
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight, are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related but mostly mutually unintelligible languages spoken by Berber communities, who are indigenous to North Africa. The languages are primarily spoken and not typically written. Historically, they have been written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh. Today, they may also be written in the Berber Latin alphabet or the Arabic script, with Latin being the most pervasive.

The Eastern Berber languages are a group of Berber languages spoken in Libya and Egypt. They include Awjila, Sokna and Fezzan (El-Fogaha), Siwi and Ghadamès, though it is not clear that they form a valid genealogical group.
Siwi is the easternmost Berber language, spoken in the western Egyptian desert by an estimated 15,000 to 20,000 people in the oases of Siwa and Gara, near the Libyan border.
The Northern Berber languages are a dialect continuum spoken across the Maghreb, constituting a subgroup of the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. Their continuity has been broken by the spread of Arabic, and to a lesser extent by the Zenati group of Northern Berber. The Zenati idioms share certain innovations not found in the surrounding languages; notably a softening of k to sh and an absence of a- in certain words, such as "hand"
The Zenati languages are a branch of the Northern Berber language family of North Africa. They were named after the medieval Zenata Berber tribal confederation. They were first proposed in the works of French linguist Edmond Destaing (1915) (1920–23). Zenata dialects are distributed across the central Berber world (Maghreb), from northeastern Morocco to just west of Algiers, and the northern Sahara, from southwestern Algeria around Bechar to Zuwara in Libya. The most widely spoken Zenati languages are Tmazight of the Rif in northern Morocco and Tashawit Berber in northeastern Algeria, each of which have over 3 million speakers.

The Mzab–Wargla languages or Northern Saharan oasis dialects are a dialect cluster of the Zenati languages, within the Northern Berber subbranch. They are spoken in scattered oases of Algeria and Morocco.

Tarifit Berber, also known as Riffian or locally as Tamazight is a Zenati Berber language spoken in the Rif region in northern Morocco. It is spoken natively by some 1,271,000 Rifians primarily in the Rif provinces of Al Hoceima, Nador and Driouch.
Nafusi is a Berber language spoken in the Nafusa Mountains, a large area in northwestern Libya. Its primary speakers are the Ibadi communities around Jadu, Nalut and Yafran.
Proto-Berber or Proto-Libyan is the reconstructed proto-language from which the modern Berber languages descend. Proto-Berber was an Afroasiatic language, and thus its descendant Berber languages are cousins to the Egyptian language, Cushitic languages, Semitic languages, Chadic languages, and the Omotic languages.

South Oran Berber, or Tachelhit, is a cluster of the Zenati languages, which belong to the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. It is spoken in a number of oases of southwestern Algeria and across the border in Morocco.

Gurara (Gourara) is a Zenati Berber language spoken in the Gourara (Tigurarin) region, an archipelago of oases surrounding the town of Timimoun in southwestern Algeria. Ethnologue gives it the generic name Taznatit ("Zenati"), along with Tuwat spoken to its south; however, Blench (2006) classifies Gurara as a dialect of Mzab–Wargla and Tuwat as a dialect of the Riff languages.

Zuwara Berber or Twillult language (also: Zuara, Zwara, is a Berber dialect, one of the Berber Zenati languages. It is spoken in Zuwara city, located on the coast of western Tripolitania in northwestern Libya.

Matmata Berber is a Zenati Berber dialect spoken around the town of Matmâta in southern Tunisia, and in the villages of Taoujjout, Tamezret and Zrawa. According to Ben Mamou's lexicon, its speakers call it Tmaziɣṯ or Eddwi nna, meaning "our speech", while it is called Shelha or Jbali (جبالي) in local Tunisian Arabic dialects. The total population speaking this variety was estimated at 3,726 in 1975.
Ait Seghrouchen Berber, or Seghroucheni (Seghrusheni), is a Zenati Berber language of the Eastern Middle Atlas Berber cluster. It is spoken by the Ait Seghrouchen tribe inhabiting east-central Morocco.

The official language of Libya is Modern Standard Arabic. Most residents speak one of the varieties of Arabic as a first language, most prominently Libyan Arabic, but also Egyptian Arabic and Tunisian Arabic.
Tuwat is a Zenati Berber language. It is spoken by Zenata Berbers in a number of villages in the Tuat region of southern Algeria; notably Tamentit and Tittaf, located south of the Gurara Berber speech area. Ethnologue considers them a single language, "Zenati", but Blench (2006) classifies Gurara as a dialect of Mzab–Wargla and Tuwat as a dialect of the Riff cluster.
Sheliff Basin Berber is a variety of the Berber languages that is spoken in Algeria. It is traditionally taken to be a dialect of Shenwa, one of the Western Algerian Zenati languages. Blench (2006) argues instead that the variety is part of the Riffian dialect cluster.

Eastern Middle Atlas Berber is a cluster of Berber dialects spoken in the eastern and north-eastern parts of the Middle Atlas, in Morocco. These dialects are those of the tribes of Ait Seghrouchen, Ait Warayn, Marmoucha, Ait Alaham, Ait Youb and Ait Mourghi.
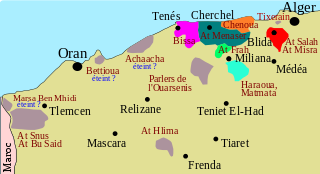
The Western Algerian Zenatic dialects are a diffuse set of Zenati Berber dialects spoken in north-western Algeria, west of the capital Algiers.
Iznasen (Iznassen) is a Berber language, belonging to the Zenati group. It is spoken in the extreme northeast of Morocco, in a speech area near the border of western Algeria.










