
Lake County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the population was 8,160. Its county seat is Lakeview. The county is named after the many lakes found within its boundaries, including Lake Abert, Summer Lake, Hart Lake, and Goose Lake.

Lakeview is a town in Lake County, Oregon, United States. The population was 2,418 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Lake County. The city bills itself as the "Tallest Town in Oregon" because of its elevation, 4,757 feet (1,450 m) above sea level. Lakeview is situated in the Goose Lake Valley at the foot of the Warner Mountains and at the edge of Oregon's high desert country. Its economy is based on agriculture, lumber production, and government activities. In addition, tourism is an increasingly important part of the city's economy. Oregon's Outback Scenic Byway passes through Lakeview.
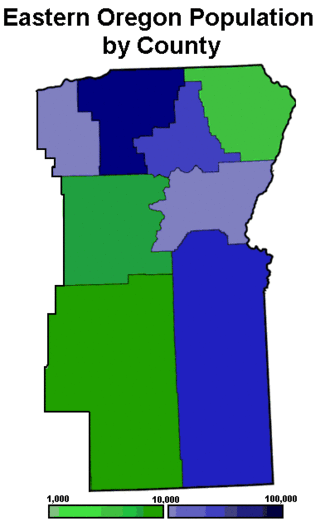
Eastern Oregon is a region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is not an officially recognized geographic entity; thus, the boundaries of the region vary according to context. It is sometimes understood to include only the eight easternmost counties in the state; in other contexts, it includes the entire area east of the Cascade Range. Cities in the basic eight-county definition include Baker City, Burns, Hermiston, Pendleton, Boardman, John Day, La Grande, and Ontario. Umatilla County is home to the largest population base in Eastern Oregon, accounting for 42% of the region's residents. Hermiston, located in Umatilla County, is the largest city in the region, accounting for 10% of the population. Major industries include transportation/warehousing, timber, agriculture and tourism. The main transportation corridors are I-84, U.S. Route 395, U.S. Route 97, U.S. Route 26, U.S. Route 30, and U.S. Route 20.

Area codes 541 and 458 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for most of the U.S. state of Oregon, excluding only the northwestern corner of the state. The service area includes the cities of Eugene, Springfield, Corvallis, Albany, Medford, Bend, Ashland, Klamath Falls, The Dalles, Burns, Lakeview, and Pendleton, as well as the coastal region from Lincoln County to the California border. Area code 541 was created in an area code split from area code 503 on November 5, 1995. Area code 458 was added to the same service area on February 10, 2010 to form an overlay.

Oregon Route 140 is a state highway in southern Oregon, United States. It is the longest state highway in Oregon, running 237 miles (381 km) from the community of White City, Oregon, through Klamath Falls and on to Lakeview. It then continues east, eventually descending into the state of Nevada.

The Fremont–Winema National Forest is a United States National Forest formed from the 2002 merger of the Fremont and Winema National Forests. They cover territory in southern Oregon from the crest of the Cascade Range on the west past the city of Lakeview to the east. The northern end of the forests is bounded by U.S. Route 97 on the west and Oregon Route 31 on the east. To the south, the state border with California forms the boundary of the forests. Klamath Falls is the only city of significant size in the vicinity. The forests are managed by the United States Forest Service, and the national forest headquarters are located in Lakeview.

Oregon Outback is an unofficial term generally used to reference the high desert Basin and Range country of the central southern portion of the U.S. state of Oregon and covers most of Lake County, Klamath County, Malheur County, and Harney County.

Chandler State Wayside is a state park in south-central Oregon in the United States. It is named in honor of Solomon and Hattie Chandler, who donated the land for the park. The park covers 85 acres (34 ha) of pine forest along a creek. The park provides restrooms and other basic facilities to accommodate the traveling public. Chandler State Wayside is administered by the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department.

The Wood River is a short river in the southern region of the U.S. state of Oregon, and part of the Klamath Basin drainage. It flows 18 miles (29 km) through the Fremont-Winema National Forests, Bureau of Land Management land, and private property in southern Oregon. Its watershed consists of 220 square miles (570 km2) of conifer forest, rural pasture land, and marsh. The river provides habitat for many species of wildlife including an adfluvial (migratory) and resident populations of native Great Basin redband trout.

Valley Falls is a small unincorporated community in Lake County, Oregon, United States. The settled area is located at the junction of U.S. Route 395 and Oregon Route 31. The community is named for a small falls on the Chewaucan River just north of the occupied site. East of Valley Falls, the cliff face of Abert Rim overlooks the community.

The Oregon Eastern Railway was a predecessor of the Southern Pacific Company that acquired or built most of the Natron Cutoff in northern California and southern Oregon, United States. It also made surveys and acquired right-of-way in eastern Oregon, which were subsequently sold to Union Pacific Railroad subsidiary Oregon–Washington Railroad and Navigation Company.

The Goose Lake Valley is located in south-central Oregon and northeastern California in the United States. It is a high valley at the northwestern corner of North America's Great Basin. Much of the valley floor is covered by Goose Lake, a large endorheic lake that straddles the Oregon–California border. Native Americans inhabited the Goose Lake Valley for thousands of years before explorers arrived in the 19th century. The pioneer wagon route known as the Applegate Trail crossed the Goose Lake Valley on its way to southern Oregon. At the south end of Goose Lake, the Lassen Cutoff separated from the Applegate Trail and headed south toward the Sacramento Valley. Today, Lakeview, Oregon, is the largest settlement in the valley. Livestock ranching and lumber mills are the valley's main commercial activity. The Goose Lake Valley offers a number of recreational opportunities including hang-gliding, hunting, fishing, and birdwatching.
Charles William Emanuel Jennings, known as Pop Jennings, was a businessman and Oregon state legislator. He was an early settler in the Chewaucan Valley in south-central Oregon, where he established the community of Valley Falls. Jennings was also a Democratic member of the Oregon House of Representatives for one term, serving from 1937 through 1938.
Warner Buck Snider, also known as W. B. Snider or Buck Snider, was a city recorder, county sheriff, rancher, and Oregon state legislator. He was a Republican member of the Oregon House of Representatives for two terms, from 1933 through 1936. After leaving the legislature, Snider returned to cattle ranching. He served as president of the Oregon Cattlemen's Association and actively advocated for grazing rights and highway construction in eastern Oregon.

The Barry Point Fire was a wildfire that burned over 92,977 acres (376.26 km2) of Oregon and California forest land during the summer of 2012. The fire began on 5 August 2012, the result of a lightning strike. The fire consumed public forest and rangeland as well as private forest and grazing land located in Lake County, Oregon and Modoc County, California. The public lands affected by the fire are administered by the United States Forest Service and the Oregon Department of Forestry. The largest part of the private land was owned by the Collins Timber Company. At the peak of the firefighting effort, there were 1,423 personnel working on the fire. It took 22 days to fully contain the fire and then an additional three weeks to mop it up.

Stephen Pike Moss was a rancher, businessman, and state legislator from the state of Oregon. He was a Democrat who served two terms in the Oregon House of Representatives. In the house, Moss represented a very large rural district in south central Oregon. He was also a co-founder of the Lake County Examiner, a newspaper published in Lakeview, Oregon.

Mark W. Bullard, also known as M. W. Bullard, was an American pioneer who established homesteads in Oregon and Washington state. As a young man, he traveled from his family home in Vermont to California and then on to Oregon and Washington. He eventually settled in what is now Pacific County, Washington. He served in the Washington territorial militia during a regional Indian war in the mid-1850s. After the war, he moved to the Goose Lake Valley in south central Oregon. While there, he donated property to establish a new town that became Lakeview, Oregon, the county seat of Lake County. He later returned to his farm in Pacific County, Washington.

Deep Creek Falls is a waterfall formed along Gibson Canyon on the south end of Warner Valley, east side of the city of Lakeview in Lake County, Oregon. Access to Deep Creek Falls is located along Oregon Route 140 through unmarked paths that lead down to the stream and the base of the waterfall.

The Tennant Fire was a wildfire that burned in the Klamath National Forest in Siskiyou County, California, in the United States as part of the 2021 California wildfire season. The fire was first reported just east of Highway 97, three miles northwest of Bray, California on June 28, 2021. The fire was contained on July 12, 2021. The fire burned 10,580 acres (4,282 ha), destroyed five structures, and caused evacuations in Macdoel, California. The cause remains under investigation. The Tennant Fire was one of three fires burning at the same time in the Lake Shasta region, the others being the Lava Fire and the Salt Fire.

Fleetwood was an unincorporated community located in Lake County, Oregon, United States. The first homesteaders arrived in the area around Fleetwood in 1905. The Fleetwood post office was opened in 1913. By 1920, the local population was declining due to a severe drought that dried up surface water and lowered the water table in the area around Fleetwood. Today, Fleetwood is a ghost town with no population and no surviving structures at the townsite. The site is located approximately 10 miles (16 km) east of Fort Rock state park. The nearest inhabited place is the small unincorporated community of Fort Rock, Oregon, which is 9 miles (14 km) west of the Fleetwood townsite.



















