
The siege of Port Hudson, Louisiana, was the final engagement in the Union campaign to recapture the Mississippi River in the American Civil War.

USS Tyler was originally a merchant ship named A. O. Tyler, a commercial side-wheel steamboat with twin stacks and covered paddles positioned aft. Constructed in Cincinnati, Ohio in 1857, it was acquired by the United States Navy, 5 June 1861 for service in the American Civil War and converted into the gunboat USS Tyler on 5 June 1861. She was commissioned in September 1861. She was protected with thick wooden bulwarks.

The third USS Lexington was a timberclad gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.

The Battle of St. Charles was fought on June 17, 1862, at St. Charles, Arkansas, during the American Civil War. Earlier in 1862, a Union Army force commanded by Major General Samuel R. Curtis moved against Little Rock, Arkansas, but became bogged down in the Batesville area due to lack of supplies. The Union leadership decided to send a naval force from Memphis, Tennessee, up the White River to resupply Curtis's men. Major General Thomas C. Hindman, the Confederate commander in Arkansas, had fortifications constructed near St. Charles to stop the Union movement. Two artillery positions were built, and three ships, including CSS Maurepas, were scuttled to obstruct the river.
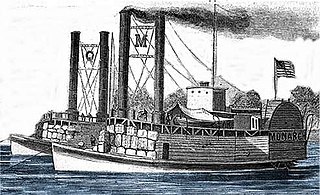
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

The City-class ironclad USS Cincinnati was a stern-wheel casemate gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for Cincinnati, Ohio, and was the first ship to bear that name in the United States Navy.

CSS Chattahoochee was a twin-screw steam powered gunboat built at Saffold, Georgia; she was christened for the river upon which she was built. The gunboat entered Confederate States Navy service in February 1863.

The Battle of Baton Rouge was a ground and naval battle in the American Civil War fought in East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, on August 5, 1862. The Union victory halted Confederate attempts to recapture the capital city of Louisiana.

USS Mound City was a City-class ironclad gunboat built for service on the Mississippi River and its tributaries in the American Civil War. Originally commissioned as part of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla, she remained in that service until October 1862. Then the flotilla was transferred to the Navy and she became part of the Mississippi River Squadron, where she remained until the end of the war.

USS Signal (1862) – a small 190-ton steamship – was acquired during the second year of the American Civil War by the Union Navy and outfitted as a gunboat. She also served other types of duty, such as that of dispatch vessel and convoy escort.

The Battle of St. John's Bluff was fought from October 1–3, 1862, between Union and Confederate forces in Duval County, Florida, during the American Civil War. The battle resulted in a significant Union victory, helping secure their control of the Jacksonville area.
The Port Hudson State Historic Site is located on the Mississippi River north of Baton Rouge in East Feliciana Parish, Louisiana, just outside the limits of Port Hudson and in the vicinity of Jackson. The site preserves a portion of the fortifications and battle area of the longest siege in American history, during the American Civil War from May 23 through July 9, 1863. The state of Louisiana maintains the site, which includes a museum about the siege, artillery displays, redoubts, and interpretive plaques. Historical reenactments are held each year. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1974, significant as the first place where African-American military units fought for the Union Army under African-American field leadership.

Battery White was an artillery battery constructed by the Confederates during the American Civil War. Built in 1862–63 to defend Winyah Bay on the South Carolina coast, the battery was strongly situated and constructed; however, it was inadequately manned, and was captured without resistance during the final months of the war.
The Monticello Artillery (1862–1865) was a Confederate Army artillery battery during the American Civil War. The unit was also known as: Owen's Battery, or Howell's Battery. Some post war records refer to the unit as the Drew Light Artillery because most original members were from Drew County, Arkansas.

The Camp White Sulphur Springs Confederate Cemetery is an American Civil War cemetery in Arkansas. It is located northeast of the village of Sulphur Springs, also known as White Sulphur Springs, in Jefferson County.

The Civil War batteries of Helena, Arkansas are a series of four defensive earthworks erected in Helena, Arkansas by Union Army forces during the American Civil War. The four batteries played a significant role in the Battle of Helena, fought on July 4, 1863, which secured the Arkansas side of the Mississippi River for the Union. They are listed individually on the National Register of Historic Places.

The St. Charles Battle Monument is located at the center of the intersection of Broadway and Arkansas Street in the center of St. Charles, Arkansas. It commemorates the 1862 Battle of Saint Charles, a naval and land engagement of the American Civil War that took place just downriver from the city. It is a square granite monument, topped by an inverted cannon barrel. It is 18 feet (5.5 m) high and 9.5 feet (2.9 m) square. Its inscriptions commemorate the 148 Union soldiers who died in the explosion of the USS Mound City, caused by what is sometimes described as the single deadliest shot fired in the entire Civil War. Inscriptions on another side memorialize the smaller number of Confederate dead in the engagement. The monument was placed in 1919 through the efforts of a relative of William Hickman Harte, the master on board the Mound City who died in the explosion, and is one of the few memorials placed in a Confederate state by a northerner in commemoration of both Union and Confederate war dead.
CSS Maurepas was a sidewheel steamer that briefly served as a gunboat in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Built in 1858 in Indiana as Grosse Tete, the vessel was used in commercial trade until 1860 and then delivered mail until 1861, when she was acquired by the Confederate Navy.
CSS Pontchartrain was a gunboat that served in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Built in 1859 for passenger and cotton trade, she was purchased by the Confederates in October 1862. After seeing action against Union land positions during the campaigns for New Madrid, Missouri, and Island Number Ten, she was transferred to serve on the Arkansas River and the White River. In June 1862, two of her cannons were taken to a land fortification at St. Charles, Arkansas, where part of her crew saw action in the Battle of St. Charles while manning the guns. Her other cannons were then offloaded at Fort Hindman, where more of her crew were captured while fighting on land at the Battle of Arkansas Post in January 1863. Pontchartrain herself remained inactive at Little Rock, Arkansas, and was burned to prevent capture in September 1863 when the Confederates abandoned the city.


















