Related Research Articles
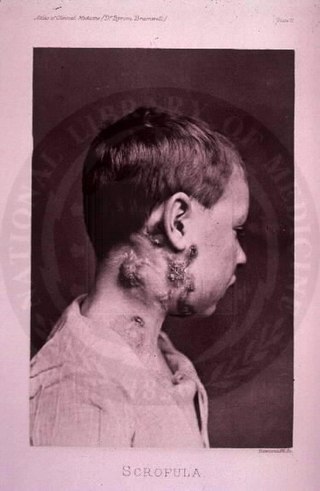
The disease mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis, also known as scrofula and historically as king's evil, involves a lymphadenitis of the cervical (neck) lymph nodes associated with tuberculosis as well as nontuberculous (atypical) mycobacteria.

A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving behind only 5–15 millilitres of fluid, which helps to maintain a functional vacuum between the parietal and visceral pleurae. Excess fluid within the pleural space can impair inspiration by upsetting the functional vacuum and hydrostatically increasing the resistance against lung expansion, resulting in a fully or partially collapsed lung.

Pulmonology, pneumology or pneumonology is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.
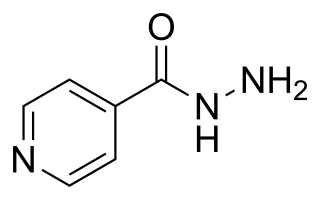
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis, it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. For latent tuberculosis, it is often used alone. It may also be used for atypical types of mycobacteria, such as M. avium, M. kansasii, and M. xenopi. It is usually taken by mouth, but may be used by injection into muscle.

Tuberculosis is diagnosed by finding Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria in a clinical specimen taken from the patient. While other investigations may strongly suggest tuberculosis as the diagnosis, they cannot confirm it.

Management of tuberculosis refers to techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB), or simply a treatment plan for TB.

Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenitis is a form of tuberculosis infection occurring outside of the lungs. In general, it describes tuberculosis infection of the lymph nodes, leading to lymphadenopathy. When cervical lymph nodes are affected, it is commonly referred to as "Scrofula." A majority of tuberculosis infections affect the lungs, and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis infections account for the remainder; these most commonly involve the lymphatic system. Although the cervical region is most commonly affected, tuberculous lymphadenitis can occur all around the body, including the axillary and inguinal regions.

Miliary tuberculosis is a form of tuberculosis that is characterized by a wide dissemination into the human body and by the tiny size of the lesions (1–5 mm). Its name comes from a distinctive pattern seen on a chest radiograph of many tiny spots distributed throughout the lung fields with the appearance similar to millet seeds—thus the term "miliary" tuberculosis. Miliary TB may infect any number of organs, including the lungs, liver, and spleen. Miliary tuberculosis is present in about 2% of all reported cases of tuberculosis and accounts for up to 20% of all extra-pulmonary tuberculosis cases.

4-Aminosalicylic acid, also known as para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) and sold under the brand name Paser among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used to treat active drug resistant tuberculosis together with other antituberculosis medications. It has also been used as a second line agent to sulfasalazine in people with inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is typically taken by mouth.

Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection (MAI) is an atypical mycobacterial infection, i.e. one with nontuberculous mycobacteria or NTM, caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), which is made of two Mycobacterium species, M. avium and M. intracellulare. This infection causes respiratory illness in birds, pigs, and humans, especially in immunocompromised people. In the later stages of AIDS, it can be very severe. It usually first presents as a persistent cough. It is typically treated with a series of three antibiotics for a period of at least six months.
Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis (IPH) is a lung disease of unknown cause that is characterized by alveolar capillary bleeding and accumulation of haemosiderin in the lungs. It is rare, with an incidence between 0.24 and 1.23 cases per million people.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and leprosy.

Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity of pulmonary impairment. Pulmonary function testing has diagnostic and therapeutic roles and helps clinicians answer some general questions about patients with lung disease. PFTs are normally performed by a pulmonary function technologist, respiratory therapist, respiratory physiologist, physiotherapist, pulmonologist, or general practitioner.
Pulmonary hygiene, also referred to as pulmonary toilet, is a set of methods used to clear mucus and secretions from the airways. The word pulmonary refers to the lungs. The word toilet, related to the French toilette, refers to body care and hygiene; this root is used in words such as toiletry that also relate to cleansing.

Geotrichosis is a mycosis caused by Geotrichum candidum.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite standard medical treatment. It is a broad therapeutic concept. It is defined by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society as an evidence-based, multidisciplinary, and comprehensive intervention for patients with chronic respiratory diseases who are symptomatic and often have decreased daily life activities. In general, pulmonary rehabilitation refers to a series of services that are administered to patients of respiratory disease and their families, typically to attempt to improve the quality of life for the patient. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be carried out in a variety of settings, depending on the patient's needs, and may or may not include pharmacologic intervention.
Tuberculous pericarditis is a form of pericarditis. It is a condition in which the pericardium surrounding the heart is infected by the bacterial species Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculous pericarditis accounts for a significant percentage of presentations of tuberculosis worldwide. The condition has four stages of disease which manifests with clinical presentations ranging from acute pericarditis to overt heart failure. Tuberculous pericarditis is an under-diagnosed condition. Diagnosis often requires a range of diagnostic tools, including pericardiocentesis, biochemical tests, and imaging. Treatment of this disease is similar to treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Alternative treatment options to reduce cardiac complications are also available.
Tuberculous dactylitis, also known as spina ventosa, is a skeletal manifestation of tuberculosis, one of the commonest forms of bacterial osteitis. It affects children more often than adults. The first radiological description of the condition is credited to Feilchenfeld in 1896; however, the first histological description was given by Rankin in 1886. The Swedish botanist and physician Carl von Linne was the first to mention the condition by the name spina ventosa.

Abdominal tuberculosis is a type of extrapulmonary tuberculosis which involves the abdominal organs such as intestines, peritoneum and abdominal lymph nodes. It can either occur in isolation or along with a primary focus in patients with disseminated tuberculosis.
Horton Corwin Hinshaw Sr. was an American pulmonologist, known for the use of streptomycin as the first effective antibiotic for the treatment of tuberculosis (TB).
References
- ↑ Shubin H, Heiken CA, Glaskin A, Pennes E, Chakravarty S, Rutberg F (October 1955). "A study of the neurotoxicity of streptoduocin on tuberculous patients". Diseases of the Chest. 28 (4): 447–450. doi:10.1378/chest.28.4.447. PMID 13261867.