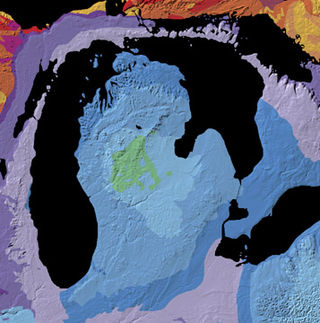
The Michigan Basin is a geologic basin centered on the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The feature is represented by a nearly circular pattern of geologic sedimentary strata in the area with a nearly uniform structural dip toward the center of the peninsula.
The Devonian Mahantango Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Maryland. It is named for the North branch of the Mahantango Creek in Perry and Juniata counties in Pennsylvania. It is a member of the Hamilton Group, along with the underlying the Marcellus Formation Shale. South of Tuscarora Mountain in south central Pennsylvania, the lower members of this unit were also mapped as the Montebello Formation. Details of the type section and of stratigraphic nomenclature for this unit as used by the U.S. Geological Survey are available on-line at the National Geologic Map Database.

The Marcellus Formation or the Marcellus Shale is a Middle Devonian age unit of sedimentary rock found in eastern North America. Named for a distinctive outcrop near the village of Marcellus, New York, in the United States, it extends throughout much of the Appalachian Basin.

The Trenton Gas Field is located in east central Indiana and the most western portion of west central Ohio. The field was discovered in 1876, but the size and magnitude of the field was not known until the 1880s. The field was the largest natural gas discovery up to that time, with an area of 5,120 square miles (13,300 km2), somewhat smaller in area than the state of Connecticut, containing over 1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. The field also contained the first giant oil reserve discovered in the United States, with an estimated 1 billion barrels of oil. The discovery led to the Indiana Gas Boom.
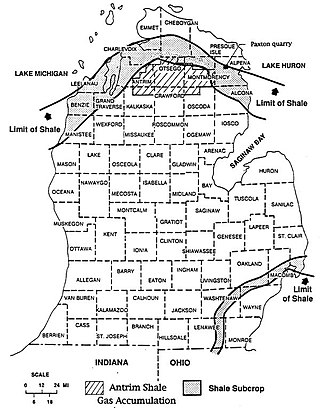
The Antrim Shale is a formation of Upper Devonian age in the Michigan Basin, in the US state of Michigan, and extending into Ohio, Indiana and Wisconsin. It is a major source of natural gas in the northern part of the basin.

The petroleum industry in Ohio dates from 1859. Ohio continues to produce significant quantities of oil and gas, having produced more than 1 billion barrels of oil and 9 trillion cubic feet of natural gas since 1860. Unconventional resources, primarily in eastern Ohio, are likely to increase production in Ohio.

The New Albany Shale is an organic-rich geologic formation of Devonian and Mississippian age in the Illinois Basin of the United States. It is a major source of hydrocarbons.

Berea Sandstone, also known as Berea Grit, is a sandstone formation in the U.S. states of Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Kentucky. It is named after Berea, Ohio. The sandstone has been used as a building stone and is a source of oil and gas.

The Glenshaw Formation is a mapped sedimentary bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, and Ohio, of Pennsylvanian age. It is the lower of two formations in the Conemaugh Group, the upper being the Casselman Formation. The boundary between these two units is the top of the marine Ames Limestone. The Conemaugh Group overlies the Upper Freeport coal bed of the Allegheny Formation and underlies the Pittsburgh coal seam of the Monongahela Group.

The Waverly Group is a geologic group in Michigan and Ohio. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period.

The Whitewater Formation is a geologic formation in Ohio and Indiana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period.

The Maxville Limestone is a geologic formation in Ohio. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period.

The Salem Formation is a geologic formation in Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, and Missouri. It preserves fossils dating back to the Mississippian subperiod. This formation is quarried and used as a building material, known as "Indiana limestone", also called Bedford limestone.
The Linton Formation is a geologic formation in Indiana. It is the lower formation in the Carbondale Group, and includes six named members, "which, in ascending order, are the Seelyville Coal, Coxville Sandstone, Colchester Coal, Mecca Quarry Shale, Velpen Limestone, and Survant Coal Members, and unnamed units of sandstone, shale, and clay".

The Black River Group is a geologic group that covers three sedimentary basins in the Eastern and Midwestern United States. These include the Appalachian Basin, Illinois Basin and the Michigan Basin. It dates back to the Late Ordovician period. It is roughly equivalent to the Platteville Group in Illinois. This Geologic group covers a large geographic area of the United States. In areas where this Geologic Unit thins it is also called the Black River Formation (undifferentiated). One example of this is over the Cincinnati Arch & Findley Arch.
The Franconia Formation is a geologic formation in the upper mid-western United States, with outcroppings found in Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Ohio, and Wisconsin. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period. It was named the Franconia Formation due to the first published documentation of exposures in vicinity of Franconia, Minnesota in the 1897 Ph.D. dissertation by Charles P. Berkley at the University of Minnesota titled Geology of the St. Croix Dalles. The Franconian stratigraphic stage was named after this formation.

The Smackover Formation is a geologic formation in Arkansas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Jurassic period.
The Mount Hawk Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Devonian age. It is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the Rocky Mountains and foothills of Alberta. It consists primarily of limestone and mudstone, and was named for Hawk Mountain in Jasper National Park by R. de Wit and D.J. McLaren in 1950.
The Mount Whyte Formation is a stratigraphic unit that is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the southern Canadian Rockies and the adjacent southwestern Alberta plains. It was deposited during Middle Cambrian time and consists of shale interbedded with other siliciclastic rock types and limestones. It was named for Mount Whyte in Banff National Park by Charles Doolittle Walcott, the discoverer of the Burgess shale fossils, and it includes several genera of fossil trilobites.
The Mansfield Natural Gas Field is located west of Mansfield, Ohio, within the Appalachian foreland basin. The field is 1.5 miles (2.4 km) long by 1.4 miles (2.3 km) wide and is in a general oval shape, stretching northward. This field, although small, is an analog for many of the natural gas fields that occur within the Appalachian Basin. It was first discovered by the Pan American Petroleum and Transport Company in the early 1930s. It is part of the Utica – Lower Paleozoic system, which is estimated to make up 15 to 20 percent of the total hydrocarbon abundance of the Appalachian Basin.
















