
The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae.

Weevils are beetles belonging to the superfamily Curculionoidea, known for their elongated snouts. They are usually small – less than 6 mm in length – and herbivorous. Approximately 97,000 species of weevils are known. They belong to several families, with most of them in the family Curculionidae. It also includes bark beetles, which while morphologically dissimilar to other weevils in lacking the distinctive snout, is a subfamily of Curculionidae. Some other beetles, although not closely related, bear the name "weevil", such as the biscuit weevil, which belongs to the family Ptinidae.
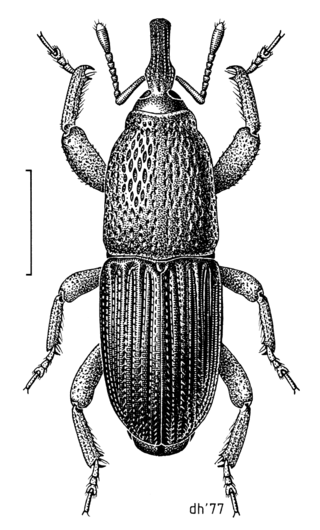
The wheat weevil, also known as the grain weevil or granary weevil, is an insect that feeds on cereal grains, and is a common pest in many places. It can cause significant damage to harvested stored grains and may drastically decrease crop yields. The females lay many eggs and the larvae eat the inside of the grain kernels.

The khapra beetle, also called cabinet beetle, which originated in South Asia, is one of the world's most destructive pests of grain products and seeds. It is considered one of the 100 worst invasive species in the world. Infestations are difficult to control because of the insect's ability to survive without food for long periods, its preference for dry conditions and low-moisture food, and its resistance to many insecticides. There is a federal quarantine restricting the importation of rice into the U.S. from countries with known infestations of the beetle. Khapra beetle infestation can spoil otherwise valuable trade goods and threaten significant economic losses if introduced to a new area. Handling or consuming contaminated grain and seed products can lead to health issues such as skin irritation and gastrointestinal distress.

Curculio is a genus of weevils belonging the family Curculionidae and subfamily Curculioninae. Members of the genus are commonly referred to as acorn weevils or nut weevils as they infest the seeds of trees such as oaks and hickories. The adult female weevil bores a tiny hole in the immature nut to lay her eggs, which then hatch into legless grubs. In autumn, the grubs bore holes through the shells from the inside to emerge into the soil where they may live for a year or two before maturing into adults.

Curculio nucum, the nut weevil, is a medium-sized beetle, with an especially elongated snout, characteristic of the Curculionini tribe of the weevil family (Curculionidae). Its larvae develop in hazel nuts Corylus avellana, being a serious pest in hazelnut orchards. It occurs in most of Europe, from south Sweden, Finland and Great Britain to the Mediterranean.
Home-stored product entomology is the study of insects that infest foodstuffs stored in the home. It deals with the prevention, detection and eradication of pests.

The rice weevil is a stored product pest which attacks seeds of several crops, including wheat, rice, and maize.

Rhyzopertha is a monotypic genus of beetles in the family Bostrichidae, the false powderpost beetles. The sole species, Rhyzopertha dominica, is known commonly as the lesser grain borer, American wheat weevil, Australian wheat weevil, and stored grain borer. It is a beetle commonly found within store bought products and pest of stored cereal grains located worldwide. It is also a major pest of peanuts. The first documentation of wheat infestation by R. dominica was observed in Australia. R. dominica are usually reddish brown to dark brown in coloration, vary in sizes, elongated and cylindrical.

The Angoumois grain moth is a species of the Gelechiidae moth family, commonly referred to as the "rice grain moth". It is most abundant in the temperate or tropical climates of India, China, South Africa, Indonesia, Malaysia, Japan, Egypt and Nigeria, with its location of origin being currently unknown. It is most commonly associated as a pest of field and stored cereal grains as they burrow within the kernel grains of crop plants, rendering them unusable for human consumption. By laying eggs between the grains themselves and hatching at a later time, often during the processing, transportation or storage stages, the moth can be transported to households or countries presently free of Angoumois grain moth infestations. Thus, constant protection against the Angoumois grain moth is required for grain up till the time of consumption.

The maize weevil, known in the United States as the greater rice weevil, is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae. It can be found in numerous tropical areas around the world, and in the United States, and is a major pest of maize. This species attacks both standing crops and stored cereal products, including wheat, rice, sorghum, oats, barley, rye, buckwheat, peas, and cottonseed. The maize weevil also infests other types of stored, processed cereal products such as pasta, cassava, and various coarse, milled grains. It has even been known to attack fruit while in storage, such as apples.

Liposcelis bostrychophila is a species of booklouse in the family Liposcelididae. It is known nearly worldwide as a common pest of stored products. It is especially prevalent in cereals. In 2019 it was identified as a predator of mosquito eggs in a FAO/IAEA Insect Pest Control Laboratory which developed sterile males.

Securidaca longipedunculata is a species of tree in the genus Securidaca. It is most commonly found in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, and it was given protected status in South Africa. The generic name is derived from Latin securis, as the shape of the wing on the nut recalls a hatchet. The specific name longipedunculata hints at the long peduncle on which the flowers are borne.
Theocolax elegans is a parasitic wasp species in the genus Theocolax. It is a parasite of immature stages of stored grain pest insects such as Sitophilus granarius or Rhyzopertha dominica

Curculio elephas is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae, the true weevils. It is known commonly as the chestnut weevil. It is a serious pest of chestnut in Europe.
A storage pest is an insect or other animal that damages or destroys stored food or other stored valuable organic matter. Insects are a large proportion of storage pests with each type of crop having specific insects that gravitate towards them such as the genus Tribolium that consists of insects such as Tribolium castaneum or Tribolium confusum which damage flour crops primarily.
Lariophagus distinguendus is a idiobiont ectoparasitoid hymenopteran in the family Pteromalidae, superfamily Chalcidoidea. It parasitizes small beetle larvae concealed in seeds, as well as prepupae and pupae in their cocoons. It is used for the biological control of several beetle pests of stored products, particularly in central Europe, where it is produced commercially and distributed by at least 11 companies.
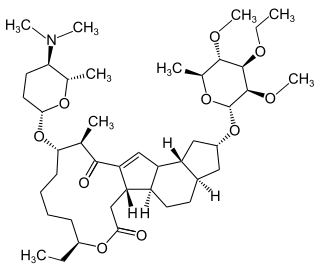
Spinetoram is an insecticidal mixture of two active neurotoxic constituents of Saccharopolyspora spinosa. It is used to control pest insects in stored grain and on domestic cats.














