
Vanuatu, officially the Republic of Vanuatu, is an island country in Melanesia, located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) east of northern Australia, 540 km (340 mi) northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.

Port Vila, or simply Vila, is the capital and largest city of Vanuatu. It is located on the island of Efate.

Espiritu Santo is the largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, with an area of 3,955.5 km2 (1,527.2 sq mi) and a population of around 40,000 according to the 2009 census.
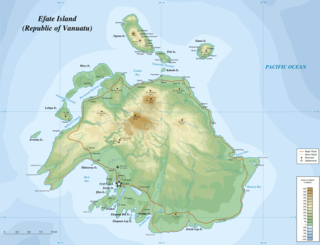
Efate is an island in the Pacific Ocean which is part of the Shefa Province in Vanuatu. It is also known as Île Vate.

Luganville is the second largest city in Vanuatu after the capital Port Vila; it is located on the island of Espiritu Santo and has a population of 18,062 as of the 2020 census. Those on Vanuatu's northern islands who regard Luganville as their big city, particularly indigenous populations, call it Santo; rural residents of Espiritu Santo call it Kanal. Luganville served as a major base of operations for American troops during World War II.

Tanna is an island in southern Vanuatu.

Pentecost Island is one of the 83 islands that make up the South Pacific nation of Vanuatu.
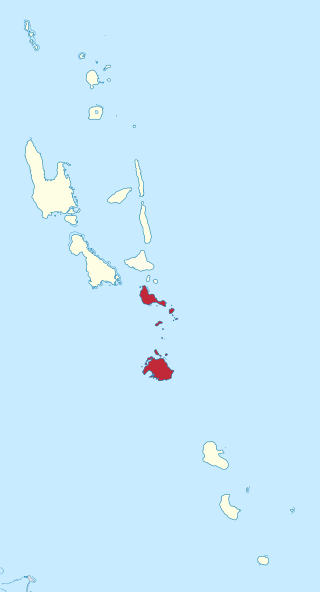
Shefa is one of the six provinces of Vanuatu, located in the center of the country and including the islands of Epi and Efate and the Shepherd Islands. The province's name is derived from the initial letters of SHepherd and EFAte. It has a population of 78,723 people and an area of 1,455 km2. Its capital is Port Vila, which is also the capital of the nation.

Ni-Vanuatu is a large group of closely related Melanesian ethnic groups native to the island country of Vanuatu. As such, Ni-Vanuatu are a mixed ethnolinguistic group with a shared ethnogenesis that speak a multitude of languages.

Vanuatu Cricket, officially the Vanuatu Cricket Association, is the national governing body of the sport of cricket in Vanuatu. Its current headquarters is in Port Vila, Vanuatu. Vanuatu Cricket Association is Vanuatu's representative at the International Cricket Council and is an associate member and has been a member of that body since 2009. It is also a member of the East Asia-Pacific Cricket Council. The Senior Men's Team achieved Associate status with the ICC after winning the prestigious ICC EAP Cup in 2009 (undefeated).

The cuisine of Vanuatu incorporates fish, root vegetables such as taro and yams, fruits, and vegetables. Most island families grow food in their gardens, and food shortages are rare. Papayas, pineapples, mangoes, plantains, and sweet potatoes are abundant through much of the year. Coconut milk and cream are used to flavour many dishes. Most food is cooked using hot stones or through boiling and steaming; little food is fried. Since Vanuatu is one of the few South Pacific regions influenced by the outside world, Vanuatu's food has a multicultural nature.

The Vanuatu Labour Party is a political party in Vanuatu. The party was established on 3 June 1987. It was founded on the initiative of various trade union organizations in order to contest the 1987 parliamentary election. The proposal to found the party was first presented by Ephraim Kalsakau, a leader of the Vanuatu Municipal Workers Union.

Four by-elections to the Parliament of Vanuatu were held in 2009 to fill seven vacant seats.
Life expectancy in Vanuatu is 67 years for men, and 70 years for women.
A by-election was held in the Tanna constituency in Vanuatu on 27 May 2013. It followed the death of incumbent MP Harry Iauko, who was also the Minister for Infrastructure, Public Utilities and Public Service.

Squatting in Fiji is defined as being "a resident of a dwelling which is illegal according to planning by-laws regardless of whether the landowner has given consent". As of 2018, an estimated 20% of the total population was squatting, including people living on land owned by indigenous clans with informal permission. Most squatters are on the larger islands such as Vanua Levu and Viti Levu.

Squatting in Chile is the occupation of unused land or derelict buildings without the permission of the owner. From the 1960s onwards, informal settlements known as callampas were permitted although there were also evictions such as the massacre of Puerto Montt in 1969. In the 1970s, the government of Salvador Allende encouraged occupations, then following the coup d'état, the military junta repressed squatting. Callampas then became known as campamentos.

Squatting in Iran mostly occurs around the major cities, as rural migrants move to urban centres. From the 1950s onwards shanty towns have been set up and inhabitants are known as "koukhnishinan". Following the Iranian Revolution of 1979, squatter settlements increased, with the state sometimes evicting and sometimes legalizing the areas.

Squatting in Mexico has occurred on the periphery of Mexico City from the 19th century onwards. As of 2017, an estimated 25 per cent of Mexico's urban population lived in informal settlements. In Mexico City, there are self-managed social centres. The CORETT program aims to help squatters to register their land plots

Squatting on Solomon Islands occurs in informal settlements. The Ministry of Lands and Survey reported in 2006 that there were 17,000 squatters in the capital Honiara. Disputes over land use have generated tensions in recent years, particularly between 1998 and 2003.


















