| Tundra vole | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Tundra vole in Alaska | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Cricetidae |
| Subfamily: | Arvicolinae |
| Genus: | Alexandromys |
| Species: | A. oeconomus |
| Binomial name | |
| Alexandromys oeconomus (Pallas, 1776) | |
 | |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
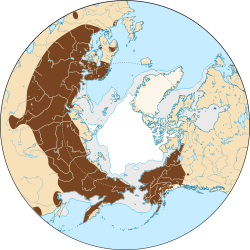
The tundra vole (Alexandromys oeconomus) or root vole is a medium-sized vole found in Northern and Central Europe, Asia, and northwestern North America, including Alaska and northwestern Canada. [2] In the western part of the Netherlands, the tundra vole is a relict from the ice age and has developed into the subspecies A. o. arenicola.
