Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials.

A radiator is a heat exchanger used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.
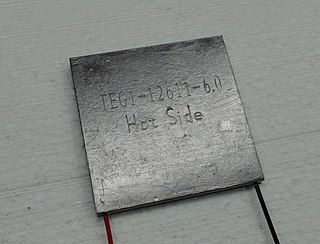
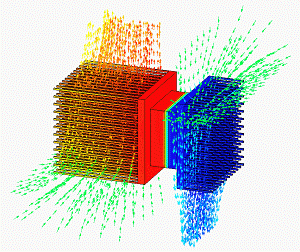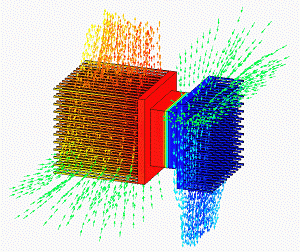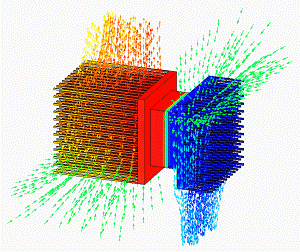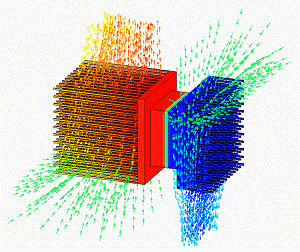
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current. Such an instrument is also called a Peltier device, Peltier heat pump, solid state refrigerator, or thermoelectric cooler (TEC) and occasionally a thermoelectric battery. It can be used either for heating or for cooling, although in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools.

A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with other high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature.
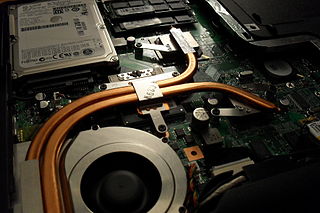
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that employs phase transition to transfer heat between two solid interfaces.

Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Components that are susceptible to temporary malfunction or permanent failure if overheated include integrated circuits such as central processing units (CPUs), chipsets, graphics cards, hard disk drives, and solid state drives.
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corrosion of the cooling system. Some applications also require the coolant to be an electrical insulator.

A computer fan is any fan inside, or attached to, a computer case used for active cooling. Fans are used to draw cooler air into the case from the outside, expel warm air from inside and move air across a heat sink to cool a particular component. Both axial and sometimes centrifugal (blower/squirrel-cage) fans are used in computers. Computer fans commonly come in standard sizes, such as 92 mm, 120 mm, 140 mm, and even 200–220 mm. Computer fans are powered and controlled using 3-pin or 4-pin fan connectors.
The role of the substrate in power electronics is to provide the interconnections to form an electric circuit, and to cool the components. Compared to materials and techniques used in lower power microelectronics, these substrates must carry higher currents and provide a higher voltage isolation. They also must operate over a wide temperature range.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.
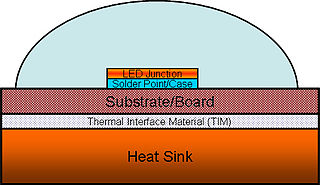
High power light-emitting diodes (LEDs) can use 350 milliwatts or more in a single LED. Most of the electricity in an LED becomes heat rather than light. If this heat is not removed, the LEDs run at high temperatures, which not only lowers their efficiency, but also makes the LED less reliable. Thus, thermal management of high power LEDs is a crucial area of research and development. It is necessary to limit both the junction and the phosphor particles temperatures to a value that will guarantee the desired LED lifetime.
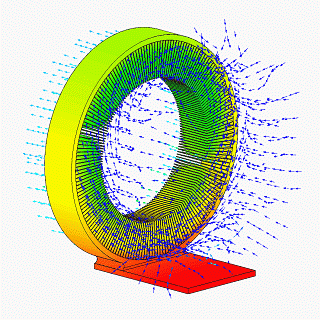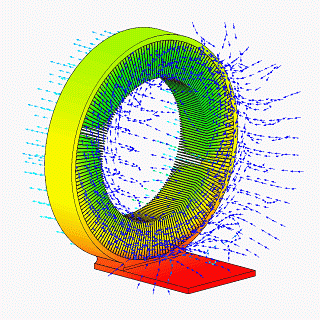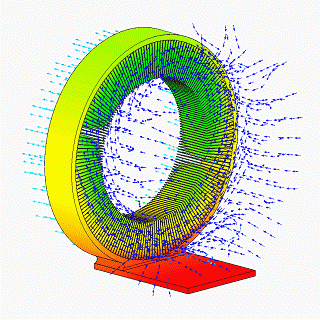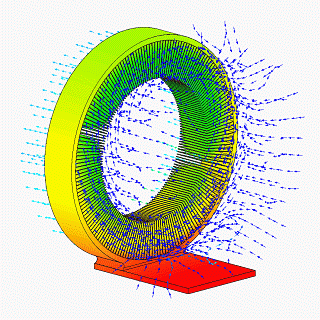
A heat spreader transfers energy as heat from a hotter source to a colder heat sink or heat exchanger. There are two thermodynamic types, passive and active. The most common sort of passive heat spreader is a plate or block of material having high thermal conductivity, such as copper, aluminum, or diamond. An active heat spreader speeds up heat transfer with expenditure of energy as work supplied by an external source.

Radiators and convectors are heat exchangers designed to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of space heating.
HVAC is a major sub discipline of mechanical engineering. The goal of HVAC design is to balance indoor environmental comfort with other factors such as installation cost, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. The discipline of HVAC includes a large number of specialized terms and acronyms, many of which are summarized in this glossary.
In heat transfer, thermal engineering, and thermodynamics, thermal conductance and thermal resistance are fundamental concepts that describe the ability of materials or systems to conduct heat and the opposition they offer to the heat current. The ability to manipulate these properties allows engineers to control temperature gradient, prevent thermal shock, and maximize the efficiency of thermal systems. Furthermore, these principles find applications in a multitude of fields, including materials science, mechanical engineering, electronics, and energy management. Knowledge of these principles is crucial in various scientific, engineering, and everyday applications, from designing efficient temperature control, thermal insulation, and thermal management in industrial processes to optimizing the performance of electronic devices.
Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat to achieve desired heating or cooling. An important design aspect of heat exchanger technology is the selection of appropriate materials to conduct and transfer heat fast and efficiently.
Electronics cooling encompasses thermal design, analysis and experimental characterization of electronic systems as a discrete discipline with the product creation process for an electronics product, or an electronics sub-system within a product. On-line sources of information are available and a number of books have been published on this topic.

Immersion cooling is an IT cooling practice by which complete servers are immersed in a dielectric, electrically non-conductive fluid that has significantly higher thermal conductivity than air. Heat is removed from a system by putting the coolant in direct contact with hot components, and circulating the heated liquid through heat exchangers. This practice is highly effective because liquid coolants can absorb more heat from the system, and are more easily circulated through the system, than air. Immersion cooling has many benefits, including but not limited to: sustainability, performance, reliability and cost.
Kambiz Vafai is a mechanical engineer, inventor, academic and author. He has taken on the roles of Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering and the Director of Bourns College of Engineering Online Master-of-Science in Engineering Program at the University of California, Riverside.