Zuwara in Libya. The most widely spoken Zenati languages are Tmazight of the Rif in northern Morocco and Tashawit Berber in northeastern Algeria, each of which have over 3 million speakers.

The Mzab–Wargla languages or Northern Saharan oasis dialects are a dialect cluster of the Zenati languages, within the Northern Berber subbranch. They are spoken in scattered oases of Algeria and Morocco.

Tarifit Berber, also known as Riffian or locally as Tamazight is a Zenati Berber language spoken in the Rif region in northern Morocco. It is spoken natively by some 1,271,000 Rifians primarily in the Rif provinces of Nador, Al Hoceima and Driouch.

Roger Marsh Blench is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and works as a consultant.
The Berber Latin alphabet is the version of the Latin alphabet used to write the Berber languages. It was adopted in the 19th century, using a variety of letters.
Proto-Berber or Proto-Libyan is the reconstructed proto-language from which the modern Berber languages descend. Proto-Berber was an Afroasiatic language, and thus its descendant Berber languages are cousins to the Egyptian language, Cushitic languages, Semitic languages, Chadic languages, and the Omotic languages.

South Oran Berber, or Tachelhit, is a cluster of the Zenati languages, which belong to the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. It is spoken in a number of oases of southwestern Algeria and across the border in Morocco.

Gurara (Gourara) is a Zenati Berber language spoken in the Gourara (Tigurarin) region, an archipelago of oases surrounding the town of Timimoun in southwestern Algeria. Ethnologue gives it the generic name Taznatit ("Zenati"), along with Tuwat spoken to its south; however, Blench (2006) classifies Gurara as a dialect of Mzab–Wargla and Tuwat as a dialect of the Riff languages.
Northern Songhay is the smaller of the two branches of the Songhay languages. It is a group of heavily Berber-influenced dialects spoken in scattered oases of the Sahara.
Tuwat is a Zenati Berber language. It is spoken by Zenata Berbers in a number of villages in the Tuat region of southern Algeria; notably Tamentit and Tittaf, located south of the Gurara Berber speech area. Ethnologue considers them a single language, "Zenati", but Blench (2006) classifies Gurara as a dialect of Mzab–Wargla and Tuwat as a dialect of the Riff cluster.

The East Zenati languages or Tunisian and Zuwara are a group of the Zenati Berber dialects spoken in Tunisia and Libya.
The Hilalian dialects are a continuum of Arabic dialects of the Maghreb, which were introduced during the Hilalian invasions between the 11th and 12th centuries, as well as the migration of Arab Hilalian tribes to the Western Maghreb. These dialects played a great role in the emergence of the Egyptian and Maghrebi dialects. The Bani Hilal tribes settled in the region of Casablanca-Settat in Morocco, parts of Libya, central Algeria, and Tunisia.
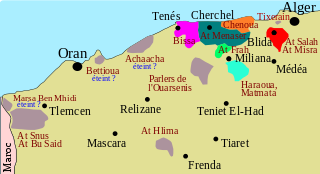
The Western Algerian Zenatic dialects are a diffuse set of Zenati Berber dialects spoken in north-western Algeria, west of the capital Algiers.