Veterinary parasitology is a branch of veterinary medicine that deals with the study of morphology, life-cycle, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and control of eukaryotic invertebrates of the kingdom Animalia and the taxon Protozoa that depend upon other invertebrates and higher vertebrates for their propagation, nutrition, and metabolism without necessarily causing the death of their hosts. Modern parasitology focuses on responses of animal hosts to parasitic invasion. Parasites of domestic animals,, as well as wildlife animals are considered. Data obtained from parasitological research in animals helps in veterinary practice and improves animal breeding. The major goal of veterinary parasitology is to protect animals and improve their health, but because a number of animal parasites are transmitted to humans, veterinary parasitology is also important for public health.

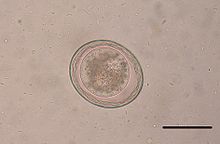
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems.
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm and, less frequently, the cat roundworm. These are the most common intestinal roundworms of dogs, coyotes, wolves and foxes and domestic cats, respectively. Humans are among the many "accidental" or paratenic hosts of these roundworms.

The Toxocaridae are a zoonotic family of parasitic nematodes that infect canids and felids and which cause toxocariasis in humans. The worms are unable to reproduce in humans.

Ascaris is a nematode genus of parasitic worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms". One species, Ascaris lumbricoides, affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, Ascaris suum, typically infects pigs. Other ascarid genera infect other animals, such as Parascaris equorum, the equine roundworm, and Toxocara and Toxascaris, which infect dogs and cats.
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease of the intestinal tract of animals caused by coccidian protozoa. The disease spreads from one animal to another by contact with infected feces or ingestion of infected tissue. Diarrhea, which may become bloody in severe cases, is the primary symptom. Most animals infected with coccidia are asymptomatic, but young or immunocompromised animals may suffer severe symptoms and death.
Visceral larva migrans (VLM) is a condition in humans caused by the migratory larvae of certain nematodes, humans being a dead-end host, and was first reported in 1952. Nematodes causing such zoonotic infections are Baylisascaris procyonis, Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati, and Ascaris suum. These nematodes can infect but not mature in humans and after migrating through the intestinal wall, travel with the blood stream to various organs where they cause inflammation and damage. Affected organs can include the liver, heart and the CNS. A special variant is ocular larva migrans where usually T. canis larvae travel to the eye.

A pooper-scooper, or poop scoop, is a device used to pick up animal feces from public places and yards, particularly those of dogs. Pooper-scooper devices often have a bag or bag attachment. 'Poop bags' are alternatives to pooper scoopers, and are simply a bag, usually turned inside out, to carry the feces to a proper disposal area. Sometimes, the person performing the cleanup is also known as the pooper-scooper.
Uncinaria stenocephala is a nematode that parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. Uncinaria stenocephala is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such as Canada and the northern regions of the US, where it can be found primarily in foxes (40%). U. stenocephala is also one of the most common hookworms in the UK, called the northern hookworm, however it has a rather low prevalence. U. stenocephala is also considered to be zoonotic hookworms because they live in animals but can be transmitted to humans.

Trichuris, often referred to as whipworms or the silent serpent, is a genus of parasitic helminths from the roundworm family Trichuridae. The name whipworm refers to the shape of the worm; they look like whips with wider "handles" at the posterior end.

Toxocara canis is a worldwide-distributed helminth parasite that primarily infects dogs and other canids, but can also infect other animals including humans. The name is derived from the Greek word "toxon," meaning bow or quiver, and the Latin word "caro," meaning flesh. T. canis live in the small intestine of the definitive host. This parasite is very common in puppies and somewhat less common in adult dogs. In adult dogs, infection is usually asymptomatic but may be characterized by diarrhea. By contrast, untreated infection with Toxocara canis can be fatal in puppies, causing diarrhea, vomiting, pneumonia, enlarged abdomen, flatulence, poor growth rate, and other complications.

Toxocara cati, also known as the feline roundworm, is a parasite of cats and other felids. It is one of the most common nematodes of cats, infecting both wild and domestic felids worldwide. Adult worms are localised in the gut of the host. In adult cats, the infection – which is called toxocariasis – is usually asymptomatic. However, massive infection in juvenile cats can be fatal.
The combination milbemycin oxime/lufenuron is a parasite control drug in which the active ingredient, milbemycin oxime, eliminates worms, while a second active ingredient, lufenuron, arrests the development of eggs and larvae, preventing them from maturing and continuing the infestation of an animal. This combination is registered for animal use only. To achieve efficacy, the treatment is administered once monthly, together with food, in a dosage suitable for the weight of the affected animal. The usual ratio is 500 μg milbemycin oxime and 10 mg lufenuron/kg body weight. Novartis indicates the proper dosage by color-coding the packages.
Human parasites include various protozoa and worms.

Baylisascaris procyonis, also known by the common name raccoon roundworm, is a roundworm nematode, found ubiquitously in raccoons, the definitive hosts. It is named after H. A. Baylis, who studied them in the 1920s–30s, and Greek askaris. Baylisascaris larvae in paratenic hosts can migrate, causing larva migrans. Baylisascariasis as the zoonotic infection of humans is rare, though extremely dangerous due to the ability of the parasite's larvae to migrate into brain tissue and cause damage. Concern for human infection has been increasing over the years due to the urbanization of rural areas, resulting in the increase in proximity and potential human interaction with raccoons.

Moniliformis moniliformis is a parasite of the Acanthocephala phylum in the family Moniliformidae. The adult worms are usually found in intestines of rodents or carnivores such as cats and dogs. The species can also infest humans, though this is rare.
Cystoisospora canis, previously known as Isospora canis, is a microscopic, coccidian parasite that causes an intestinal tract infection in dogs. The intestinal tract infection is coccidiosis caused by a protozoa called coccidia.
Wolves may suffer from various pathogens, both viral and bacterial, and parasite, both external and internal. Parasitic infection in wolves is of particular concern to people. Wolves can spread them to dogs, which in turn can carry the parasites to humans. In areas where wolves inhabit pastoral areas, the parasites can be spread to livestock.

Cat worm infections, the infection of cats (Felidae) with parasitic worms, occur frequently. Most worm species occur worldwide in both domestic and other cats, but there are regional, species and lifestyle differences in the frequency of infestation. According to the classification of the corresponding parasites in the zoological system, infections can be divided into those caused by nematode and flatworms - in the case of the latter, mainly cestoda and trematoda - while other strains are of no veterinary significance. While threadworms usually do not require an intermediate host for their reproduction, the development cycle of flatworms always proceeds via alternate hosts.
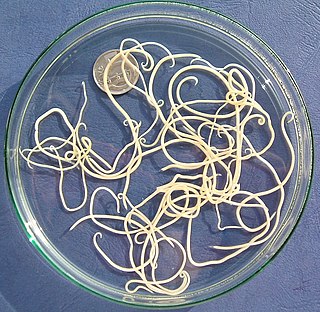
Nematode infection in dogs - the infection of dogs with parasitic nemamotodes - are, along with tapeworm infections and infections with protozoa, frequent parasitoses in veterinary practice. Nematodes, as so-called endoparasites, colonize various internal organs - most of them the digestive tract - and the skin. To date, about 30 different species of nematode have been identified in domestic dogs; they are essentially also found in wild dog species. However, the majority of them often cause no or only minor symptoms of disease in adult animals. The infection therefore does not necessarily have to manifest itself in a worm disease (helminthosis). For most nematodes, an infection can be detected by examining the feces for eggs or larvae. Roundworm infection in dogs and the hookworm in dogs is of particular health significance in Central Europe, as they can also be transmitted to humans (zoonosis). Regular deworming can significantly reduce the frequency of infection and thus the risk of infection for humans and dogs.